In an era where digital payments are becoming increasingly prevalent, payments through Amazon Pay have emerged as a significant player in the ecommerce and online transaction space. This service, offered by the ecommerce giant Amazon, has transformed the way consumers and merchants approach online transactions.
So what is Amazon Pay? This article aims to demystify payments through Amazon Pay, offering an in-depth look into its setup, usage, benefits, and broader implications in the digital payment sphere.
What is Amazon Pay?
Amazon Pay is a digital payment service developed by Amazon. It allows customers to use the payment methods already associated with their Amazon accounts to make purchases on third-party websites and apps. This payment service simplifies the checkout process for users who shop outside of Amazon’s platform, enabling them to pay for products and services using the information they’ve stored in their Amazon account, like credit card and shipping details. It’s integrated into various ecommerce platforms and can be used for a variety of transactions, providing a familiar and streamlined payment experience for users who frequently shop online using Amazon.
Key aspects of Amazon Pay
- Integration with Amazon accounts
Amazon Pay allows users to use their existing Amazon account credentials to purchase on third-party websites. This integration means that customers can use their stored payment methods without the need to re-enter their details on each new site.
- Security and trust
Security is a cornerstone of payments through Amazon Pay. It benefits from Amazon’s robust security systems, which help in safeguarding user information. This high level of security, combined with the trust in the Amazon brand, often makes consumers more comfortable using it on new or unfamiliar websites.
- Convenience
The service streamlines the checkout process by reducing the number of steps required to complete a purchase. This convenience is particularly beneficial in mobile transactions, where entering payments information can be cumbersome.
- Flexibility in payment options
Amazon Pay accepts a variety of payment methods, including credit and debit cards. Some regions may also allow the use of Amazon gift cards and other localized Amazon payments.
- Wide acceptance
Being a product of Amazon, Amazon Pay is widely accepted by a large number of online retailers and services. This widespread acceptance makes it a versatile payment option for users.
- Fraud protection
Amazon Pay offers fraud protection policies to consumers and merchants, which helps mitigate unauthorized transactions and other forms of online payments fraud.
- Merchant services
Amazon Pay provides tools and services for sellers and businesses to integrate these payments into their websites and systems. This integration can help businesses by providing their customers with a familiar and trusted payment option.
- Customer experience
Amazon Pay focuses on enhancing the customer experience with features like easy checkout and quick payments processing. This focus on customer satisfaction helps build loyalty and repeat business for merchants using Amazon Pay.
- Global reach
Payments via Amazon Pay are available in numerous countries, making it a viable option for international transactions and businesses operating in multiple regions.
Enhance your Amazon workflow by automating your bookkeeping processes with the help of Synder! Learn how the Amazon QuickBooks connection works, and give Synder a try!
Setting up Amazon Pay (for the merchants)
Setting up Amazon Pay involves a few steps, primarily focused on creating an Amazon Pay merchant account and integrating it into your website. Here’s a general guide on how to do this:
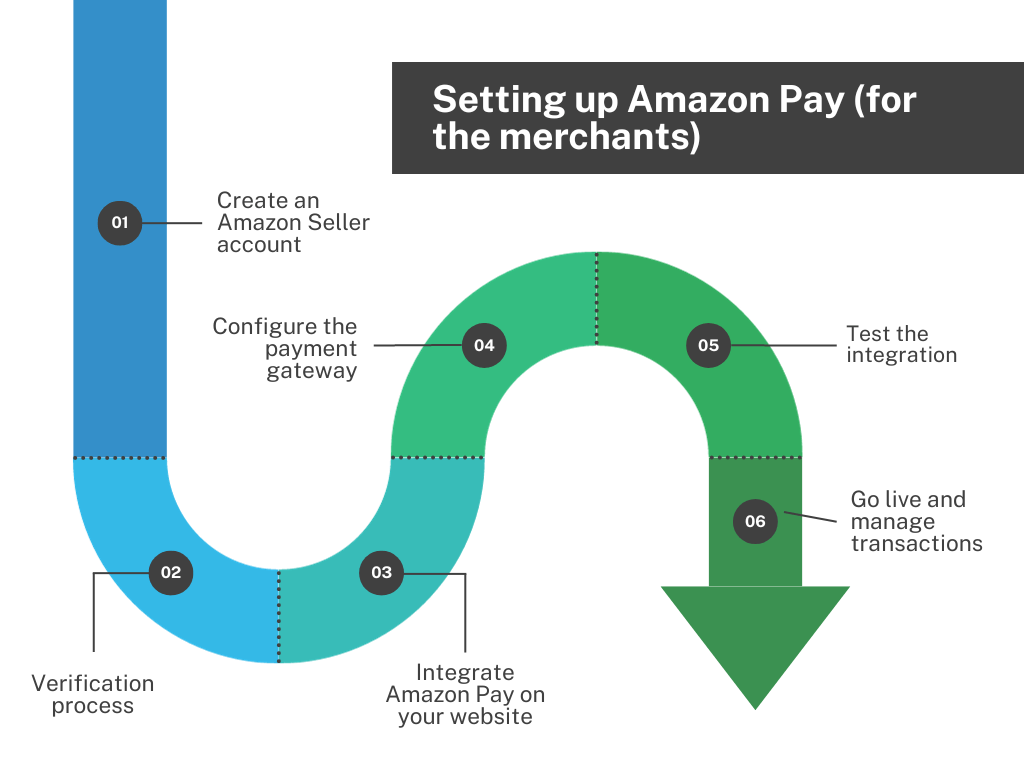
Create an Amazon account (Amazon Seller account)
If you don’t already have an Amazon Seller account, you’ll need to create one. Go to the Amazon Pay website and choose to sign up as a merchant.
