Ecommerce shines as a unique player in the business grounds, marked by its distinct characteristics and hurdles. Given the digital nature and global reach of online commerce, managing finances for ecommerce businesses demands a tailored approach to bookkeeping.
Let’s take a closer look at ecommerce bookkeeping, the challenges setting it apart from traditional methods, and shed light on effective bookkeeping strategies for the digital marketplace.
Key takeaways
- Ecommerce bookkeeping presents unique challenges due to its digital nature, high transaction volume, diverse payment methods, and global reach. It requires accurate inventory management, tax compliance, and a peculiar approach to bookkeeping to enable business growth.
- Challenges include handling merchant fees, third-party payment processing, multi-platform inventory tracking, alternative sales methods, international sales, and shipping fees, all crucial for maintaining accurate financial records and tax compliance.
- Businesses should leverage accounting software, establish clear procedures, automate tasks, track expenses closely, implement internal controls, stay updated on tax regulations, and invest in bookkeeper training and education to optimize ecommerce bookkeeping and drive business growth.
What is ecommerce bookkeeping?
With the significant shift towards ecommerce over recent years, the business has undergone a profound transformation. The rise of ecommerce platforms has led to a surge in online transactions, creating a need to treat ecommerce bookkeeping as a distinct type of accounting compared to traditional brick-and-mortar or service businesses.
What makes ecommerce stand out?
Ecommerce stands out due to its digital nature, high volume of transactions, diverse payment methods, and often global reach, which pose unique challenges to bookkeeping practices.
One prominent challenge is the sheer volume of transactions that ecommerce businesses typically handle. The constant influx of online sales, refunds, exchanges, and payments requires careful recording and tracking to maintain accurate financial records.
Ecommerce transactions may involve various payment gateways, currencies, and state and international tax regulations, adding layers of complexity to bookkeeping processes.
That’s not to mention inventory management that, in ecommerce, requires careful monitoring of stock levels, fulfillment processes, and cost of goods sold.
So, what’s ecommerce bookkeeping?
With all the above in mind, we can define ecommerce bookkeeping as specialized accounting practices and procedures tailored to online businesses’ unique needs and challenges.
It encompasses the recording, categorization, and reconciliation of financial transactions specific to ecommerce operations and ensuring compliance with tax regulations applicable to online transactions.
Ecommerce bookkeeping aims at maintaining accurate and up-to-date financial records that enable informed decision-making, tax compliance, and online business growth.
Below, we’ll look at different aspects of ecommerce bookkeeping in more detail, so keep reading.
What are the challenges of ecommerce bookkeeping?
Ecommerce bookkeeping comes with challenges, distinct from other business models such as services or software sales.
Let’s look at some of the most common pains and hurdles ecommerce businesses face when managing their finances.
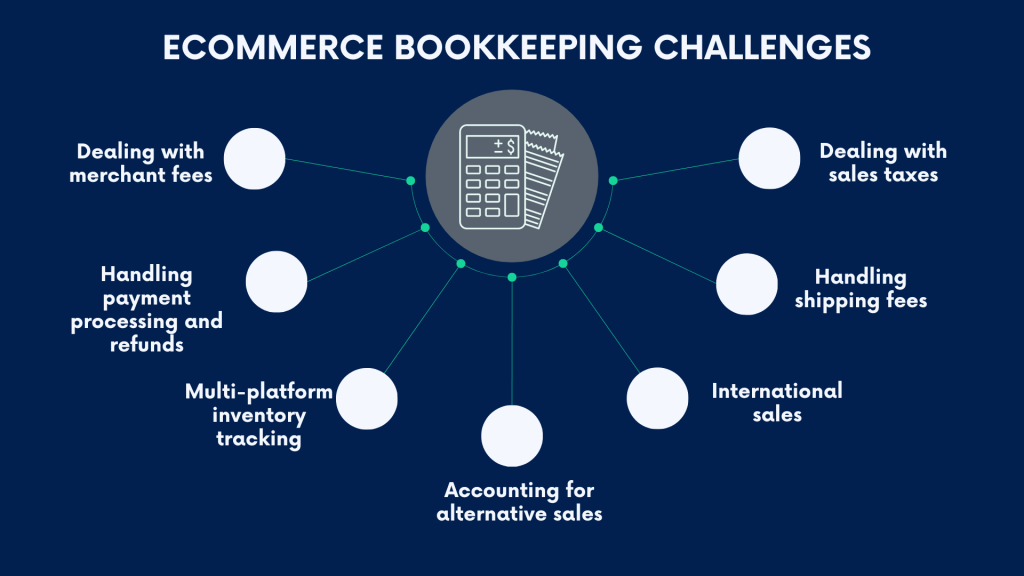
#1 – Dealing with merchant fees
Ecommerce platforms charge merchant fees, which are a percentage of each sale. Shopify and BigCommerce charge transaction fees ranging from 2.9% to 3.5%. Amazon and other marketplaces may also charge referral, fulfillment, and subscription fees.
