In the world of business transactions, organization and efficiency are key factors for success. One vital tool that aids in achieving these objectives is the Purchase Order (PO) number. Whether you are a buyer or a supplier, understanding the importance of a PO number and its role in streamlining transactions is crucial.
In this article, we will delve into the concept of a PO number, its components, and why it is essential for businesses across various industries.
Understanding the purchase order number
What is a purchase order?
A purchase order (PO) is a commercial document issued by a buyer to a seller or supplier. It serves as a formal request to purchase goods or services and outlines the terms and conditions of the transaction. A purchase order typically includes essential details such as the description of the items or services being purchased, quantity, agreed-upon price, delivery date, payment terms, shipping instructions, and any other specific requirements.
Definition and purpose
A Purchase Order number is a unique identifier assigned to a purchase order, serving as a reference point for all related transactions. Its primary purpose is to streamline and document business transactions, ensuring accuracy, transparency, and accountability throughout the procurement process. By providing a standardized reference, the PO number facilitates tracking, communication, and financial record-keeping.
Components of a PO number
PO numbers can vary in structure, depending on organizational preferences. However, they generally consist of specific components. These may include prefixes, sequential numbers, and suffixes. For example, a PO number may have a prefix indicating the department or project, followed by a unique numerical sequence, and possibly a suffix indicating the year or supplier code. The format can differ from one organization to another, but the core objective remains consistent – to provide a unique identifier for each purchase order.
How to create a PO number
Creating a Purchase Order number involves establishing a systematic approach that generates unique and easily identifiable numbers for each purchase order. While the specific method may vary depending on organizational preferences, here are some tips for creating P.O. numbers.
Tip 1. Determine the format
Decide on the format and structure of your PO numbers. This may include considering prefixes, sequential numbers, suffixes, or a combination of these elements. The format should be consistent and easy to understand.
Tip 2. Choose prefixes (optional)
If applicable, select prefixes to indicate specific departments, projects, or categories. Prefixes help categorize and organize purchase orders, especially in larger organizations with multiple departments or divisions. Examples of prefixes could be “HR-” for Human Resources or “PRJ-” for Projects.
Tip 3. Sequential numbering
Assign sequential numbers to your purchase orders to ensure uniqueness and a logical order. Sequential numbers help with tracking and referencing orders over time. It is essential to have a system that generates numbers without duplications or gaps.
Tip 4. Consider suffixes (optional)
Suffixes can be used to indicate additional information, such as the year, supplier code, or any other relevant identifiers. For instance, adding “-2023” for the year or “-XYZ” for a specific supplier.
Tip 5. Standardize and document
Establish clear guidelines for creating PO numbers within your organization. Document the format, any specific rules or conventions, and communicate these guidelines to all relevant stakeholders. This ensures consistency and facilitates understanding across departments or teams.
Tip 6. Utilize technology
Implement an electronic purchase order management system or software that can generate PO numbers automatically and manage the procurement process efficiently. These systems often provide customizable numbering options and streamline the creation and tracking of purchase orders.
Tip 7. Unique identification
Ensure that each PO number is unique to avoid confusion or conflicts. Duplicate numbers can lead to errors, delays, or misunderstandings in procurement processes. Implement checks and validation mechanisms to prevent duplicate numbers from being generated.
Remember, the primary objective of creating a PO number is to have a unique identifier for each purchase order. The number should be structured, logical, and consistent to facilitate efficient record-keeping, tracking, and communication throughout the procurement process.
Purchase orders vs invoices: how do they work?
Purchase orders and invoices are both essential components of the procurement process, but they serve different purposes and follow distinct workflows. Let’s explore how purchase orders and invoices work in conjunction with each other.
Purchase orders
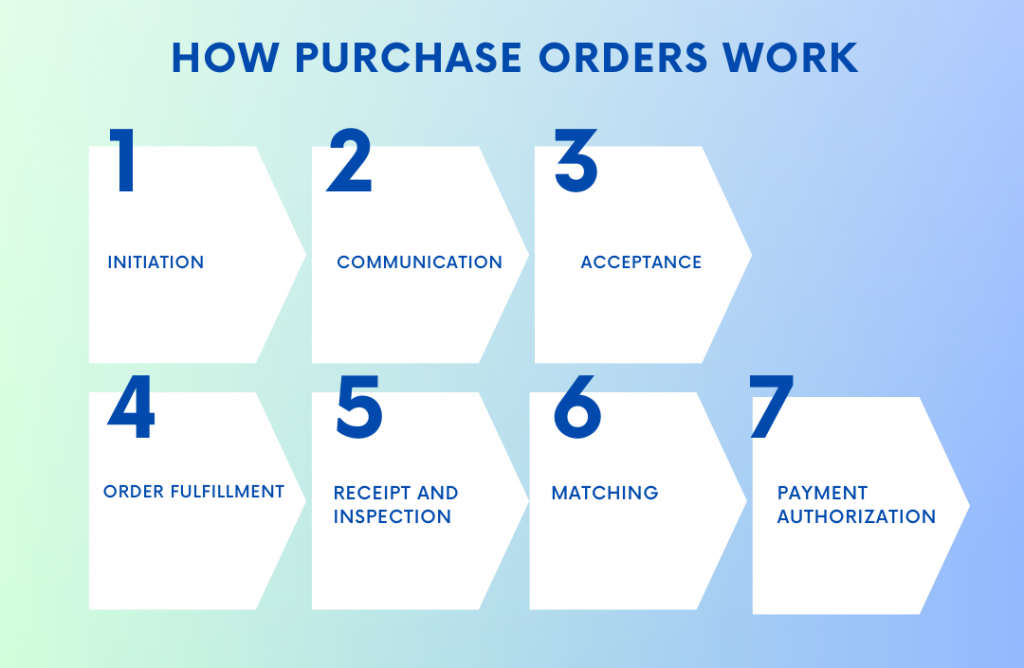
1. Initiation
A purchase order is created by the buyer as a formal request to purchase goods or services from a supplier. The PO includes details such as item descriptions, quantities, agreed-upon prices, delivery dates, payment terms, and any specific instructions.
