Taxes are an integral part of every working individual’s responsibility. The obligation to address tax matters is universal, encompassing both traditional office employees and those working remotely.
Despite the fundamental similarities in the tax-filing process, there exist nuanced differences in how individuals, whether office-based or remote, approach this task.
When you’re an office-based employee, tax procedures may seem straightforward, with employers handling much of the paperwork. However, as a contractor or someone working remotely, the dynamics shift, placing a greater responsibility on individuals to navigate the intricacies of tax reporting.
In this context, understanding the significance of the W9 form becomes paramount, as it serves as a key instrument in facilitating the seamless exchange of financial information between self-employed workers and the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
In this article, we delve into the essential aspects of the W9 form, exploring its purpose, covering popular questions related to the IRS form W9 and providing detailed insights into its significance for independent contractors, freelancers, and other non-employees.
Disclaimer: Please be aware that this guide is solely meant for informational purposes and should not be considered a replacement for seeking advice from a professional accountant regarding accounting, tax, or financial matters.
Contents:
3. Who has to fill out a W9 form?
4. What does the Form W9 look like?
5. What does the W9 form require?
10. Penalties for non-compliant Form W9
11. Tips for your business to efficiently manage W9
13. FAQs
What is an IRS tax Form W9?
Form W9 is officially called “Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification”. Businesses use this IRS Form W9 to get tax information from nonemployees who earn $600 or more during a year from the company. The form acts as an agreement that you, as a nonemployee, are responsible for withholding taxes from your income.
Who can be classified as non-employees?
Understanding the distinction between employees and non-employees is crucial for tax and reporting purposes, as it influences how income and taxes are handled for each category.
The following categories encompass those who can be classified as non-employees:
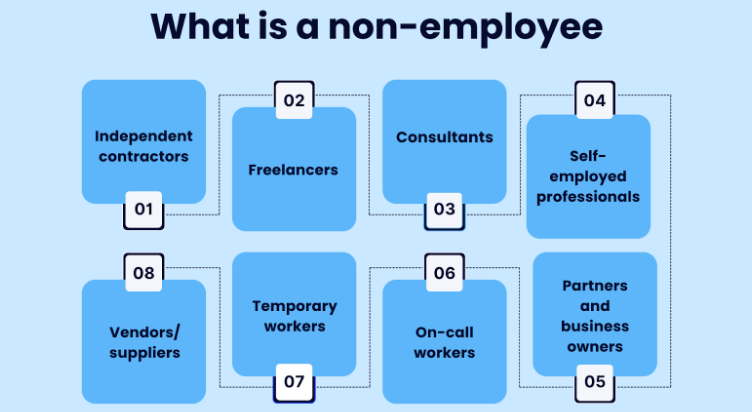
- Independent contractors – are self-employed individuals or entities hired for specific tasks. They work on a contractual basis, have control over their work, and manage their own taxes and benefits.
- Freelancers – are individuals who work independently, offering their services to clients on a project basis. They are not employees and typically have flexibility in their work arrangements and schedules. Freelancers are responsible for managing their own taxes, equipment, and benefits.
- Consultants – are hired experts who provide specialized advice or services to clients, often on a temporary basis.
- Self-employed professionals – work for themselves, managing their own businesses and providing services directly to clients.
- Vendors/suppliers – are businesses that provide goods or services to other businesses or customers, forming a crucial part of the supply chain.
- Temporary workers – are individuals hired for short-term roles, often to address project needs, seasonal demands, or staff shortages.
- On-call workers – are available as needed, with variable schedules, and are called in for specific tasks or projects.
- Partners and business owners – are individuals with ownership and managerial roles in a business, responsible for its success and operations.
- anyone else who is paid outside an employer/employee relationship.
Employee vs. non-employee
When you’re a full-time employee, your employer withholds some of your income to cover federal income taxes and FICA taxes (which include Medicare and Social Security taxes).
Employers don’t make that withholding for contractors, etc. Non-employees are responsible for their own tax obligations themselves.
What happens next?
At the end of the tax year, W9s are used by businesses to generate 1099s, which are then sent to the taxpayer and the IRS. This form outlines all the payments made to you.
Purpose of Form W9
When you engage with a company where reporting information to the IRS might be necessary, it becomes crucial to understand the nuances of tax documentation, including the use of W9 forms by businesses to get tax information from external parties.
