In such a progressive time, generating ideas remains a natural process. We may create a significant breakthrough to solve people’s problems, find ways to satisfy their needs and make a profit from it. But there’s something that lies between an idea and the actual formation of a business – a well-designed ecommerce business plan.
Some ecommerce business owners might skip this step and concentrate on the urgent tasks on their to-do list, like launching a website, connecting online payment platforms, and presenting products. However, other founders choose to take some time to research their field, come up with a business strategy, and set goals to take their business to the next level.
Creating an ecommerce business plan will give you clarity about what steps you need to take to make your dream of growing a successful ecommerce business a reality. Let’s look at an actionable guide on how to create a thorough business plan for your ecommerce business.
Contents:
1. What is an ecommerce business plan?
- What is the difference between a business model and business plan?
- Strategic business planning and business strategy
2. 4 reasons why you need an ecommerce business plan
3. Types of ecommerce business plans: Which plan works best for you?
- Traditional business plan
- Lean start-up business plan
- Which aspects to consider before creating your own business plan?
4. Structure for business plan templates: How to write a small plan for your business step-by-step
5. Ecommerce business plan tips and tricks
6. FAQs about ecommerce business plans
What is an ecommerce business plan?
A business plan is a document that details a company’s goals and how it intends to achieve them.
A business plan is best described as a roadmap from the current starting point to the goal. It includes all the possible ways to get your online store where you want it to be, sets deadlines, and covers potential issues.
Creating an ecommerce business plan is an essential exercise for any new online business owner or even those who are already on board. A good business plan won’t only help you organize your ideas and financial forecasts, but it’ll also give potential investors’ confidence in your business idea.
As the statistics show, entrepreneurs with a business plan are 16% more likely to achieve success compared to non-planning entrepreneurs. These statistics are compelling enough to prompt the creation of a business plan for every business without exceptions, wouldn’t you agree?
However, this plan comes with certain challenges. In the sphere of entrepreneurship, understanding the nuances between various concepts is crucial for effective business management. One common source of confusion is distinguishing between a business model and a business plan. Despite their apparent similarity, these terms encapsulate distinct aspects of a company’s strategy and development.
What is the difference between a business model and business plan?
If a business plan describes your business workflow, then a business model is a detailed statement of goal and action framework. When you’re deciding on a business model for your company, your main objective is to choose the right way to generate profit.
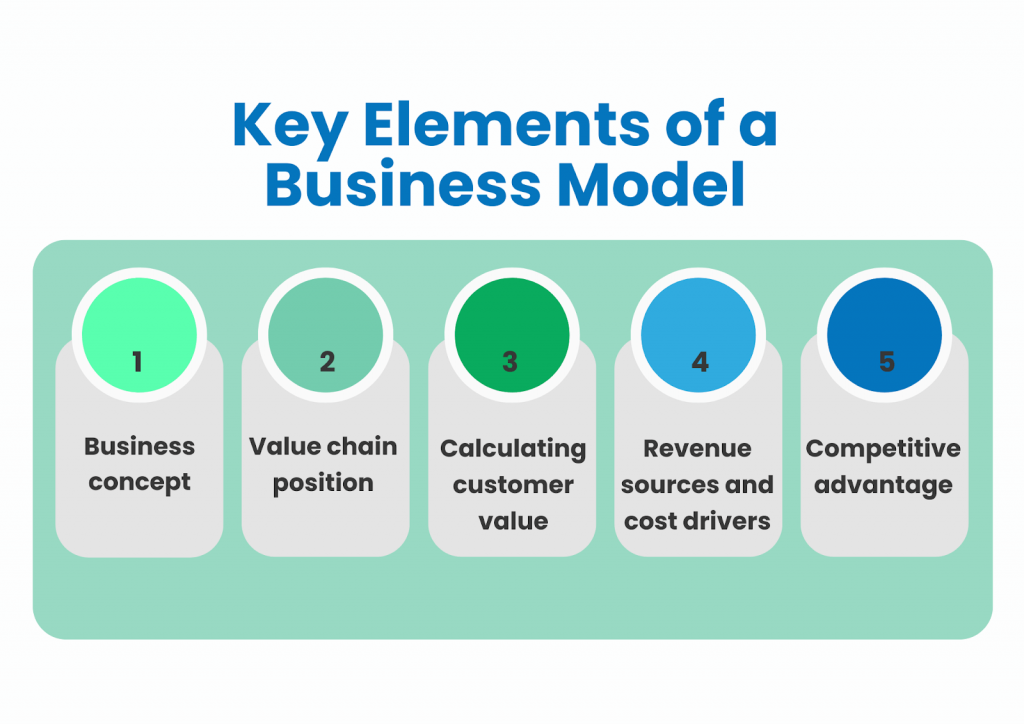
A business model includes the following five key elements:
- Business concept: A short description of your product or service, its benefits, and customer profile.