Merchant fees help platforms provide hosting, payment processing, and marketing tools, but handling them can be complex.
Ecommerce businesses must track gross sales and record the difference as merchant fees to gain insights into profitability, optimize pricing, and ensure tax compliance.
Related:
- Marketplace Fees Guide 2024
- eBay Seller Fees to Know About: A Simple Guide to eBay Selling Fees for Sellers
- Etsy Seller Fees: The Ultimate Etsy Fees Guide 2024
#2 – Using third-party payment processing tools and issuing refunds
Ecommerce businesses often use third-party payment processors like Stripe or PayPal for smooth payment experiences and essential features such as fraud protection. However, integrating these processors can complicate record-keeping, especially for returns and exchanges.
A lack of refund on fees can result in financial loss, and reconciling transactions across platforms requires careful attention to detail.
Businesses can simplify these challenges by implementing processes for returns management, integrating solutions to centralize refund management, and streamlining refund tracking and transaction reconciliation.
Related:
- What Are Processing Fees? How to Understand and Optimize Processing Costs
- Stripe Fees: A Guide to Stripe Fee Structure for an Ecommerce Business
- PayPal Fees for Sellers: A Breakdown of Seller PayPal Fee Rates
#3 – Multi-platform inventory tracking
Managing inventory on multiple ecommerce platforms can be challenging. Discrepancies can arise when selling across various channels.
An ecommerce store selling a product on both Shopify and Amazon may encounter a problem if the inventory levels on Shopify don’t sync with Amazon.
When a customer purchases an item on Shopify, the inventory levels on this platform will update automatically. This change, however, might not reflect on Amazon, leading to inaccurate stock counts (showing the item as available while it’s already out of stock). This situation might cause overselling. In this case, the business might lose customers.
Ecommerce businesses can overcome challenges by using centralized inventory management systems. Implementing inventory management software or integrations can synchronize inventory levels across multiple channels, allowing merchants to track stock levels, receive low inventory alerts, and automate order fulfillment processes seamlessly.
Related:
- Inventory Management: QuickBooks Online and Desktop Inventory Tracking Solutions
- How to Create the Best Inventory Management System: Find the Best Inventory Software for Your Business
#4 – Accounting for alternative sales
In addition to credit cards, ecommerce businesses often accept various payment methods like cash, checks, and gift cards, catering to diverse customer preferences and enhancing the shopping experience. However, each payment type introduces its complexities in bookkeeping.
Cash or check payments
For instance, when a customer pays with cash or check, the sale isn’t fully recognized in the books until the money is deposited into the business’s bank account. This delay between receiving payment and recording revenue requires careful tracking to ensure accurate financial reporting. For example, if a customer pays $100 in cash for a product, the sale isn’t recognized until the cash is deposited into the bank account.
Gift card payments
Accepting gift cards as payment creates challenges with unearned revenue. The business receives payment upfront. But until the gift card holder redeems the card for merchandise, it considers the revenue unearned.
Let’s say a customer buys a $50 gift card. The business records the payment it gets for this card as unearned revenue. Only after the customer uses this gift card to buy something, the business can record the merchandise sale.