The W9 form allows businesses to keep track of their external workforce – non-employees. Non-employees don’t send the W9 form to the IRS. Instead, they send it to their supervisor or the company’s human resources department.
The W9 is crucial in ensuring the accuracy of the information provided for this filing by directly gathering all necessary details from the non-employee.
Who has to fill out a W9 Form?
Any employee who isn’t considered an actual employee of the business should fill out a W9 form. These are often contractors who aren’t needed in the business full-time because the requested work is temporary.
The following types of independent contractors are often required to fill out a W9:
- Self-employed workers like freelancers, independent contractors and consultants.
- Workers who plan on getting paid more than $600 by one particular client in a tax year without being hired as an employee.
In what other cases do you need to fill out this form?
Form W9 is most often used between independent contractors and companies they’re working with, although it’s used in other situations as well:
- Banks sometimes also need a W9 when you open a new account with them.
- If an individual forgives or cancels a debt you owe them, that person will need to file Form 1099-C with the IRS. In order to complete this process, that individual will require you to send a completed W9 to them.
At the end of the year, businesses are expected to tally up their payments to W9 workers and report them to the IRS and the contractors, usually on Form 1099.
Important notices regarding W9 Form
Notice 1: If you did multiple jobs for multiple companies, you could fill out a number of W9 forms in the same year.
Notice 2: You’ll also have to submit new W9 forms any time you change your name, business name, address or tax ID number.
Notice 3: If someone other than a client, bank, or other financial institution asks you for a W9 form, you might want to think twice about sending one. This type of information can lead to identity theft and should be protected as such.
What does the Form W9 look like?
W9 is a one-page form from the IRS. It also comes with 5 pages of instructions.
The business needs pertinent information from you to report the payments accurately, such as your name, address, Social Security number (SSN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN), and your federal tax classification.
What information does the W9 Form require?
The form itself isn’t even an entire page long, excluding the instructions. Filling out a W9 is pretty straightforward. The form is made up of several parts:
- Top information.
- Part I.
- Part II.
Let me briefly acquaint you with these parts.
Top information
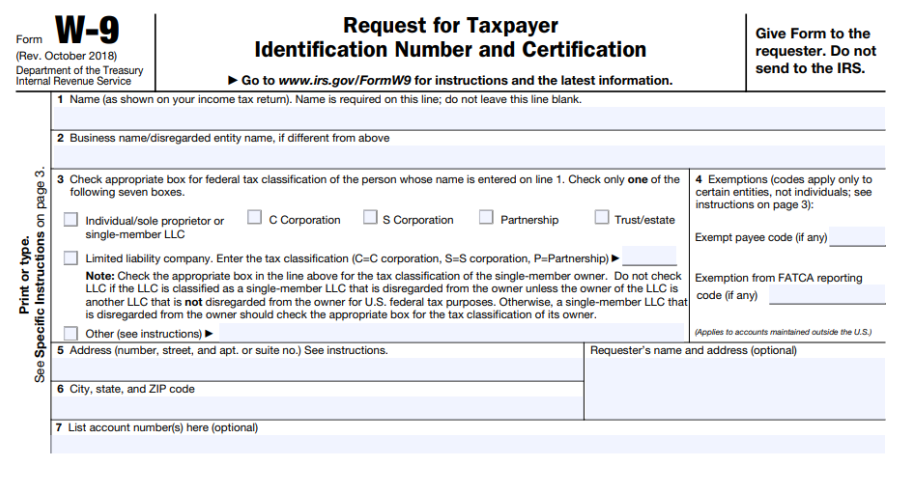
The top of the Form W9 includes:
- Full legal name.
- Your business’s name, if any.
- Federal tax classification (sole proprietorship, LLC, partnership, etc.).
- Contact information
- Backup withholding.
- Any tax reporting exemptions.
- Address.
- Account number(s).
Part I
The principal piece of information that businesses collect on a Form W9 is the tax identification number (TIN) of whomever they’re paying.