- Value chain position: Your business’s place in the value chain.
- Calculating customer value: The estimated value of your product or service for the core audience.
- Revenue sources and cost drivers: Sources of income and expenditure.
- Competitive advantage: Outstanding and unique features that help you stand out from your competition.
It’s important to look closely at these similar-sounding terms to understand the differences to make sure we understand things correctly and don’t get confused.
Strategic business planning and business strategy
Ecommerce business strategy is the art of thinking ahead and making informed decisions about where your business will go next. It’s the science of figuring out how you can help your business get there.
In other words, a business strategy is a high-level plan for what you want your business to achieve in the future and how you intend to get there.
Strategic planning, on the other hand, is an activity that precedes business strategy. It’s a detailed process of analyzing the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats that your ecommerce business faces or is likely to face. This helps you understand where your company is now and where it needs to get to next.
In a nutshell, a business strategy is an outcome based on a particular theory that was converted from verbal ideas to a step-by-step strategic plan that will be taken into action.
According to Roger Martin, Professor Emeritus at the University of Toronto’s Rotman School of Management, here’s how you can distinguish these two terms:
| Strategic business planning | Business strategy |
| “We’re going to…” | “We want this to happen” |
| You control costs. | The costs are dictated by your customers. |
| It’s up to you how to organize everything (how much to offer, raw materials to buy, etc.). | You need to take into consideration your customers’ opinions and preferences. |
4 reasons why you need an ecommerce business plan
If you’re running a startup, your ecommerce business plan will show your potential partners how profitable your small business strategy is and how likely it is to succeed. When presenting your idea to future investors, you may use the most powerful and persuasive words.
However, when it’s put on paper, your investors will see clear ideas, numbers, and perspectives. As a result, they’ll be able to evaluate your deal and make business decisions quicker.
A well-structured business plan acts as a foundation for building trust and credibility with potential investors, demonstrating the viability of your marketing strategies and positioning in the market.