Buy now pay later
The rise of buy now pay later (BNPL) methods adds complexity to ecommerce bookkeeping. With BNPL, customers can split their purchases into installments and pay over time. It requires careful bookkeeping to ensure accurate revenue recognition. Businesses must track installment payments and reconcile transactions across different payment periods.
Related:
#5 – International sales
Expanding your ecommerce business to global markets allows you to grow. However, managing finances when dealing with multiple currencies can be difficult.
You receive sales in various currencies and should reconcile them with local currency deposits.
To do this, you convert foreign currency sales into your business’s base currency, typically the currency in which you operate or the currency of your primary bank account.
Conversion rate discrepancies between foreign sales and bank deposits can result in gains or losses on foreign exchange, depending on fluctuations in exchange rates.
Related:
- Handling Foreign Currency Transactions with Synder Multi-Currency
- Marius Gunvaldsen, SaaS owner, “Finally, a solution to organize multi-currency payments!”
#6 – Handling shipping fees
Shipping charges in ecommerce can create discrepancies between customer-paid fees and actual expenses.
A customer may pay a flat rate of $5 for shipping. However, the actual cost to ship the package may vary based on package weight, dimensions, and destination. So, upon processing the order, the business ends up with $8 to send the package to the customer. In this case, there is a discrepancy of $3 between the shipping fee collected from the customer and the actual shipping expenses. And you might want to reflect it in bookkeeping.
Integrated shipping solutions can streamline logistics. Implementing dynamic shipping rates or surcharges for large packages (and other strategies) can help manage shipping costs effectively.
Related:
#7 – Sales tax
Ecommerce businesses must collect and remit sales tax in jurisdictions where it applies.
Some ecommerce platforms offer built-in features for handling sales tax. But usually, it’s a business’s responsibility to track and record sales tax transactions accurately, as the sales tax is a liability owed to the government.
Businesses must maintain detailed records of sales transactions and segregate and set aside the tax amount in a separate account. They must also reconcile sales tax liabilities with payments made to tax authorities. Any discrepancies must be promptly addressed and corrected to avoid penalties and fines.
Related:
What is the basic accounting for ecommerce?
Basic accounting for ecommerce involves applying fundamental principles to accurately track financial transactions, assess business performance, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Let’s break them down.
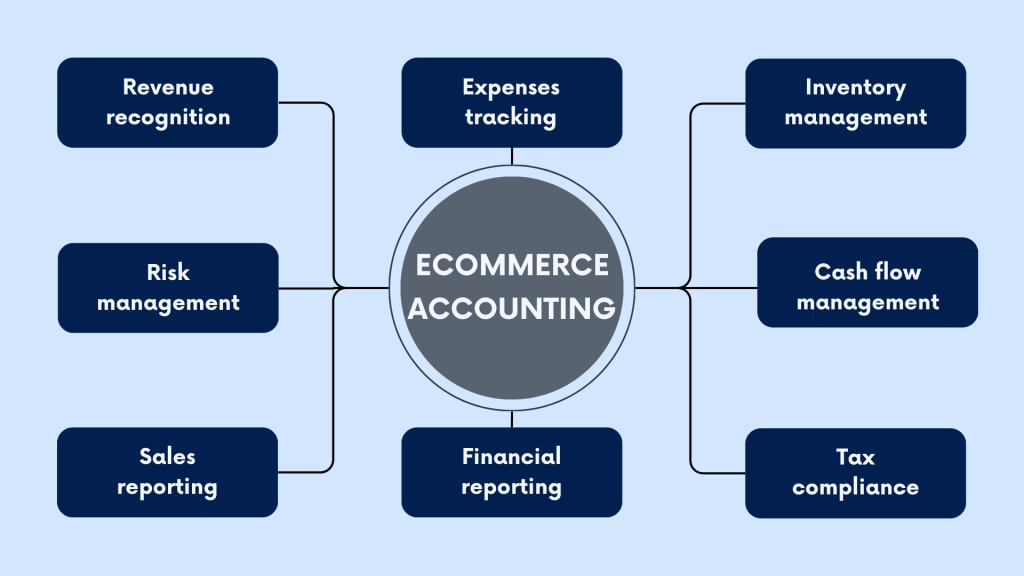
Revenue recognition
Ecommerce businesses recognize revenue upon delivering goods or services to customers and receiving or expecting to receive the payment. Usually, they record revenue at the gross amount of sales before deducting any fees or discounts.