Part II
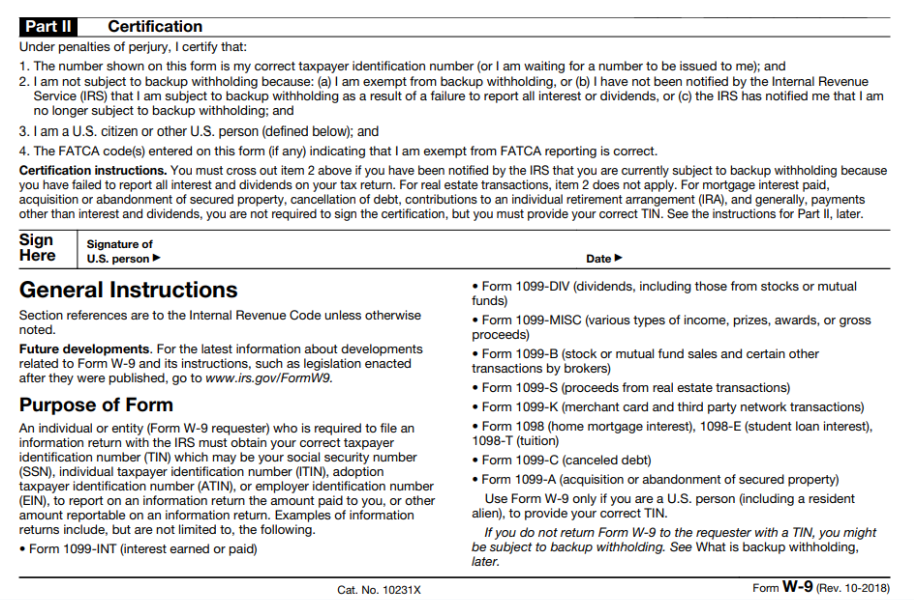
Sign and date the form.
This information is crucial for accurate reporting on your annual tax returns. Providing the correct details ensures that the payer can generate accurate 1099s at the end of the year, which are essential for completing your tax returns.
When to ask for a W9
The best time to ask for a completed W9 Form is while on-boarding a new vendor or as soon as a financial transaction is anticipated. Vendors that are operating legally will have no problem providing this information.
This proactive approach ensures that the payer has the necessary information to fulfil their reporting obligations to the IRS and helps streamline the tax documentation process for all parties involved.
However, in ongoing relationships, it’s crucial to update the information if there are any changes, such as a legal name change or an updated TIN. Timely submission of the W9 helps prevent potential delays in processing payments and ensures compliance with tax regulations.
Note: If a vendor provides any pushback to the request or fails to provide complete and accurate information, it can be a red flag. Knowing this early on in the relationship can eliminate penalties down the road. For example, penalties up to $270 may apply for each 1099 form that includes an incorrect TIN.
How to fill out a W9
When you hear that you need to fill out a W9, you might think it will be a complicated tax form. The good news here is that filling out a W9 is a fairly short form. See how to fill out a W9 in these steps.
The top section of the W9 tax form
- Write the name as shown on your income tax return.
- Write the business name/disregarded entity name if different than above.
- Fill out the federal tax classification. The taxpayer must select whether they are
- a corporation,
- an individual,
- a sole proprietor,
- a single-member LLC,
- a limited liability company,
- a partnership,
- a trust/estate.
- Include any exemption codes, if applicable.
- Write the business’ address (number, street and apartment number or suite number).
- Write the business’ city, state, and zip code.
- List account numbers, if applicable.
Part I
Enter the SSN or EIN.
You have 2 options in this section. You can enter
- either your SSN;
- or your employer’s EIN.
Again, you may want to check with your tax advisor or contact the IRS directly to double-check your information.
Note: Providing an incorrect TIN can cause issues with your payments or tax return. It can also lead to future backup withholding.
Part II
Signing and dating this section certifies that all of the information you’re entering here is correct.
Ensure that all necessary information is provided in each section and line in the W9 form to avoid any issues with payroll processing or tax reporting.
When is a W9 not required?
Understanding the nuances of W9 requirements is vital for businesses aiming for IRS compliance. While the standard threshold for collecting a W9 is $600 or more in payments per calendar year, exceptions exist.
1. Payments less than $600 in a calendar year
According to IRS regulations, businesses are generally required to collect a W9 from vendors if payments are expected to be $600 or more in a calendar year.
However, if the total payments to a vendor are anticipated to be less than $600 in a given year, the IRS does not mandate the submission of a W9. This threshold is essential for businesses to be aware of, as it influences the documentation requirements for tax reporting purposes.
2. Certain types of corporations
Corporations classified as tax-exempt entities, such as 501(c)(3) organizations, are generally exempt from W9 reporting.