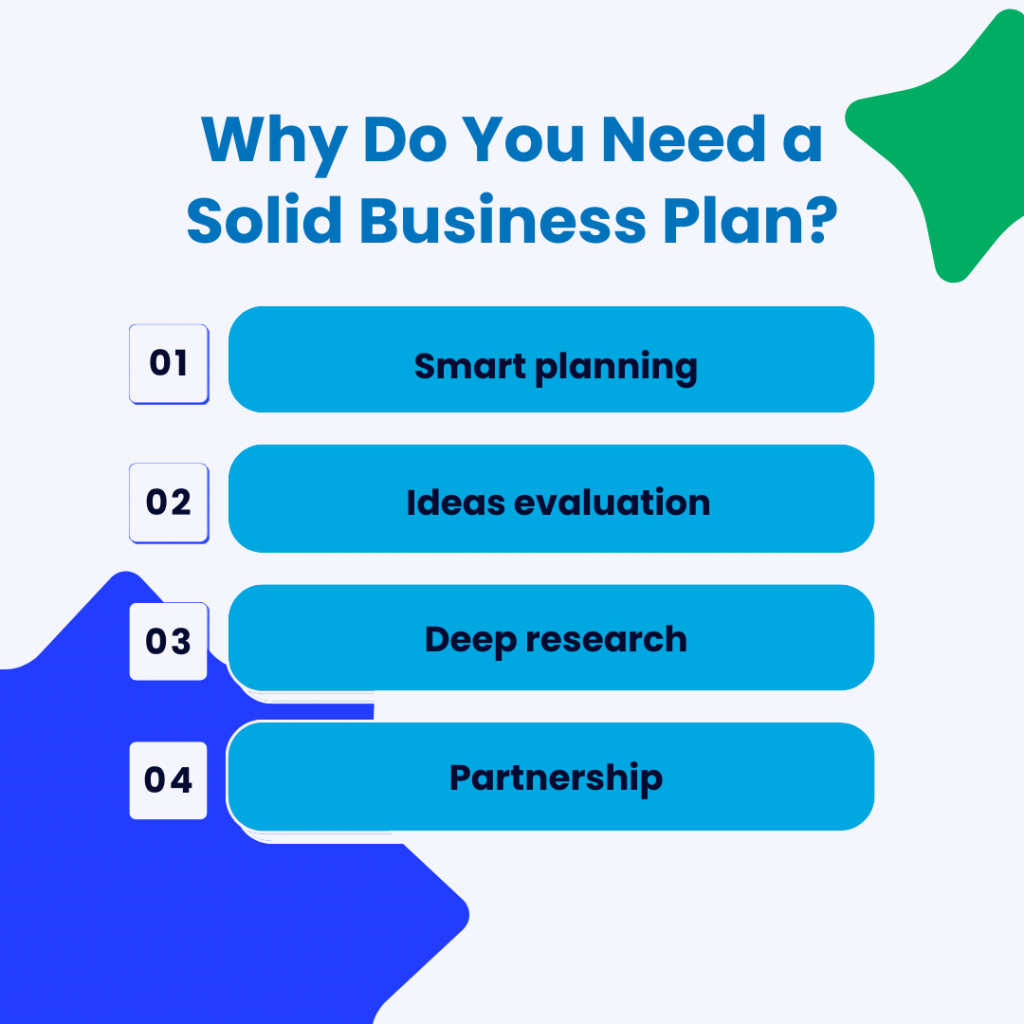
Here are 4 things any seasoned entrepreneurs and businesses will achieve, with a solid business plan:
- Smart planning. Thorough planning of your actions, goals, expenses, and business activities will save you time, money, and, consequently, your business.
- Ideas evaluation. If you find it difficult to focus on one single idea in your head, a strict business plan could help you choose the most successful one and devote all your attention to it.
- Deep research. You’ll need to find your target audience and research the industry market. Studying your competitors will help you analyze your strengths and weaknesses in order to improve and beat them in the long run.
- Partnership. If you plan to integrate with other companies, it’d be easier for them to understand your company and product when they see your ecommerce business plan, especially if these companies are more developed than yours. This not only enhances your credibility but also facilitates potential collaborations and partnerships.
Types of ecommerce business plans: Which plan works best for you?
There are two different types of ecommerce business plans:
- a traditional business plan;
- a lean start-up business plan.
Let’s look at them in more detail.
Traditional business plan
The traditional business plan is more widely used. They’re standard and contain many details. Typically, they include an executive summary, marketing and sales strategy, financial analysis, and other sections on operations, management, products and services. For those looking for a cost-effective option, a lean start-up business plan, often available as a free business planning template, offers a streamlined approach with essential details.
The traditional business plan is often used for outside funding or when applying for grants or loans, making it a valuable tool when presenting your business to a potential partner. It’s applicable, especially if your business model revolves around an online platform. For example, for businesses operating on platforms like Shopify, the traditional plan can provide a comprehensive roadmap for growth and success.
