Every business thrives on its total income through goods or services. Yet, accurately accounting for that revenue can sometimes be complex, particularly when it comes to understanding and applying the concept of “revenue recognition.” Revenue recognition is a critical component of accounting and business. It is the process of recording revenue in a company’s financial statements when specific criteria have been met, not necessarily when the cash payment occurs. It is fundamental to reflect a company’s financial health and overall performance accurately.
Learn how to manage your bookkeeping and accounting efficiently with Synder!
Overview of revenue recognition
Revenue recognition comprises different methods and standards. The two major sets of standards used globally are GAAP and IFRS (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles and International Financial Reporting Standards). Both have specific rules and guidelines concerning when revenue should be recognized. Under these standards, revenue is recognized when it is realized or realizable and earned. This concept fundamentally means that goods or services have been provided, and either payment has been received or there is reasonable assurance that payment will be received.
The manner of revenue recognition has a significant impact on financial reporting. Since revenue is a vital line item in the income statement, the way it’s recognized can alter the entire outlook of the business’s financial health. Thus, it is essential for businesses to understand and correctly apply the principles of revenue recognition.
Key principles of revenue recognition
The major principles of revenue recognition are outlined in a five-step model as provided by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). This model helps businesses determine when and how to recognize revenue from contracts with customers. These principles are:
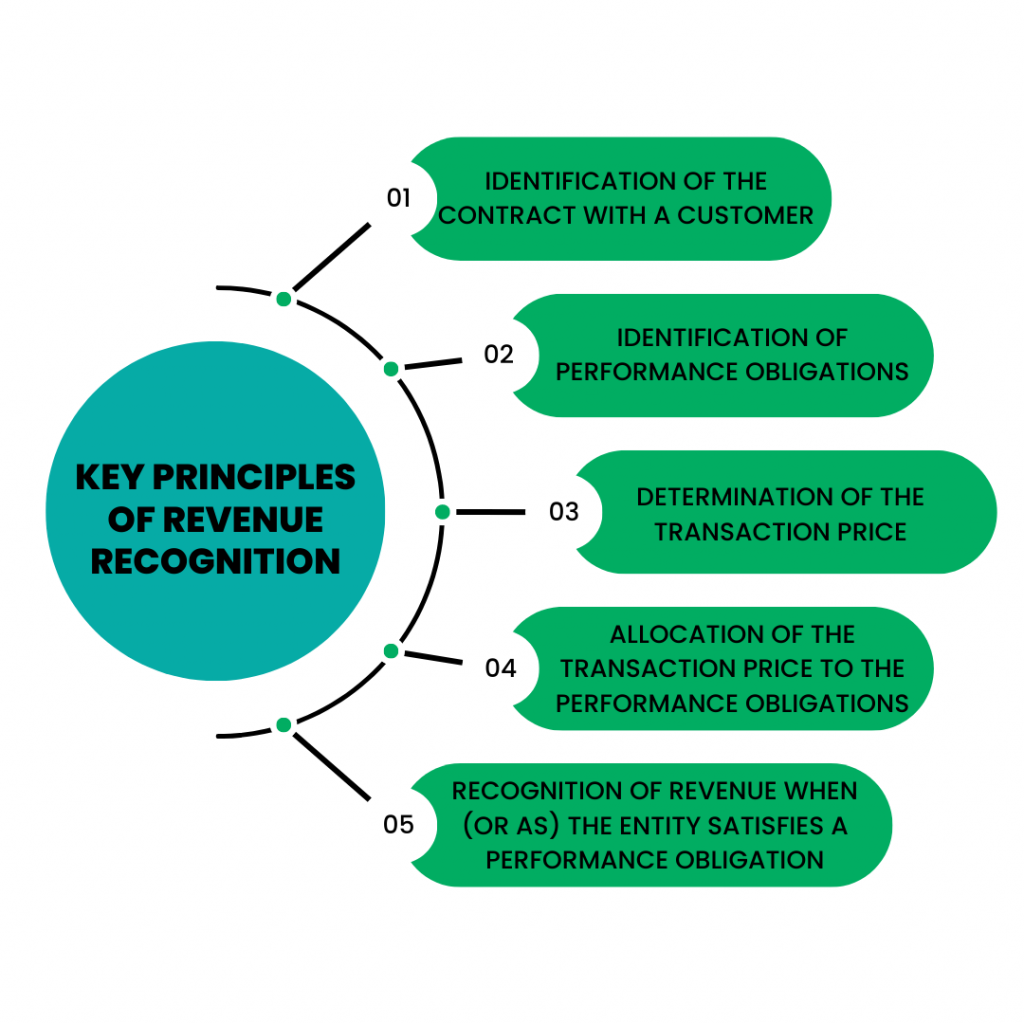
Identification of the contract with a customer
This revenue recognition principle states that a contract, whether written, oral, or implied by an entity’s business practices, must exist between the customer and the company. The contract should clearly outline the rights of both parties, the payment terms, and the goods or services that the company has agreed to provide.