3. Certain foreign entities
Payments made to certain foreign entities or individuals may be exempt from W9 reporting.
4. Personal payments
A W9 form is generally not required for personal payments between individuals. If you are making a casual payment to a friend, reimbursing someone for shared expenses, or settling a personal debt, a W9 is usually not needed.
5. Gifts and inheritances
Transactions involving gifts or inheritances are exempt from W9 reporting. When money or property is given as a gift, or inherited, the recipient is not required to fill out a W9 form.
It’s important to note that while the IRS provides guidelines on when a W9 is required, businesses may still choose to request W9 forms from vendors, even if the payments are expected to be below $600 or are not directly related to business activities.
Collecting W9 forms as a standard practice helps maintain accurate records and facilitates compliance with tax regulations, making it easier for businesses to fulfil reporting requirements if payment thresholds increase or if business activities evolve.
When should I send W9?
Although there’s no official deadline for filing your W9, you should fill it out as soon as you get one. Promptly completing form W9 ensures you will get your tax forms in return as quickly as possible.
Note: If you fail to send someone a W9 or send one with the wrong information, you may be subject to a $50 penalty of perjury. Double-check that your completed form W9 has the correct TIN before sending it.
If you want to learn more about tax filing strategies, take a moment to read through this insightful article: How to File Taxes for Ecommerce.
Penalties for non-compliant Form W9
It’s important to note that the W9 form itself is not filed with the IRS. Instead, it is a request for the recipient’s TIN and other information.
Non-compliance with providing a W9 does not result in penalties directly associated with the form itself. However, failure to provide accurate information on the form can have consequences when it comes to tax reporting and compliance.
Here are some key points related to penalties for non-compliance with tax reporting requirements:
1. Backup withholding
If a payee fails to provide a TIN or provides an incorrect TIN on the W9 form, the payer may be required to initiate backup withholding. Backup withholding is a withholding tax on income payments made to the payee, and it is generally set at a flat rate.
2. Penalties for providing false information
Intentionally providing false information on the W9 form or any other tax-related document can lead to penalties. Penalties may include fines and, in some cases, criminal charges.
3. IRS audits
Inaccurate or incomplete information on the W9 form may trigger IRS audits. If the IRS discovers discrepancies during an audit, it can result in additional business taxes, interest, and potential penalties.
It’s crucial for both payers and payees to understand the importance of providing accurate information on the W9 form to avoid these potential consequences.
Payers are responsible for ensuring that they have the correct TIN for tax reporting purposes, and payees must cooperate by providing truthful and up-to-date information.
It’s recommended that individuals and businesses consult with tax professionals or legal advisors to understand the specific implications of non-compliance with tax reporting requirements and to ensure proper adherence to tax laws and regulations. The IRS provides guidelines and resources on these matters, and staying informed is essential to avoid potential penalties.
Tips for your business to efficiently manage W9
Want to submit your W9 Form stress-free? Here are some valuable tips for a worry-free process, all for free.
1. Incorporate W9 requests into the onboarding process
Integrate the request for a W9 form into your standard onboarding process for new vendors, contractors, or service providers. Make it clear that providing accurate tax information is a standard requirement, whether you’re onboarding them in person or through a desktop application.
2. Clearly communicate the requirement
Clearly explain to the individual why you need the W9 form. Emphasize that it is necessary for tax reporting purposes, ensuring compliance with IRS regulations.
3. Provide detailed instructions
Offer clear instructions on how to complete the form. Highlight the essential information required, such as the individual’s name, address, and taxpayer identification number (TIN).
4. Offer multiple submission options
Provide various options for submitting the W9 form to accommodate different preferences. Options may include email, postal mail, secure online portals, or electronic signature platforms.
5. Use electronic methods for collection
Implement electronic methods for collecting W9 forms, such as secure online portals or electronic signature platforms. This can streamline the process, reduce paperwork, and facilitate easier tracking.
6. Automate follow-up reminders
Use automated reminders to prompt individuals or entities to submit their W9 forms. This can be done through email reminders or notifications within your business management services.
7. Provide assistance and support
Offer assistance and support to individuals who may have questions or concerns about the W9 form. Having a designated contact person or a helpdesk can facilitate the process and address any issues promptly.