2. Communication
The buyer sends the purchase order to the supplier, typically through email, electronic systems, or dedicated procurement platforms. This serves as a clear communication of the buyer’s intent to purchase and establishes the terms of the transaction.
3. Acceptance
Upon receiving the purchase order, the supplier reviews and verifies the details. If the supplier agrees to the terms and can fulfill the order, they acknowledge the PO and confirm acceptance. This can be done through a formal acceptance notification or by initiating the fulfillment process.
4. Order fulfillment
The supplier prepares and ships the ordered items or provides the agreed-upon services within the specified timeframe. They may generate their own internal documentation, such as picking lists or work orders, to facilitate the fulfillment process.
5. Receipt and inspection
Upon receiving the shipment or completion of services, the buyer verifies the received items against the purchase order. They may conduct inspections or quality checks to ensure the order’s accuracy and conformity to the agreed specifications.
6. Matching
The buyer matches the received items or services with the corresponding purchase order to validate the accuracy of the delivery. This process helps in identifying any discrepancies or issues that need to be resolved.
7. Payment authorization
After successful matching and verification, the buyer authorizes payment to the supplier based on the agreed-upon payment terms. The purchase order serves as a reference for initiating payment processes, including generating invoices.
Invoices
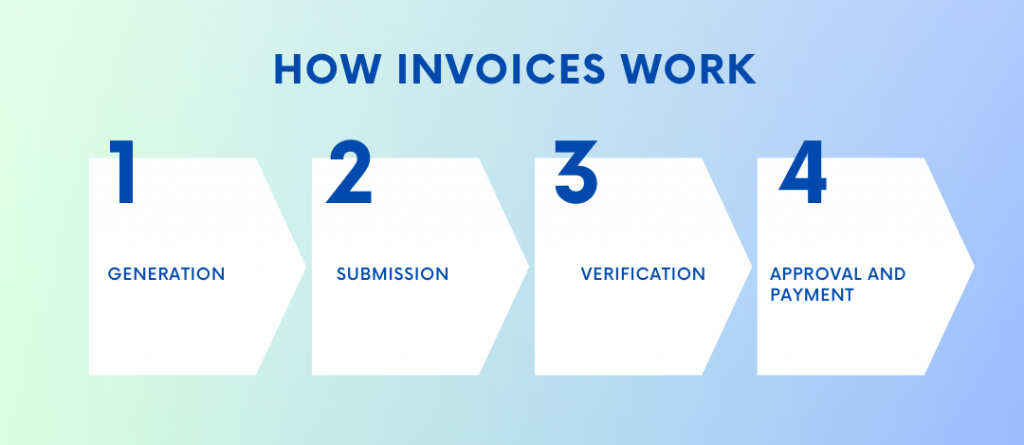
1. Generation
The supplier prepares an invoice, which is a detailed document requesting payment for the goods or services provided. The invoice includes information such as the supplier’s contact details, payment due date, item descriptions, quantities, prices, taxes, and any additional charges.
2. Submission
The supplier sends the invoice to the buyer, typically through electronic means or traditional mail. It is important for the supplier to reference the relevant purchase order number on the invoice to link it to the corresponding transaction.
3. Verification
Upon receiving the invoice, the buyer reviews it to ensure its accuracy and conformity to the original purchase order. They compare the invoice details with the purchase order and the received items or services.
4. Approval and payment
If the invoice aligns with the purchase order and there are no discrepancies, the buyer approves the invoice for payment. The payment is made according to the agreed-upon payment terms, which may include issuing a check, initiating a bank transfer, or using electronic payment methods.
Overall, purchase orders serve as the initial request and agreement between the buyer and the supplier, specifying the details of the transaction. Invoices, on the other hand, are generated by the supplier to request payment for the goods or services provided. The purchase order and invoice are closely linked, with the purchase order providing the basis for the invoice and the invoice serving as a request for payment against the agreed terms outlined in the purchase order. The proper coordination and matching of purchase orders and invoices ensure accurate record-keeping, efficient payment processing, and smooth procurement operations.
