As technology shapes our way of doing things, understanding EDI payments is essential for smoother and more efficient financial processes. Knowing how EDI automates transactions and boosts security helps business leaders thrive in the digital era, making things faster, more accurate, and improving relationships with partners and suppliers.
Let’s look at the basics of EDI payments and why business owners should care.
Key takeaways
- EDI payments automate the exchange of financial documents, making transactions faster, more accurate, and secure compared to traditional methods.
- Key components of EDI payment systems include standardized data formats, communication protocols, and robust security measures like encryption and digital signatures.
- EDI payments significantly enhance supply chain efficiency by automating transactions and reducing errors, with future trends pointing towards AI, machine learning, and blockchain integration.
Level up your accounting with smart automation! Integrate financial data from all your sales channels in your accounting to have always accurate records ready for reporting, analysis, and taxation. See it in action with a 15-day free trial or spare a spot at our weekly public demo to have your questions answered.
What is EDI payment, and how does it differ from traditional payment methods?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) payment is a method that enables businesses to exchange payment-related information electronically, reducing the reliance on traditional paper-based processes. Unlike traditional payment methods, which often involve manual data entry and paperwork, EDI payment automates the exchange of financial documents. It utilizes standardized data formats and communication protocols to facilitate seamless transactions between trading partners.
In essence, EDI payment streamlines the entire payment process, from the initiation of a transaction to the settlement, eliminating the need for physical checks or invoices. This not only speeds up the payment cycle but also reduces the likelihood of errors associated with manual data entry. While traditional methods may involve delays and a higher risk of inaccuracies, EDI payment promotes efficiency and accuracy in financial transactions.
Related:
- TikTok Shop Payment Methods: Everything You Need to Know
- Etsy Payment Methods: A Comprehensive Guide on Tracking Etsy Payments
- Amazon Payment Methods: How Does Amazon Pay Work?
What are the key components of an EDI payment system?
An EDI payment system comprises several key components working in harmony to facilitate electronic transactions.
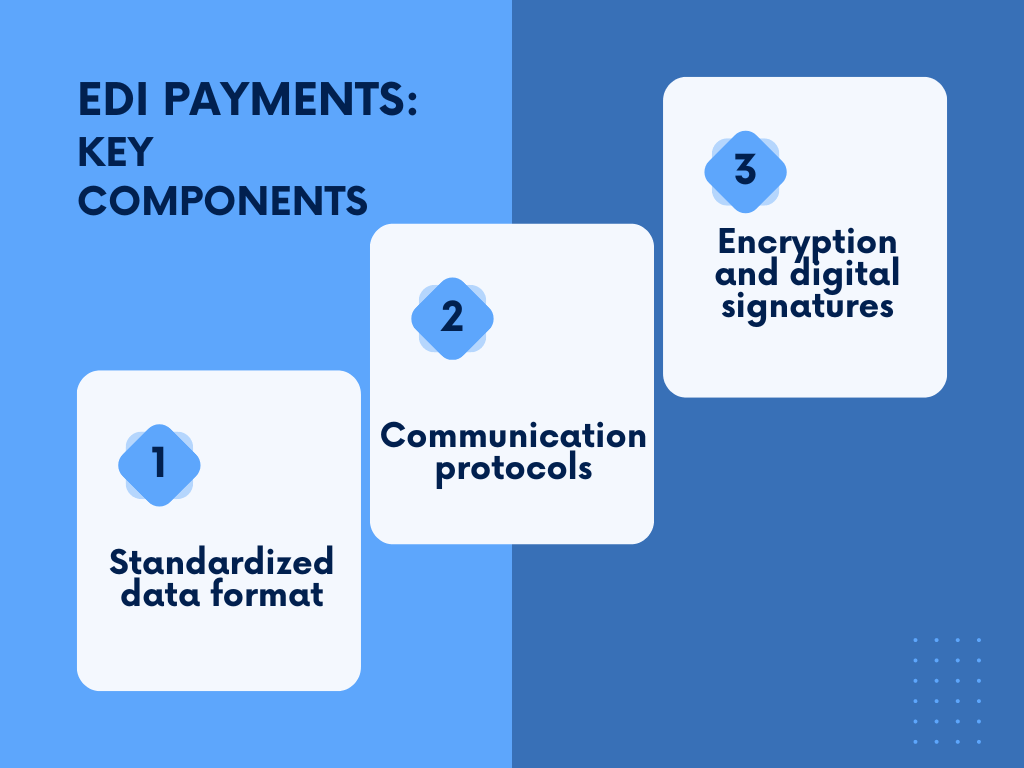
The backbone of this system is the standardized data format, which defines how information is structured and presented. Common formats include Electronic Business XML (ebXML) or Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport (EDIFACT). These formats ensure that both the sending and receiving systems understand and interpret the data consistently.