Expenses tracking
Ecommerce businesses track various expenses incurred in running their operations, including product costs, marketing expenses, shipping fees, and overhead costs like rent and utilities. Proper expense tracking allows businesses to assess profitability and make informed decisions about resource allocation.
Inventory management
As mentioned, inventory management is crucial for ecommerce businesses to monitor stock levels, track product movement, and prevent stockouts or overstocking. Accurate inventory records help optimize purchasing decisions and minimize carrying costs.
Cash flow management
Ecommerce businesses might want to manage cash flow effectively to ensure they have sufficient funds to cover operational expenses, fulfill orders, and invest in growth opportunities. Cash flow management involves monitoring incoming and outgoing cash flows, forecasting future cash needs, and maintaining adequate liquidity.
Tax compliance
Ecommerce businesses have various tax obligations, including sales and income tax and possibly international taxes (if selling globally). Businesses must accurately calculate and collect sales tax from customers, file tax returns on time, and comply with tax regulations to avoid penalties and fines.
Financial reporting
Ecommerce businesses prepare the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to communicate their financial performance to stakeholders. Financial reporting provides insights into revenue, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity, enabling stakeholders to assess the business’s financial health and make informed decisions.
Sales reporting
Ecommerce businesses rely on sales reporting to track and analyze their sales performance. Sales reports provide valuable insights into revenue trends, customer purchasing behavior, and the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. By analyzing sales data, businesses can identify top-selling products, understand seasonal sales patterns, and evaluate the performance of sales channels and marketing strategies.
Risk management
Ecommerce businesses identify and mitigate financial risks, such as fraud, chargebacks, and payment processing errors. Implementing internal controls and security measures helps protect against financial losses and safeguard sensitive customer information.
How should an ecommerce business organize its chart of accounts?
A chart of accounts is a fundamental tool in accounting that organizes a business’s financial transactions into categories for easy tracking, reporting, and analysis. As an ecommerce business, you might want to set up a chart of accounts to accommodate the unique aspects of online retail operations.
Let’s look at what to consider.
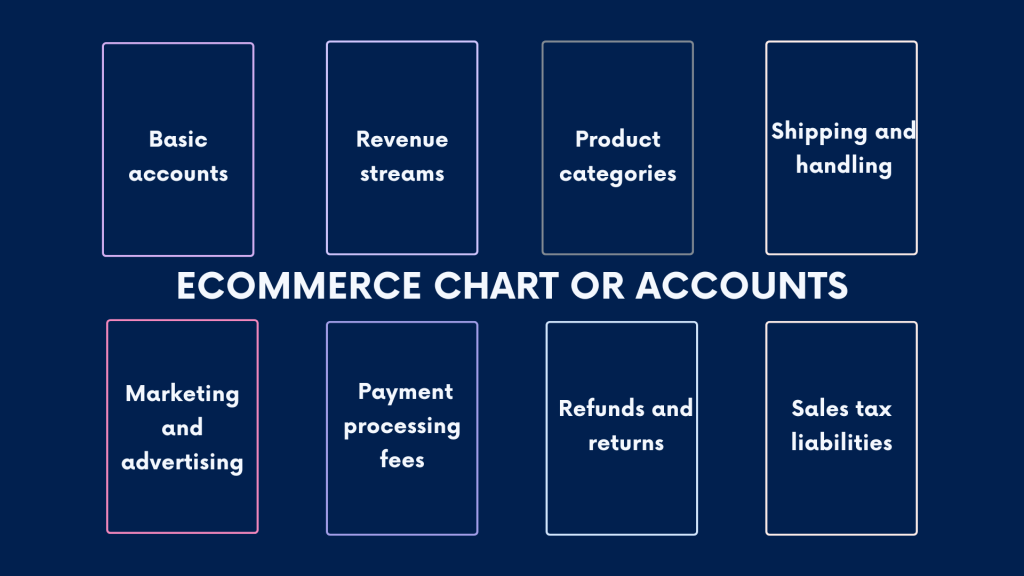
#1 – Basic structure
An ecommerce business’s chart of accounts should include standard categories such as assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses. These categories provide a framework for recording and classifying financial transactions accurately.