Identification of performance obligations
In the contract, there may be one or more performance obligations, which are promises to provide distinct goods or services to the customer. A distinct good or service is one that the customer can benefit from on its own or alongside other resources readily available to them.
Determination of the transaction price
This principle involves determining the total amount of consideration that a company expects to receive in exchange for providing the goods or services as specified in the contract. The transaction price may include fixed amounts, variable amounts, or both.
Allocation of the transaction price to the performance obligations
If the contract includes multiple performance obligations, the transaction price must be divided among these obligations. The allocation is typically based on the standalone selling price of each distinct good or service.
Recognition of revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation
This principle states that a company recognizes revenue when it satisfies a performance obligation by transferring the promised good or service to the customer. This could be done at a single point in time or over a period, depending on the nature of the good or service.
The purpose of revenue recognition in accounting
In the realm of accounting automation, revenue recognition is a principle that establishes the conditions under which revenue is recognized or accounted for. Its primary purpose is to provide an accurate and consistent method to record when sales transactions occur, thus ensuring the timely and appropriate recording of income.
Revenue recognition is essential for several reasons:
Reflects economic reality
One of the fundamental purposes of revenue recognition is to depict a business’ economic reality accurately. When revenue recognition principles are correctly applied, a business’ financial statements present an accurate picture of its financial performance and health. This accuracy is crucial for internal decision-making processes and for external parties like investors, creditors, and regulatory bodies.
Ensures comparability
Revenue recognition allows for comparability across different businesses and industries. By following set standards like GAAP or IFRS, businesses adhere to a common framework for recognizing revenue. This standardization enables stakeholders to compare the performance of different businesses more easily and reliably.
Assists in forecasting and planning
Revenue recognition principles aid businesses in financial planning and forecasting. By consistently recognizing revenue, businesses can better track their performance over time, identify trends, and make informed projections about future performance.
Maintains regulatory compliance
Compliance with recognized accounting standards is a legal requirement in many jurisdictions. Proper revenue recognition helps businesses avoid regulatory sanctions, penalties, and potential reputational damage that can come from non-compliance.
Investor confidence and market stability
Revenue recognition also contributes to investor confidence and overall market stability. By ensuring revenues are not overstated or understated, investors can trust the financial information provided by companies. This trust is crucial for the functioning of capital markets.
Revenue recognition plays an indispensable role in accounting. It ensures that revenue – a crucial indicator of a company’s success – is accurately measured and reported. This process not only reflects the true financial performance and health of a business but also helps maintain transparency, comparability, and trust among stakeholders, thereby contributing to a stable and efficient market economy.
Revenue recognition models in various industries
The implementation of revenue recognition principles can vary significantly across different industries.
For technology and software companies, recognizing revenue can be complicated due to multiple-element arrangements, licensing, and post-delivery obligations. The timing and amount of revenue recognized may vary significantly based on the specifics of each transaction.
Construction and real estate companies deal with long-term contracts, which requires careful evaluation of the percentage of completion method or the completed contract method. This industry faces unique challenges in terms of recognizing revenue, especially concerning contracts spanning multiple reporting periods.
In service-based businesses, revenue recognition often occurs over time as the service is delivered. However, determining progress towards satisfying the performance obligation can take time and effort.
Product-based businesses often recognize revenue at the point of sale when control of the goods transfers to the customer. However, issues like product returns and allowances can complicate this process.
Complexities and challenges in revenue recognition
Despite the availability of detailed revenue standard and guidelines, complexities abound in revenue recognition.
Multiple-element arrangements
If a transaction involves several distinct goods or services, the revenue must be allocated appropriately to each element, which can be complex.