Lean start-up business plan
The lean start-up (“experimental”) business plan uses the same structure. However, it’s only one page long and, therefore, has fewer details. Lean start-up methodology helps reduce risk and increase innovation by focusing on the essentials, accelerating time to market by streamlining processes, and reducing unnecessary spending. A lean start-up approach focuses on the customer, testing new ideas with customers, and measuring results to drive future decisions.
Which aspects to consider before creating your own business plan?
A well-organized and researched business plan will serve as your virtual guidepost for launching your company, keeping you on track with your objectives, budgeting, and marketing strategies throughout the life of your ecommerce business.
To get started with the creation of your business plan, ecommerce business must first decide on:
The type of products you’re selling:
- Physical products;
- Digital products;
- Services.
Your target customers:
- Business to Business (B2B);
- Business to Consumer (B2C);
- Marketplace.
Where you get the products from and how you store them:
- Manufacturer in-house;
- Third-party manufacturer;
- Dropshipping;
- Wholesale.
After deciding on these, you can go further – create a structure for the future informative business plan. Consider whether you’ll be selling your products exclusively online or if you plan to incorporate an omnichannel strategy involving both online and physical retail spaces.
Structure for business plan templates: How to write a small plan for your business step-by-step
As entrepreneur Kevin J. Donaldson put it, “Going into business without a business plan is like going on a mountain trek without a map or GPS support—you’ll eventually get lost and starve!”
While the idea of creating a business plan may appear cumbersome, once you understand the components of a business plan, it’s much simpler than you think. Especially when you have a well-designed ecommerce business plan template in front of you.
Here are 8 crucial sections of an ecommerce business plan template, each acting as a separate business plan step you need to take:
- Executive summary;
- Company analysis;
- Market and competitive analysis;
- Products and services analysis;
- Customer analysis;
- Marketing plan;
- Logistics and operations plan;
- Financial plan.
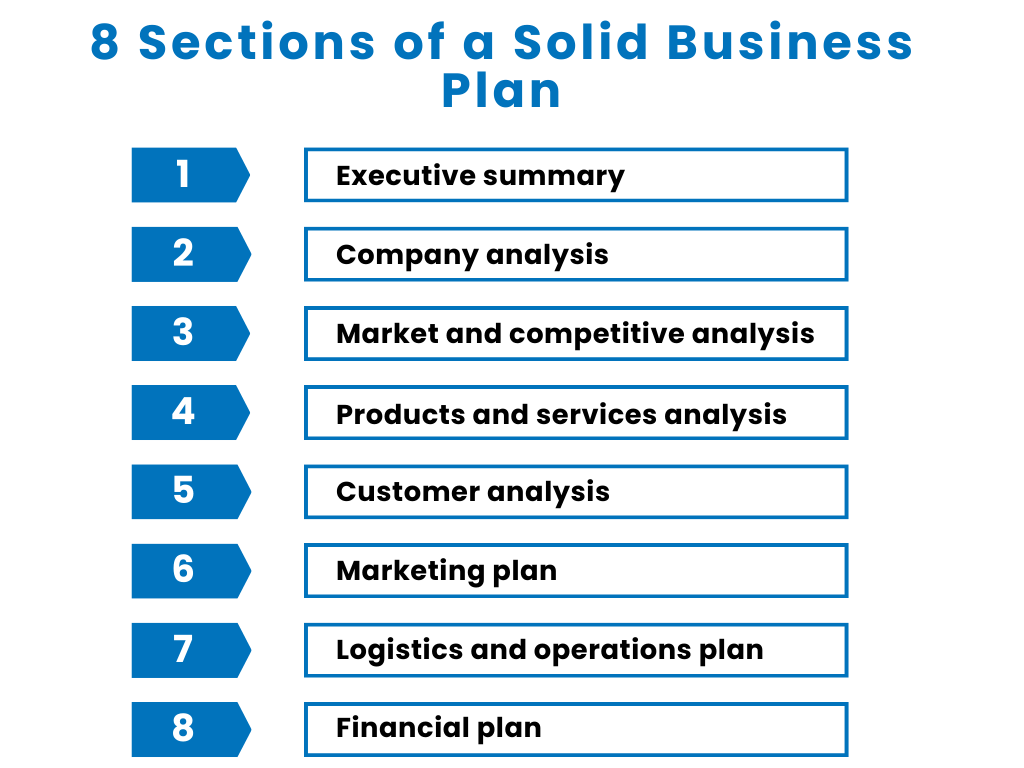
As you can see from this business plan structure, you can divide the whole process into two sections based on the information you’ve got from the first 5 steps:
- analysis;
- actual planning.