#2 – Revenue streams
Ecommerce businesses often have multiple revenue streams, including product sales, subscription services, and digital downloads. Each revenue stream should have its account within the chart of accounts to track sales performance and revenue trends separately.
#3 – Product categories
Given the diverse range of products sold by ecommerce businesses, it’s essential to create accounts for different product categories. For example, accounts can be created for electronics, apparel, accessories, and home goods, allowing businesses to analyze sales performance by product category and make informed inventory management decisions.
#4 – Shipping and handling
Ecommerce businesses frequently incur expenses related to shipping and handling. Separate accounts should be created to track shipping costs, packaging expenses, and fulfillment services. This enables businesses to monitor shipping expenses and identify opportunities for cost optimization.
#5 – Marketing and advertising
Marketing and advertising play a crucial role in driving traffic and sales for ecommerce businesses. Accounts should be created to track expenses related to digital advertising, social media marketing, influencer partnerships, and promotional campaigns. Tracking marketing expenses helps businesses assess the effectiveness of their marketing efforts and allocate resources strategically.
#6 – Payment processing fees
Ecommerce transactions often involve payment processing fees charged by payment gateways and processors. These fees should be recorded separately in the chart of accounts to track transaction costs and assess their impact on profitability.
#7 – Refunds and returns
Ecommerce businesses need accounts to track refunds and returns accurately. Separate accounts should be created to record refunds issued to customers and any associated expenses, such as restocking fees or return shipping costs. Tracking refunds and returns helps businesses evaluate customer satisfaction levels and identify opportunities to improve product quality and customer service.
#8 – Sales tax liabilities
Ecommerce businesses are responsible for collecting and remitting sales tax on taxable transactions. Accounts should be created to track sales tax collected from customers and any associated liabilities to tax authorities. Accurate tracking of sales tax liabilities helps businesses ensure compliance with tax regulations and avoid penalties.
Key components of tax compliance for ecommerce businesses
We’ve touched upon how ecommerce businesses should provide for tax compliance. But, since it’s a critical aspect of operating an ecommerce business, we’ll look at it in a bit more detail.
Here are the key components of tax compliance for ecommerce businesses.
Sales tax obligations
Ecommerce businesses are generally required to collect and remit sales tax on taxable transactions. The specific sales tax requirements vary by jurisdiction, including state, local, and international levels. To ensure compliance with sales tax laws, ecommerce businesses must follow several steps.
#1 – Determine nexus
Nexus refers to the sufficient connection between a business and a taxing jurisdiction, often based on factors like physical presence, economic activity, or sales volume. Ecommerce businesses must determine where they have nexus and are required to collect sales tax.
#2 – Collect sales tax
Once nexus is established, ecommerce businesses must collect the appropriate sales tax rate from customers at the point of sale. Sales tax rates vary by location and product type, so businesses must accurately calculate and collect the correct amount of tax.
#4 – File tax returns
Ecommerce businesses must file sales tax returns with the relevant tax authorities regularly, typically monthly, quarterly, or annually. These returns report the total sales tax collected and remitted during the reporting period.
#5 – Keep records
Maintaining detailed records of sales transactions, sales tax collected, and tax returns filed is essential for tax compliance and audit purposes. Ecommerce businesses should retain records of sales invoices, receipts, and other relevant documents for the required retention period.
International tax considerations
Selling products or services abroad introduces additional tax considerations for ecommerce businesses. The components of international tax compliance include VAT, import taxes, customs duties, etc.
#1 – Value-added tax (VAT)
Many countries impose a value-added tax (VAT) on the sale of goods and services. Ecommerce businesses may be required to register for VAT in certain countries where they have customers and remit VAT on taxable transactions.
