Choosing the right location is essential for any brick-and-mortar business to succeed. But does location play an equally important role for e-commerce businesses? Yes, it does. The difference is, it’s the customers’ location that matters.
Understanding where customers come from and how they buy can provide valuable insights into improving sales: from what e-commerce platform to choose to where to allocate marketing efforts and budgets. In most cases, businesses already have all the necessary data to find the answer. They only need to analyze it and choose a perfect business location – where their most profitable customers come from – and direct marketing activities that way.
In this article, we’ll look at leveraging customers’ location data to increase sales and possibly cut marketing costs (with some tactics you can start applying right away).
Here’s what you’ll learn about:
1. What is business location applied to e-commerce and online businesses?
2. Why is customers’ location data essential for choosing the right business location?
3. How to learn the locations your customers come from?
4. How to define the best locations for your sales and marketing efforts?
5. How to leverage customer location data for marketing?
What is business location applied to e-commerce and online businesses?
We’ll start with defining business location and how its meaning differs for brick-and-mortar and online businesses.
In its classical meaning, business location denotes the physical place where a business is represented. It can be a store or a booth in a shopping mall, an office – any place where a business meets customers to showcase and sell its products or services.
Why does business location matter for offline businesses?
For an offline business, choosing the right location plays a tremendously significant role and directly affects sales. For example, a store in the middle of nowhere, or at some distant place inconvenient to drive or walk to, is likely to be much less profitable than a boutique in the main gallery of a popular shopping center. At the same time, a shop in a suburban neighborhood, where no one else is offering such goods or providing this kind of services, might be a much better choice than a city center heavily populated with competitors. While the example is oversimplified, and more factors affect profitability, you can see the general point.
Why does business location matter for online or e-commerce businesses?
At first glance, the term ‘business location’ can’t apply to online businesses. There’s no physical sales point – people can potentially buy from you from wherever they are. But even then, location matters. If we take the point of contact between businesses and customers as a business location (in this case, a customer’s laptop or a smartphone), it all falls into place. And this way, the location of the customers who purchased goods or services can be considered the very business location that can affect sales if approached right. Perhaps the influence is indirect, but you can’t discount it.
Let’s break down how the customers’ location impacts sales.
Why is customers’ location data essential for choosing the right business location?
Back in 2013, research by David R. Bell and Jae Young Lee – Neighborhood Social Capital and Social Learning for Experience Attributes of Products – outlined how customers’ offline behavior, including their location, surprisingly affected online purchasing. For online sellers, it signaled how important customers’ location is in driving sales.
There, they spoke about the notion of ‘neighborhood social capital’, in other words, the extent to which people in a certain neighborhood tended to trust each other during offline interaction and communication. They also used the term ‘social learning’, meaning the transfer of information about some product attributes that couldn’t be acknowledged before the purchase from existing customers to potential customers.
Online businesses, including e-commerce, can have two important takeaways from this research and leverage them to make their marketing activities more efficient, less costly, and more sales-driving.
The first is that understanding the context behind your customers’ location and its influence on their online behavior can be a game-changer in finding out why you have customers in one location and no customers in another.
The second is that existing customers can often be a powerful source of new customers for an online business.
With these in mind, for an e-commerce business, customers’ location data can help decide which customers’ locations can be their perfect business location. This way, they might want to focus on promoting their products or services more for the customers they already have in those locations and acquiring more new customers in those areas. Simply put, if you have customers who already bought from you in a certain location or area, targeting more customers in this area might likely convert into more sales.
This brings us to how you can find your customers’ location and leverage it.
How to learn the locations your customers come from?
We’ve already mentioned that businesses might already have all the necessary data at hand. Let’s look at the possible customer data sources they can use to retrieve customers’ locations.
- E-commerce analytics solutions
You can find solutions on the market that provide an account of e-commerce or online business analytics, similar to how Xero alternatives offer comprehensive financial management features. The advantage of such solutions is that they can help analyze the performance of your business across multiple sales channels. They usually put together detailed data on sales, products, and customers from the e-commerce and payment platforms that a business is using. These accounts can include the data on where the customers come from, what they buy, how often they return, how much they spend, which products are more/less profitable, and more.
- Google Analytics
There’s probably no online or e-commerce business that isn’t using Google Analytics to track their web store’s performance. If set up correctly, this tool can be an invaluable source of information on customer behavior patterns a business can use to tweak their tactics and strategies for better performance: from SEO to conversions and customer acquisition.
- E-commerce platforms and payment processors
All the popular and most frequently used e-commerce platforms and payment processing services, such as a Square business account, usually collect data on your sales and other transactions (refunds, fees, etc.), including customer data, such as shipping addresses or customer addresses used for invoices. Such services usually come with user dashboards where you can find information about your customers’ whereabouts.
- CRMs
While smaller businesses might not use them, medium- and large-sized businesses are likely to use customer relationship management (CRM) systems to organize and administer the information about their interactions with customers. One of the biggest virtues of CRMs is that they organize data the way you can see all the purchases and transactions related to each customer, filter or sort the data by certain attributes, including location, etc.