8. Maintain secure storage
Establish a secure and organized system for storing W9 forms. Ensure that sensitive information is protected and accessible only to authorized personnel. This will make it easier to retrieve forms when needed for tax reporting and build trust and encourage prompt submission.
9. Integrate with accounting software
Integrate W9 information seamlessly with your accounting or financial cloud software. This integration can help automate certain aspects of tax reporting and reduce the risk of manual errors.
Simplifying your tax reporting with Synder
Experience unparalleled ease in managing your accounting processes with the ultimate data synchronization app – Synder.
From seamless income reporting to effortless expense tracking, Synder stands out with its intuitive interface, making data synchronization a breeze for small business owners.
Sign up for the free trial now and take control of your business’s financials. Dive deeper into the world of financial management through Synder’s engaging Weekly Public Demos, offering valuable insights and strategies for optimal use. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to elevate your financial processes. Synder – Simplify, Sync, Succeed!
10. Regularly audit W9 compliance
Conduct periodic audits to ensure that your business is consistently collecting W9 forms and that the information is accurate and up-to-date. This proactive approach can prevent issues during tax reporting.
By implementing these strategies, you can increase the likelihood of receiving timely and accurate W9 forms while maintaining a positive and transparent communication process with the individuals involved.
Key takeaways: Form W9
Understanding the significance of W9 forms is essential, particularly for contract workers, freelancers, and the self-employed. Completing the form accurately is crucial to avoid potential penalties. Distributing the form securely to the requesting party and safeguarding sensitive information are key considerations for individuals. As a vital component for tax filing in situations where paycheck taxes are not withheld, the W9 underscores the responsibility of independent workers for their tax obligations.
Remember, while the form doesn’t go to the IRS, its proper submission to requesting employers ensures accurate tax reporting.
If you’ve been looking into the nuances of Form W9, consider delving into our guide on “Demystifying the W2 Tax Form”. By exploring both the W9 and W2 perspectives, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the tax landscape with confidence.
FAQs
1. What is the most secure way to submit Form W9?
Ensuring the security of sensitive information, such as that found on a Form W9, is crucial. Here are some secure methods for submitting Form W9:
- Use secure online portals, encrypted emails, or electronic signature platforms for W9 submissions.
- Securely send password-protected PDFs if using email attachments.
- Opt for certified mail or in-person submission for physical delivery.
2. Can I refuse to fill out Form W9?
If you refuse in response to a legitimate request, your client will withhold taxes from your pay at a rate of 24%. Businesses have a heavy obligation from the IRS to obtain a completed Form W9 from anyone they pay $600 or more to during the year. Failure to comply can result in fines.
If you think the person requesting the form has no business asking for it, though, refusal is probably a good idea. If you’re concerned, ask a tax professional for guidance.
3. When is Form W9 not required?
A Form W9 may not be required if the transaction is exempt from IRS reporting, involves
personal non-business payments,
- gifts
- grants,
- non-taxable entities,
- specific exemptions as per IRS regulations.
If unsure, check with the entity making the payment or consult a tax professional.
4. How do I know if my W9 Form has been accepted by a payer?
The IRS doesn’t officially “accept” or process Form W9, as it’s not filed with the IRS. Contact the entity or individual who requested your W9 to confirm receipt and inquire about its status. Look for acknowledgement emails, check online portals, or follow up directly for verification.
5. Can I update the info on my W9 if there are changes in my taxes status or personal details?
Yes, it’s important to keep your information current. You may need to submit a new W9 if there are changes to
- your legal name,
- address,
- taxpayer identification number (TIN).
Or if the payer requests updated information. Always respond promptly to such requests to ensure accurate tax reporting.
6. How does the W9 differ from the 1099-MISC?
In contrast, the W9 is not a reporting form; instead, it is an informational form used by a person or entity to provide their taxpayer identification information to the payer. The payer collects this information to fulfil their reporting obligations when necessary.
The 1099-MISC form is used by businesses to report payments made to individuals or entities who are not employees. It covers various types of income, such as freelance earnings, rent, royalties, and other miscellaneous payments.
7. Can I use my Social Security Number (SSN) as the TIN on the W9 Form?
Yes, individuals can use their SSN as the TIN on the W9 form. It’s important to ensure accurate entry to avoid issues with tax reporting.
Discover our latest article: W9 vs 1099: Comparing IRS Forms 1099 vs W9 to navigate tax season with ease.







.png)