#2 – Customs duties and import taxes
Shipping products internationally may subject ecommerce businesses to customs duties, tariffs, and import taxes imposed by the destination country. Businesses should understand and comply with customs regulations to avoid delays and unexpected costs.
#3 – Tax treaties and agreements
Some countries have tax treaties or agreements with others to prevent double taxation and facilitate cross-border commerce. Ecommerce businesses should be aware of any tax treaties that may impact their international operations and take advantage of available benefits.
#4 – Currency conversion and reporting
Ecommerce businesses selling in multiple currencies must accurately convert and report sales revenue in their base currency for tax reporting purposes. Exchange rate fluctuations and currency conversion fees should be taken into account when calculating taxable income.
How does inventory management affect bookkeeping?
Inventory management is another critical aspect of ecommerce bookkeeping. It involves tracking and valuing the goods available for sale. Effective inventory management ensures accurate financial reporting and helps ecommerce businesses optimize their purchasing and sales strategies.
Several inventory tracking methods are commonly used in ecommerce bookkeeping, including FIFO (First In, First Out), LIFO (Last In, First Out), and weighted average.
Let’s break them down.
FIFO (First In, First Out)
In FIFO inventory management, the oldest inventory items are sold first, followed by the newer items. This method assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first and reflects the cost of goods sold (COGS) based on the cost of the oldest inventory in stock.
FIFO is widely used in ecommerce bookkeeping because it closely aligns with the actual flow of goods and provides a more accurate reflection of current inventory costs during periods of price fluctuations.
Suppose an ecommerce business purchases 100 units of a product at $10 each and later purchases 100 additional units at $12 each. When selling 150 units, FIFO assumes that the first 100 units sold were purchased at $10 each, followed by 50 units purchased at $12 each.
LIFO (Last In, First Out)
LIFO inventory management assumes that the most recently acquired inventory items are sold first, with the oldest items remaining in inventory. This method results in COGS being based on the cost of the most recent inventory purchases. While LIFO may be beneficial for tax purposes in certain jurisdictions, it can distort the valuation of inventory during periods of inflation or rising costs.
Using the same scenario as above, under LIFO, the 50 units sold would be valued at $12 each, representing the cost of the most recent inventory purchase.
Weighted average
The weighted average inventory method calculates the average cost of inventory based on the total cost of goods available for sale divided by the total number of units available for sale. This method smooths out fluctuations in inventory costs and is relatively simple to calculate.
If the total cost of goods available for sale is $2,000 and there are 200 units available for sale, the weighted average cost per unit would be $10. When selling inventory, the COGS would be based on this weighted average cost per unit.
Each inventory tracking method has its advantages and considerations, and the choice of method depends on the nature of the products sold, inventory turnover rates, and tax implications. Proper inventory management ensures that ecommerce businesses can effectively track costs, assess profitability, and optimize inventory levels to meet customer demand while minimizing carrying costs.
Software and tools for ecommerce bookkeeping to consider
Ecommerce businesses thrive on efficient bookkeeping practices to manage financial transactions, track expenses, and ensure compliance with tax regulations. Keeping in mind the transaction volumes they need to handle, inventory management considerations, and complex taxation, ecommerce businesses can’t go without technology to deal with bookkeeping efficiently.
Choosing the right software or tools for ecommerce bookkeeping can streamline processes, improve accuracy, and provide valuable insights into the financial health of the business. Here are some recommended software and tools for ecommerce bookkeeping, along with key features to consider when choosing one
Accounting software
Accounting software tailored to the needs of ecommerce businesses is a pure game-changer. Created with online businesses in mind, ecommerce accounting software considers all the needs and nuances of ecommerce accounting, automating a good chunk of bookkeeping tasks and helping with financial and business analytics and reporting. Basically, it’s a lifesaver for ecommerce business owners and bookkeepers.
Want to know how the right accounting software can enhance your ecommerce bookkeeping? Book your seat at our Weekly Public Demo to see how you can do it with Synder, or explore it yourself with a 15-day all-inclusive free trial.