- Accounting platforms
Many accounting platforms, especially those designed for accounting software for medium-sized business, allow for adding customer data to transactions, including information about customers’ locations. Usually, this data is used to create and send invoices. You can retrieve this data for analysis and use it to help choose the location for your e-commerce business. You might need to use some third-party solution to import customer data to your accounting platform because adding it manually might be tiresome.
How to define the best locations for your sales and marketing efforts?
Start with analyzing sales and customer data you already possess. It can help you see current locations where your business seems to be most profitable.
For better results, you might want to see customers’ locations against other important sales metrics, such as the average order value or the number of sales coming from a given location. At this point, having all the necessary data gathered in a single place, or dashboard where you can easily switch from report to report, makes the analysis more simple.
Here’s an example of what it can possibly look like if you’re using an e-commerce analytics platform like Synder Insights.
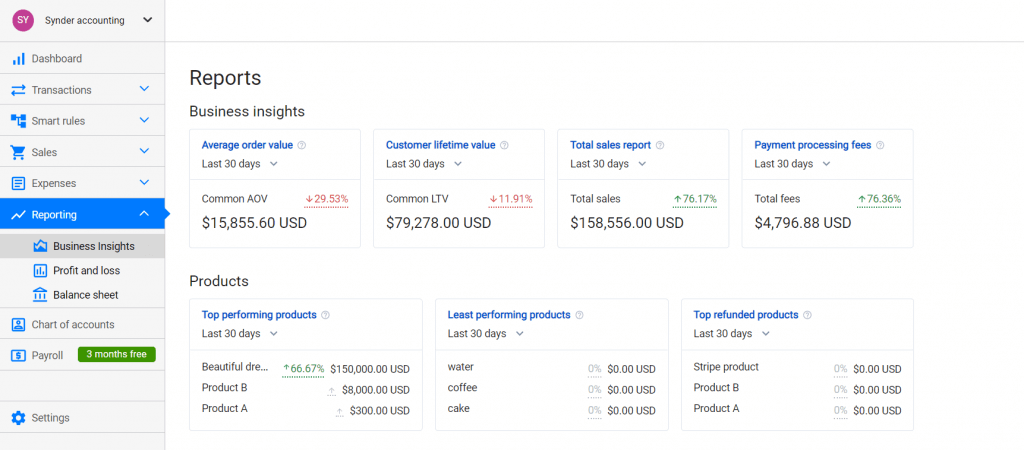
- See where your sales come from
You can start with the Total sales report for a period you want to analyze – a year, for example. By sorting the results by location, you can already figure out where most of your sales come from.
Additionally, you can break down the results by sales channels. It will be especially beneficial if you sell through multiple channels and want to know where you have more customers, which channel brings you more profit, and thus, decide on each of your channels’ efficiency.
- Learn how much customers spend on average
From the Average order value report, you can learn how much, on average, people from different locations and channels spend when buying from you. These numbers can display the profitability of your business in general and by each sales channel or location. It’s pretty straightforward: the bigger the number, the more revenue you gain.
- Meet the customers that buy a lot
Where do your most profitable customers come from? The Top performing customers report can give you the answer. Moreover, you can learn your customers’ behavior patterns, such as whether they buy more often but less expensive products or spend on more expensive items but more rarely. As customer behavior may differ from channel to channel, it might also be a good idea to break those buying patterns by sales channels. Comparing those patterns against customer locations can hint at what marketing tactics to choose to promote your products in different areas.
- By the way, what do people tend to buy from you?
Look at your Top-performing products – the products that people most frequently buy from you and bring you the most revenue. Combine it with the products people tend to buy together, and you have a ready-made strategy for increasing sales by offering customers products they’re most likely to be interested in.
- And what about how often people tend to buy from you?
You can dig even deeper into your customers’ buying habits by looking at the Purchase frequency or the Time between purchases reports. This way, you’ll be able to predict whether there’s a chance that customers will come back to buy from you and when it’s most likely going to happen.
This is a possible workflow for customer data analysis that might help you define the best location for your sales. Depending on what questions you want to have answered, you can examine various data sets on sales, products, and customers.
| A helpful tip. You might have encountered situations where you observe a huge amount of traffic with comparatively low sales. You can compare your visits or traffic data from Google Analytics, for example, with your sales data to determine which locations bring you the traffic that doesn’t convert. With this information, you might decide whether to put more marketing efforts into converting this traffic or, if it seems too costly, cut advertising targeting those locations. |
How to leverage customer location data for marketing?
Suppose you know exactly where your most profitable customers are, where you have the most loyal audience that comes back to buy from you, and where you have potential customers that fail to convert.
Now you might want to examine the location to acknowledge the context in which customers interact with each other. What are the circumstances that make people buy online and choose your business to buy from? How many competitors your business might have there? Are there any physical stores offering the same goods as you? What are their prices? How reachable are they for the customers?