Now let us tell you about each of them in detail so that you know the ins and outs of creating a solid business plan.
Section 1. Executive summary: Introduction
Even though this is one of the most crucial parts of your business plan, make sure you complete it last.
Here, in this section, you should write all key points about your business. What does it do? What is unique about it? What are your goals? How will you achieve them? How profitable will your business be? Why should your business succeed? These are the core questions that answer how your ecommerce business strategy sums up and what your end-goal is.
Here’s a short list to make it easier for you:
- Clearly explain how your business will serve the market.
- Highlight competitive advantages, emphasizing a unique brand proposition.
- Outline the schedule from the initial idea to the first online sales.
- Emphasize the steps involved in developing and establishing your brand identity.
- Provide information on any recent updates.
- Highlight significant milestones achieved since the inception of your business.
If you already have an established business, you may include your company information:
- Briefly outline the history of your company and its product or service.
- Include details such as the start date, ownership information, and key staff members.
- Describe the growth of your ecommerce business.
- Highlight key metrics like year-over-year revenue increases, profitability, market share expansion, and the growth in the number of customers.
If you’re looking for additional financing for expansion, then give a brief financial summary.
Make sure you think thoroughly about all the points and spend enough time writing them down.
Section 2. Company analysis: Background
In this section, you are to describe what your business is and what you’re planning to do. Mention your business format, business model, long-term and short-range goals. Also, write some information about each member of your staff.
Your vision and values define your company, so this is the right section to
- Clearly describe what your company will deliver to customers.
- Highlight key features and benefits of your products and services.
- Ensure that your company analysis effectively communicates the unique selling propositions.
- Emphasize distinctive features that set your products apart in the market.
Section 3. Market analysis: Search the trends
Selling online may be a struggle if you choose the wrong market.
When looking for a potential market, please pay attention to the customer profile, needs, industry trends, and audience size. Your target audience is the one that needs your product or service, who will purchase it and use it.
Utilizing advanced technologies such as AI to analyze market trends and customer behavior can provide valuable insights for strategic decision-making in your ecommerce business.
Consult government statistics offices, various associations, research news articles, and other reliable sources to collect as much precise data as possible. Serving the market that you can identify and classify is much easier.
Section 4. Products and services and competitive analysis: What makes you stand out from the competition
Extended information on your products and services is expected here. Describe the characteristics, features, and benefits of the products and services.
Are you going to launch new products or services? Great! Do mention them, as well as how products will increase the company’s income.
Analyze your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses. What is their goal? Why does your solution stand out among your competitors? Which weaknesses of the competitors can you turn into the opportunity?
Take your time to analyze as many details as possible so that you have the foundations for the future steps in planning.
Section 5. Customer analysis: Make up your ideal customer
We’ve just talked about your target audience, so now, in this section, it’s time to turn to your ideal customer. Take your average customer and describe them using general and specific criteria:
- location,
- age,
- education,
- behavior patterns,
- leisure time,
- occupation,
- preferable technology in use,
- salary,
- employment,
- beliefs,
- values,
- opinions, etc.
Understand your customer base thoroughly and employ targeted communication strategies, such as personalized email campaigns, to engage and retain customers. Tailor your products to meet the specific needs and preferences of your identified customer segments.
You should understand that a woman in her early 20s has different preferences and needs in shopping, traveling, or leisure activities when compared with a 70-year-old man.