Now, let’s look at what to pay attention to when choosing accounting software for your ecommerce business.
- Cloud-based platforms
Cloud-based accounting software offers flexibility and accessibility, allowing businesses to access financial data from anywhere with an internet connection. - Integration capabilities
Look for software that integrates seamlessly with ecommerce platforms, payment gateways, and banking institutions to automate data synchronization and streamline reconciliation processes. - Multi-currency support
Ecommerce businesses selling internationally should choose accounting software that supports multiple currencies and enables accurate conversion and reporting of foreign transactions. - Customizable chart of accounts
The ability to customize the chart of accounts allows businesses to tailor financial reporting to their specific needs and industry requirements. - Automatic tax calculations
Software with built-in tax calculation features helps ecommerce businesses accurately calculate and track sales tax, VAT, and other tax obligations.
Expense tracking tools
Expense tracking tools simplify recording expenses and provide insights into cost trends, areas for cost optimization, and accurate financial reporting. With real-time expense tracking capabilities, ecommerce businesses can make informed decisions, maintain financial transparency, and ensure compliance with tax regulations, ultimately leading to improved profitability and business growth.
Here’s what to look for when choosing an expense management tool.
- Receipt scanning
Tools that offer receipt scanning capabilities enable businesses to digitize and organize receipts for expenses incurred on purchases, travel, and other business-related activities. - Categorization and tagging
Look for tools that allow for easy categorization and tagging of expenses, making it simple to track and analyze spending across different categories and accounts. - Bank integration
Expense tracking tools that integrate with bank accounts and credit cards automate the importing of transactions, reducing manual data entry and minimizing errors. - Budgeting and forecasting
Some tools offer budgeting and forecasting features that help ecommerce businesses set financial goals, track performance against targets, and make informed decisions based on projected financial outcomes.
Inventory management software
We mentioned already several times how managing inventory is a key aspect of an ecommerce business. It’s true from a bookkeeping perspective as well. So to ensure inventory management software helps you to the full, you might want to consider the following elements it should possess.
- Real-time inventory tracking
Inventory management software should provide real-time visibility into stock levels, allowing businesses to monitor inventory levels, track sales trends, and optimize replenishment strategies. - Order management
Look for software that integrates inventory management with order processing and fulfillment, streamlining workflows and reducing fulfillment times. - Demand forecasting
Advanced inventory management tools may offer demand forecasting capabilities, leveraging historical sales data and market trends to predict future demand and optimize inventory stocking levels. - Batch and serial number tracking
For businesses dealing with serialized or batched inventory, software that enables tracking of individual items throughout the supply chain ensures traceability and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Tax compliance software
As taxes are complex on the ecommerce grounds, with many nuances and conditions to consider, you might want software that can take care of those, allowing you to have accurate data ready for taxation. At this point, you might want to pay attention to the following features of tax software:
- Automated tax calculations
Tax compliance software automates the calculation of sales tax, VAT, and other taxes based on transaction data, reducing manual errors and ensuring accurate tax reporting. - Tax filing and reporting
Choose software that facilitates tax filing and reporting processes, generates tax forms, and guides filing deadlines and requirements. - Audit trail and documentation
Tax compliance software should maintain an audit trail of tax-related transactions and provide documentation to support tax filings and audits by tax authorities. - Integration with accounting software
Seamless integration with accounting software ensures that tax data is synchronized and accurately reflected in financial reports and statements.
It’s worth mentioning that you can find plenty of solutions on the market and choose those that answer your particular needs. You might want to start with accounting software, though, as it often includes expense tracking, tax calculations, and even inventory tracking functionality. Then, if you need to cover some aspects more thoroughly, you can choose software to complement your accounting solution.
How to optimize ecommerce bookkeeping to drive business growth: best practices
When it comes to bookkeeping for ecommerce businesses, it’s important to do it efficiently and accurately. This helps entrepreneurs keep track of their finances and make informed decisions. Here are some tips to optimize ecommerce bookkeeping.
#1 – Use accounting software
We’ve just been there, but it’s worth repeating.