Communication protocols are another vital component, determining how data is transmitted between systems. Popular protocols include AS2 (Applicability Statement 2) and FTP (File Transfer Protocol). These protocols provide secure and reliable channels for the exchange of sensitive financial information.
Additionally, security measures such as encryption and digital signatures safeguard the integrity and confidentiality of the transmitted data, ensuring that financial transactions remain secure and tamper-proof.
How does EDI streamline the payment process for businesses?
EDI payment brings a significant advantage to businesses by streamlining the payment process. One of the primary benefits is the reduction of manual intervention. Traditionally, businesses had to handle paper invoices, manually enter data, and reconcile payments, leading to delays and errors. With EDI payment and the help of EDI integration tools, these processes are automated, eliminating the need for time-consuming manual tasks.
The automation of payment-related tasks through EDI also accelerates transaction speed. In a business environment where time is often a critical factor, the ability to process payments swiftly enhances cash flow and overall financial efficiency. Moreover, the accuracy of EDI transactions reduces the likelihood of errors that can result in payment disputes, late fees, or strained relationships with suppliers and partners.
What industries or sectors benefit the most from EDI payment solutions?
Various industries and sectors stand to gain significant benefits from the adoption of EDI payment solutions. Manufacturing, retail, healthcare, and logistics are among the sectors that benefit the most. For example, in manufacturing, where supply chain efficiency is paramount, EDI payment facilitates seamless transactions between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors.
In the retail sector, EDI streamlines the ordering and payment processes between retailers and suppliers, minimizing the time it takes to restock shelves. In healthcare, where precise and timely payments are crucial, EDI payment ensures that healthcare providers receive payments promptly, contributing to the overall efficiency of the healthcare system. The logistics industry also benefits from EDI payment by optimizing the flow of information related to shipments, deliveries, and invoicing.
What are the security measures in place to protect EDI payment transactions?
Security is a paramount concern in any electronic transaction, especially in the realm of financial data exchange. EDI payment systems employ robust security measures to safeguard sensitive information throughout the transaction process. Encryption is a fundamental security feature that protects data by converting it into a coded format that can only be deciphered by authorized parties.
Digital signatures add an additional layer of security by ensuring the authenticity and integrity of the transmitted data. These signatures function as electronic seals, verifying that the information has not been altered during transmission and confirming the identity of the sender. Access controls and authentication mechanisms further protect EDI payment systems, ensuring that only authorized individuals or systems can access and modify sensitive financial data.
How does EDI payment contribute to supply chain efficiency?
The integration of EDI payment into supply chain management contributes significantly to overall efficiency. In a supply chain context, where numerous transactions occur between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers, EDI payment automates and accelerates these processes. For instance, the automation of purchase orders, invoices, and payment confirmations ensures a smooth flow of information and funds across the entire supply chain.
By reducing the manual handling of documents and streamlining communication, EDI payment minimizes delays and errors associated with traditional supply chain processes. This, in turn, enhances visibility into the supply chain, allowing businesses to make informed decisions based on real-time data. Ultimately, the efficiency gained through EDI payment positively impacts inventory management, order fulfillment, and overall supply chain responsiveness.
What future trends or developments can be expected in the field of EDI payment?
The landscape of EDI payment is dynamic, with ongoing advancements that shape the future of electronic financial transactions. One notable trend is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into EDI systems. These technologies have the potential to enhance automation further by predicting transaction patterns, identifying anomalies, and improving data accuracy.
Blockchain technology is another area of interest in the future of EDI payment. Blockchain’s decentralized and secure nature could bring added trust and transparency to financial transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and enhancing the traceability of payment-related data. Additionally, ongoing efforts to standardize and simplify EDI protocols aim to make these systems more accessible to a broader range of businesses, fostering increased adoption and collaboration across industries.
Bottom line
Ling story short, understanding the basics of EDI payment involves recognizing its role in automating and securing financial transactions, streamlining processes across industries, and adapting to future technological trends. As businesses increasingly seek efficient and secure ways to conduct financial transactions, EDI payment stands out as a reliable and transformative solution to address this need.
Continue reading: What are accrued expenses?
Share your thoughts
Have you ever heard of EDI payments? What do you think? Share your opinion or experience in the comment’s section below!






.png)