Dive into our detailed article about procurement to unlock the secrets of smart purchasing and strategic supplier relationships that can propel your business forward!
Swift invoicing with automated software
There is a wide range of standalone software options for managing invoices available on the market. However, while such software can be beneficial for invoice management, businesses usually have additional requirements and needs to consider. This brings us to the idea that a more comprehensive accounting software solution with invoicing capabilities may provide better value for the money invested.
An example of such a comprehensive solution is Synder Sync. It functions as both invoicing and accounting software, offering a range of robust features and advantages.
Synder seamlessly integrates with various e-commerce platforms, payment gateways, and accounting software, enabling users to synchronize transactions and automate bookkeeping tasks. All you have to do is to connect all the channels your business has in use to the tool. Once you do this, the software provides real-time syncing of transactions, ensuring that financial data is up to date and accurate.
If your business is looking for advanced reporting, Synder offers various financial reports, such as profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and cash flow reports, empowering users to gain insights into their business performance. You’ll be able to filter your reports according to your needs and access them any time and anywhere.
The reconciliation feature automatically matches transactions with corresponding invoices and payments, streamlining the bookkeeping process and minimizing the risk of errors. Synder’s invoicing is designed specifically for online companies: one-time and recurring invoices, auto due dates reminders – everything you need to increase your conversion rates. If you’re a subscription-based business, you’ll enjoy recurring invoicing which will help you collect recurring payments regularly and thus decrease the number of late payments, save a lot of time on invoice processing and have clear estimates of your revenue. The tool also allows users to personalize invoices and receipts with your own branding, logos, and messaging, creating a more professional and cohesive appearance.
What sets Synder apart from its competition is its user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate, simplifying financial management and report generation for users. To further enhance excellent user experience, Synder provides exceptional customer support, with a knowledgeable and responsive team available to assist users with any inquiries or concerns they may have.
By utilizing Synder, a business can enjoy the benefits of comprehensive invoicing and accounting capabilities, ensuring efficient financial management and streamlined operations. Experience the many capabilities of Synder on a 15-day free trial, or visit our webinar to see what the tool can do for your business and ask questions. Work smarter and let automation ease your business accounting!

Importance of using PO numbers
Organizational efficiency
The utilization of purchase order numbers significantly enhances organizational efficiency. By assigning a distinct PO number to each purchase order, businesses can minimize errors, confusion, and miscommunication. When invoices and receipts are matched with their corresponding PO numbers, it becomes easier to verify the accuracy of orders, ensuring that the right products or services are delivered. This streamlining of processes reduces time wastage, minimizes discrepancies, and improves overall operational efficiency.
Financial accountability
PO numbers play a vital role in financial accountability. They provide a clear and systematic method for tracking expenses associated with specific purchase orders. With accurate record-keeping, businesses can effectively manage budgets, monitor spending patterns, and generate reliable financial reports. Moreover, during auditing and compliance processes, PO numbers serve as a valuable reference point for validating transactions, ensuring transparency, and maintaining financial accuracy.
Supplier relationships
Efficient communication and transparency are crucial elements for fostering healthy supplier relationships. PO numbers contribute to both aspects. By using PO numbers, businesses can clearly communicate their expectations to suppliers, ensuring that orders are placed accurately. In case of any disputes or discrepancies, the PO number serves as evidence to resolve conflicts swiftly and amicably. Additionally, suppliers appreciate the professionalism and organization reflected in the consistent use of PO numbers, which ultimately helps build trust and strengthens long-term relationships.
Best practices for utilizing purchase order numbers
Creating and issuing PO number
To ensure effectiveness, it is important to create unique and easily identifiable PO numbers. Businesses should establish a system that generates numbers sequentially, avoiding duplications or confusion. Consistency and standardization in PO number generation are key. It is advisable to include relevant information, such as project or department codes, while ensuring the numbers remain concise and easy to read.
Communicating PO number
Clear and consistent communication of PO numbers with suppliers is essential. Whether through email, electronic systems, or dedicated portals, it is crucial to share the PO number promptly and accurately. Requesting confirmation of receipt and acknowledgment from the supplier helps avoid any potential misunderstandings or oversights.
Integrating PO numbers into business systems
Incorporating PO numbers into automated procurement and accounting systems offers numerous benefits. It enables seamless integration of purchase orders, invoices, and financial records, reducing manual data entry and minimizing errors. Utilizing electronic purchase order management systems streamlines the entire process, from creating and issuing PO numbers to tracking and reconciling transactions. Businesses can explore software solutions that simplify and optimize PO number management, ensuring efficient and accurate processing.
Conclusion
The Purchase Order (PO) number serves as a crucial tool in modern business transactions. Its significance lies in its ability to enhance organizational efficiency, ensure financial accountability, and foster strong supplier relationships. By implementing best practices for utilizing PO numbers, businesses can streamline processes, minimize errors, and cultivate an environment of transparency and professionalism. Whether you are a buyer or a supplier, adopting the use of PO numbers is essential for optimizing operations, maintaining accurate records, and building lasting business partnerships.
Learn more about YTD meaning and Form 944.