Leveraging cloud-based accounting software allows ecommerce businesses to fetch financial data from all their sales channels and put it together in a single hub to have a comprehensive picture of their business performance. Solutions like Synder, QuickBooks Online, Xero, FreshBooks, and more allow for connecting various data sources (like ecommerce platforms, payment processors, and marketplaces) to accounting, offering automatic data synchronization, bank reconciliation, and customizable financial reporting. By centralizing financial data in the cloud, businesses can streamline bookkeeping workflows and ensure data integrity across multiple devices and locations.
#2 – Establish clear accounting procedures
Establishing clear accounting procedures and workflows ensures consistency and accuracy in financial record-keeping. Documenting standard operating procedures for invoicing, expense tracking, reconciliation, and tax compliance helps maintain transparency and accountability within the organization. By defining roles and responsibilities, businesses can prevent errors and reduce the risk of financial mismanagement.
#3 – Regular accounts reconciliation
Reconciling bank accounts, credit card statements, and financial transactions regularly is essential for detecting discrepancies and identifying errors in financial records. Ecommerce businesses should reconcile accounts monthly or quarterly to ensure that recorded transactions match actual bank balances and statements. Reconciliation also helps identify fraudulent activities, bank errors, and unauthorized charges on time.
#4 – Automate routine tasks
Automating routine bookkeeping tasks helps save time and minimize manual errors. As mentioned, ecommerce businesses can automate processes such as invoice generation, payment reminders, recurring expenses, and bank reconciliations using accounting software and integrated third-party apps. Businesses can and should leverage automation to streamline workflows, reduce administrative overhead, and focus on core business activities.
#5 – Track expenses closely
Tracking expenses closely is essential for managing cash flow, monitoring spending patterns, and optimizing financial performance. Ecommerce businesses should accurately categorize expenses and regularly reconcile them against budgetary targets. This way, businesses can identify cost-saving opportunities, negotiate better vendor terms, and allocate resources strategically to drive profitability.
#6 – Implement internal controls
Implementing internal controls helps safeguard assets, prevent fraud, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Ecommerce businesses should establish segregation of duties, authorization procedures, and access controls to protect sensitive financial information and prevent unauthorized transactions. Regular audits and reviews of financial processes help identify weaknesses and improve internal controls over time.
#7 – Stay updated on tax regulations
Staying updated on tax regulations and compliance requirements is essential for ecommerce businesses to avoid penalties and fines. It involves monitoring changes in sales tax laws, international tax treaties, and reporting obligations to ensure compliance with tax authorities. Engaging with tax professionals and attending relevant training sessions or webinars can help ecommerce entrepreneurs stay informed about evolving tax regulations and industry best practices.
#8 – Invest in ecommerce bookkeeper training and education
Overall, investing in training and education for accounting staff and employees is a good practice. It enhances their skills and knowledge in bookkeeping practices and software usage.
You might want to provide your staff access to online tutorials, webinars, and certification programs to help stay abreast of industry trends, best practices, and emerging technologies in ecommerce bookkeeping. Well-trained employees are better equipped to handle complex financial tasks, troubleshoot issues, and contribute to organizational success.
Long story short
As you can see, bookkeeping for online and ecommerce businesses requires a different approach than other business models. Like other industries, ecommerce presents distinct challenges, making accountants and bookkeepers adjust their practices to address them.
If you’re accounting for SaaS, you pay attention to revenue recognition. In the case of business leasing or renting property, you’ll be catching up with ASC 842 lease accounting, and so on.
Ecommerce is challenging due to digital transactions, diverse payments, complex tax structures, and global operations. Managing merchant fees, third-party processors, and inventory across platforms while adhering to tax regulations demands attention.
To handle these complexities effectively, businesses should employ accounting software, establish clear procedures, and automate tasks. By tracking expenses, keeping up with tax rules, and investing in training, businesses can manage finances adeptly and foster growth. Through strategic approaches and technological solutions tailored to ecommerce, businesses can thrive and make informed decisions for sustained success.
Share your thoughts
Share your thoughts and experience in the comments section below. We’re fond of good stories!










.png)