Choose relevant information according to your products or services and find out who your customers are and what they’re interested in. It’ll help you understand the consumer needs better.
Section 6. Marketing plan: Create a marketing strategy for your business
First, you need to choose your market and a platform on which you’ll be selling.
If you want to launch an online business on Instagram, you should invest in this platform. However, if your target audience isn’t on Instagram, you should change your marketing strategy and start selling where your customers may easily find you.
Identify an optimal hubspot with your target audience, considering social media platforms, online forums, or other channels that align with your customers’ preferences and behaviors.
Here’s a short list of exactly what to look out for:
- Set a price for your product or service, emphasizing its value.
- Clearly describe what you’re selling and highlight its differentiation from competitors’ offerings.
- Explain how you’ll promote products to your target customers.
- Specify the channels or methods you plan to use for effective promotion.
Consider which marketing channels you’ll be utilizing to reach your customers:
| Paid marketing channels | Organic marketing channels |
| PPS advertising | SEO |
| Affiliate marketing | Social media posts |
| Social media marketing | Content marketing |
| Influencer marketing | Email marketing |
Planning to open your store on Amazon? Learn how!
Section 7. Logistics and operations plan for your business
The logistics and operations section is everything you own physically – from technical equipment to a warehouse. All information about the suppliers, production, shipping and fulfillment, facilities (you may have to include an address), equipment, and inventory, including the integration of a POS system, should be mentioned here, highlighting each essential part of the operational process.
Show that you have a decent understanding of how to run an ecommerce company. Your product pricing will also depend on how much you spend on logistics and other operations included in your workflow.
Section 8. Financial plan for your ecommerce business
Financial planning helps you track your financial health.
Do you have a good command of accounting basics? Is your cash flow positive or negative? Where do you record your business transactions?
Below are the statements that you usually need to have the full picture of your financials:
- Income statement. Your income statement shows your income and expenses over a month, a quarter, or a year. If you subtract your expenses from your income, you’ll come up with your net profit.
- Balance sheet. In order to calculate how much equity you’ve got in your business, you should use your balance sheet. In the left column, you should write all your assets (machinery, stock, business premises, vehicles, etc.). In the right column, you should point out all your liabilities (accounts and wages payable, business loan repayment, business credit card payments, taxes, etc.). If you subtract your liabilities from your assets, you’ll get your business’ shareholder equity.
- Cash-flow statement. Cash-flow statements are almost like your real-time income statements. Preparing a cash-flow statement manually involves summarizing and categorizing cash inflows and outflows over a specific period. Start with the net income, adjust for non-cash items, account for changes in working capital, include investing and financing activities, and calculate the net cash flow. Ensure the ending cash balance matches the balance sheet.
Why go through the trouble of manual financial management when Synder can streamline the process for you automatically? Synder is a cutting-edge software that seamlessly connects your ecommerce channels with popular accounting platforms like QuickBooks or Xero. It not only saves you hours on bookkeeping but also ensures accurate and organized financials for your business.
Now you can say goodbye to the overwhelming task of manually managing your financial statements:
- Income statement. Let Synder effortlessly compile comprehensive P&L statements, providing invaluable insights into item and customer information, discounts, shipping fees, and locations. With a simple click, synchronize your transactions to your accounting books and watch as Synder accurately calculates your net profit.
- Balance sheet becomes a breeze with Synder. Synder takes care of the calculations, subtracting your liabilities from your assets to reveal your business’s shareholder equity.
- Cash-flow statement. Why manually track your cash flow statements when Synder can do it in real-time? Say hello to hassle-free financial management – just one click, and Synder synchronizes your transactions, ensuring 100% precise reconciliation.
In addition to Synder providing your partners with accurate and well-organized statements, it’s specifically tailored for ecommerce business owners who use multiple sales channels and payment platforms. The software facilitates automatic and 100% precise reconciliation of all financial activities, allowing you to focus on growing your business. No more manual data entry, no more discrepancies — just seamless synchronization that ensures your financial records are always accurate and up-to-date.