You can use this information to tweak your marketing strategy to consider those audiences, their needs, and their behavioral patterns. Here are some tactics you can consider.
Based on where your most profitable customers come from
Once you define the location from where your most profitable customers come from, what they are most interested in, and how often they make online purchases, you’ll have enough data to target more like-minded buyers from that area and convert them at potentially lower costs.
- Narrow down your target audience.
If you go with paid advertising, like Google Ads or Facebook Ads, etc., you might prefer to pay for more clicks that convert. Knowing where the audience is most interested in certain products and most ready to buy them, you can narrow your targeting to these areas. This way, you’ll trigger more conversions and decrease your spending on bounced clicks (considering how expensive some clicks are, you might significantly cut your costs).
- Tweak SEO to improve your visibility in search results for those areas.
As you might know, search results, especially in Google, are highly location-based. Depending on where people are located when performing their search, algorithms show them the results they consider to be the most relevant to them. Though it’s commonly believed that local SEO works best for brick-and-mortar businesses, online businesses might also adopt some of these tactics.
The simplest example is location-based keyword research, which can be greatly facilitated by tools like the local citation finder. Find out how people in your target area search for the goods you offer. You might be surprised that people can use different search queries depending on their location.
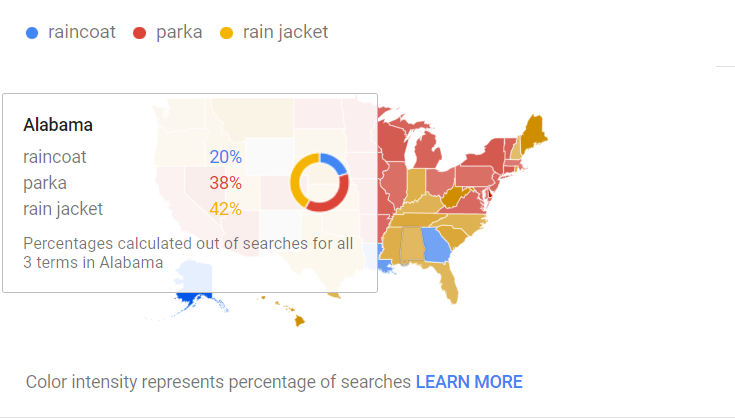
Here’s an amazing illustration from Google Trends – a tool that analyzes the popularity of search queries or topics in Google Search across various regions and languages.
Imagine you sell outerwear that protects from rain and wind. How’d you call it: a raincoat? But should you like to advertise it in Alabama, for example, you’d better call it a rain jacket – this is how people interested in buying this item will likely search for it in this region.
- Segment audiences for remarketing based on their location.
Remarketing can be a great means of engaging audiences who have already interacted with your online store to encourage them to take the desired action that may interest them, for example, to buy more products from you. You can use it to attract your customers with special promo codes or discounted pricing for some products – anything you can think might help get them back to your store. Knowing what people in a certain area are likely to be interested in, you might segment your remarketing audiences based on their location and trigger them with the offer that is more likely to resonate with them.
Based on how often customers from different locations tend to buy from you
Customer engagement plays a significant role in increasing sales, especially when it comes to customers who return to buy from you more than once. However, it can be hard to choose the right time to re-engage. At this point, knowing when people are naturally ready to buy again, based on the purchase frequency and time between purchases, can be of great help.
- Set up effective email outreach campaigns
Trigger customers with your new arrivals or an upcoming sale just in time they’re ready to purchase. Come up with personalized campaigns aimed at customers from different locations – offer popular goods, discounts, or promo codes. Sending such emails at the right time might increase the possibility of converting sales by leveraging customers’ loyalty and eagerness to buy more from you.
- Inspire customers’ loyalty and profit from it
Knowing your returning customers, you can trigger them with loyalty programs – encourage them to buy more products or do it more often. You can offer different levels of loyalty rewards: for example, let customers earn points or bonuses depending on a single order value or the frequency they buy from you a month, that they can later spend on new purchases in your store.
Those are just a few examples of how you can improve your marketing based on customers’ location and behavioral patterns typical to customers in given areas. The general point is, knowing when and how to approach your customers helps drastically cut marketing costs by putting your efforts in the right direction.
Choosing the right e-commerce business location: the conclusion
As you can see, choosing the right business location can be game-changing for e-commerce businesses, just like it’s for brick-and-mortar ones. For online businesses, it works differently – it’s their customers’ location that matters. By leveraging the data on where their customers come from and the context behind those locations, e-commerce businesses can define their perfect business locations and focus their marketing efforts to bring more customers from those areas.
Synder Insights is an e-commerce analytics platform capable of analyzing sales, customer, and product data from multiple platforms and helping online businesses find the best location to drive their sales. It allows for informed decision-making and ensures efficient allocation of marketing budgets and better results.
Try Synder Insights for free to see how it can help your e-commerce business or book an online demo with Synder’s Success team to find out more.