The timing and pattern of revenue recognition
In some cases, it may be difficult to determine whether revenue should be recognized at a point in time or over a period.
Changes in contract terms (modifications or cancellations)
These can further complicate the revenue recognition process, as they may require reassessment of the transaction amount or the performance obligations.
Revenue recognition software: Revolutionizing financial management
As businesses grow and their transactions become increasingly complex, managing and implementing revenue recognition rules can become a monumental task. This is where revenue recognition software steps in, providing an efficient and automated solution for handling the complexities of revenue recognition.
Revenue recognition software is a specialized tool designed to manage, process, and report revenue in line with the latest accounting standards (GAAP and IFRS). It enables businesses to automate the revenue recognition process, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors.
The capabilities of revenue recognition software can vary, but most offer features like automated calculation of recognized revenue, tracking of performance obligations, transaction price allocation, and detailed reporting and SaaS analytics. They can handle various types of revenue streams and complex multi-element contracts, ensuring that revenue is recognized accurately and in compliance with relevant accounting standards.
Furthermore, these tools often come with integration capabilities, allowing them to work seamlessly with other financial systems such as ERP or CRM software. This enables businesses to consolidate their financial data in one place, simplifying the process of revenue management.
In today’s digital age, revenue recognition software is not just a nice-to-have but rather a must-have for businesses aiming to maintain regulatory compliance while achieving efficiency and accuracy in their financial reporting. As the rules around revenue recognition are evolving, these software solutions will be key in helping businesses navigate the complexities of revenue recognition.
Read our article to learn more about revenue recognition software solutions and check available options – check it here.
The role in financial analysis
Revenue recognition plays a fundamental role in financial analysis as it directly influences the measurement of a company’s performance and profitability. Below are key ways in which revenue recognition impacts financial analysis:
Profitability metrics
Since revenue is a primary determinant of many profitability metrics such as gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin, the timing and manner of revenue recognition can significantly influence these calculations. A change in revenue recognition policy might lead to a significant shift in these ratios, altering the perceived profitability of the company.
Trends and comparability
Revenue recognition policies impact the comparability of a company’s financial performance over different periods and against other companies. If businesses in the same industry use different revenue recognition methods, it can distort comparisons. Similarly, changes in revenue recognition policies can make year-over-year comparisons misleading.
Cash flow analysis
While revenue recognition doesn’t directly affect cash flow, as it’s based on accrual accounting, the timing of revenue recognition can impact the indirect method of cash flow statement preparation. For instance, if a company recognizes revenue before receiving payment, this will increase accounts receivable, which would be adjusted for in the operating cash flows section.
Read more about the way How to calculate Accounts Payable.
Valuation metrics
Revenue recognition affects various valuation ratios like Price/Sales, EV/Sales, or those based on EBITDA, all of which use revenue as a component. Changes in recognition policies can thus lead to significant shifts in a company’s valuation ratios.
Investor revenue perception
Investors and analysts often base their perception of a company’s performance on reported revenue. Thus, revenue recognition policies can impact investment decisions. If investors believe a company’s revenue recognition policies are aggressive or not in line with industry norms, it might affect the company’s perceived riskiness and attractiveness as an investment.
Risk assessment
Analysts and auditors assess a company’s risk based on its revenue recognition policies. Companies with complex revenue recognition processes (such as long-term contracts or multiple performance obligations) might be deemed higher risk due to the potential for error or manipulation in recognizing revenue.
Future trends
As we look towards the future, several trends may impact revenue recognition.
First, technology is set to play a significant role. As companies’ transactions become increasingly complex, technological solutions can help automate and streamline the revenue recognition process. This development could help reduce errors and increase efficiency.
Regulatory requirements are also likely to continue evolving, and companies will need to stay up-to-date with these changes. These could include more detailed disclosure requirements or further changes to the timing or manner of revenue recognition.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning will likely play a significant role in revenue recognition in the future. These technologies could be used to automate the recognition process and analyze patterns to identify potential issues or anomalies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and accurately implementing revenue recognition is crucial for any business. It impacts not only the company’s financial statements but also how the business is perceived by investors and other stakeholders. As the world continues to change, and business transactions become more complex, it will be increasingly important for companies to stay up-to-date with revenue recognition standards and practices.