Create an account in the most detailed and accurate ecommerce business accounting software. Do you have questions about the software? Or want to find out how Synder can benefit your business? Receive answers to all your queries during our Weekly Public Demo.
Ecommerce business plan tips and tricks
When it comes to bringing your ecommerce business idea to life, there are tons of things you need to consider. From accounting and taxes to market research and competition, you’ll need to think about almost every aspect of launching your business. Keep the following things in mind when you start the ecommerce business plan writing process:
1) Make your ecommerce goal clear
If you rely on funding for your ecommerce business, make sure you write a comprehensive business plan. If you’re writing it just for yourself, you can make it less detailed.
2) Know your ecommerce audience
It is crucial to focus on understanding your audience to create a precise plan and implement strategies that align with their needs. Tailor your approach to resonate effectively with your target demographic, ensuring your business plan addresses their specific requirements and objectives.
Modify or incorporate sections accordingly to enhance the relevance of your plan.
3) Keep your plan short and stick to the point
Your business plan shouldn’t be longer than 15-20 pages. Valuable additional materials may be added as appendices at the end of the plan.
4) Invest time in research for a perfect ecommerce business plan
Most of the sections can be written according to your vision of the ecommerce business. However, some sections might require some additional study or a specialist’s consultation.
5) Avoid mistakes and inconsistency in your business plan
To enhance the quality of your business plan, consider having someone else proofread it. Having a fresh set of eyes can help identify potential mistakes and ensure a consistent and logical structure. It’s always beneficial to seek another perspective to catch any overlooked errors.
6) Building your ecommerce Plan B
Investors prioritize gaining profits from their investment in your ecommerce business. It’s valuable to present them with strategies for maximizing profitability, emphasizing the importance of having a contingency plan. This ensures flexibility and options, allowing for adaptability in various situations.
Tying it all together
What’s one purpose of writing a business plan before entering the market? It’s to be ready for the challenges that naturally occur in every ecommerce business owner’s life.
A business plan is a foundation for your business to grow. Some business plans include more detailed information, some less. You may choose the one that’ll correspond to your business needs.
If you’re new to the ecommerce business industry, writing a business plan isn’t just compulsory. It’ll help you learn more specific details about your own company, product or service, management, finances, and much more. However, if you’ve had your ecommerce store for a while, creating a business plan may help you improve your business services level, increase your profit, set bigger goals, and achieve them.
FAQs about ecommerce business plans
Who needs an ecommerce business plan?
Any would-be ecommerce entrepreneur can benefit from writing a business plan. Actually, the biggest letdown new sellers often make is not having a business plan. This document helps you figure out how big your product’s market is, estimate the funding you’ll require, and plan how to make and deliver the product to customers.
What will a business plan be useful for?
A business plan is useful for setting specific goals and making a plan to reach them. Additionally, if you’re thinking about leaving your job to run your business, the business plan can help you decide if that’s a good idea.
What advantages come with developing a business plan?
An ecommerce business plan gives you a roadmap, clarity of goals, target audience, and strategies. This helps stay focused and organized, guiding efforts in the right direction.
The plan also aids in budgeting, ensuring wise resource allocation and avoiding unnecessary expenses. It enhances your appeal to investors or lenders, showcasing commitment and foresight.
How do I start an ecommerce business with no money?
Ecommerce business models are inherently cost-effective, making it feasible to begin on a tight budget. To start an ecommerce business with no money, pick a low-cost niche and use free platforms like social media.
Consider dropshipping to avoid inventory expenses. Dropshipping allows you to launch a business without holding inventory; just secure a domain, create a website, and promote the supplier’s products.
Another budget-friendly option is print-on-demand, involving collaboration with a supplier offering customizable white-label products like T-shirts, mugs, backpacks, and smartphone cases, eliminating the need for inventory investment.