Follow the registration process, which includes providing business details bank account information, and agreeing to the Amazon Pay terms of service.
Verification process
Amazon will require you to verify your identity and business information. This process may include submitting documents like business licenses, bank account statements, or tax information.
The verification process is crucial for security and compliance reasons.
Integrate Amazon Pay on your website
Once your account is set up and verified, the next step is integrating Amazon Pay into your website.
Amazon provides APIs and SDKs (Software Development Kits) for various platforms. You can choose the one that matches your website’s platform (like Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento, etc.).
Note: If you’re not familiar with web development, you might need the assistance of a developer or use the plugins/modules provided by your ecommerce platform to integrate Amazon Pay.
Configure the payment gateway
Add Amazon Pay as a payment option to your website’s payments settings. Configure the payments settings as per your preference, like specifying the transaction types, setting up payment authorization and capture methods, etc.
Test the integration
Before going live, it’s important to test the payment process. Amazon Pay provides a sandbox environment for this purpose.
Conduct test transactions to ensure that the payment processes work smoothly and securely.
Go live
After successfully testing Amazon Pay, switch from the sandbox environment to the live environment. Now, the payments through Amazon Pay will be available as a payment option for your customers.
Monitor and manage transactions
Once Amazon Pay is live on your site, monitor received payments regularly. Use the Amazon Pay merchant account to manage transactions, process refunds, and handle disputes.
Note: Ensure you comply with Amazon Pay’s policies and provide customer support for payment-related queries.
Bonus step: Promote Amazon Pay
Consider promoting Amazon Pay as a payment option for your customers, highlighting its convenience and security.
Learn how to delete your Amazon account.
How does Amazon Pay work?
As said above, Amazon Pay allows customers to use their Amazon account credentials to make payments for purchases on third-party websites and apps, streamlining the online shopping experience. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
Customer’s perspective
Choosing Amazon Pay for payment → Login with Amazon → Payment option selection → Transaction completion.
When a customer shops on a website that offers payments through Amazon Pay, they can select it at checkout. The customer then logs in using their Amazon account credentials. This step is secure and does not share the customer’s Amazon account password with the merchant.
The customer can choose from the payment methods (like credit or debit cards) already stored in their Amazon account. After confirming the payments details and shipping address (also pulled from the Amazon account), the customer completes the transaction.
Merchant’s perspective
Integration of Amazon Pay → Transaction processing → Receiving payment → Order fulfillment.
The merchant integrates Amazon Pay into their website, typically through APIs or plugins provided by Amazon.
When a customer uses Amazon Pay, the merchant’s site communicates with Amazon’s servers to process the transaction. The funds are transferred from the customer’s payment method to the merchant’s account associated with Amazon Pay. The merchant then processes and ships the order as usual.
Note: If a customer requests a refund or returns a product, the process is handled through the merchant, similar to other payment methods. The refund is then processed through Amazon Pay.
Amazon fees and charges
Payments fees and charges for merchants vary based on factors like the region and the specific type of transaction. Here’s a general overview of how these payments fees and charges work:
Transaction fees
Amazon Pay typically charges a percentage of each transaction, along with a flat fee. The transaction fee is composed of a domestic processing fee + authorization fee ($0.30) + tax, where applicable, charged when the payments are successfully authorized and processed.
Learn how to manage your Amazon sales taxes with Synder.
Cross-border fees
Amazon Pay may charge additional cross-border fees for transactions where the merchant and the customer’s bank are in different countries. These fees are usually higher than domestic transaction fees.
Refund fees
In some cases, Amazon Pay may retain the original transaction fees even if the merchant issues a refund to the customer.
Note: The authorization fee and disputed chargeback fee are non-refundable.
Chargeback fees
If a customer disputes a charge and it results in a chargeback, Amazon Pay may charge a fee for this process. Amazon will assess a fee of $20.00 plus tax where applicable.
Amazon Pay drawbacks
While Amazon Pay offers several advantages, like convenient and secure payments, it also has certain drawbacks that users and merchants should consider.
Limited to Amazon users
Amazon Pay’s efficiency largely depends on whether customers already have an Amazon account. Those who don’t might be less inclined to use it for payments, preferring other payment methods that don’t require an Amazon account.
Transaction fees for merchants
As was said above, merchants are subject to transaction fees when using Amazon Pay. These fees can be a significant consideration, especially for small business owners operating with thin margins.
Integration complexity
Integrating Amazon Pay into a website can be complex, particularly for small business owners without technical expertise. While plugins and APIs are available, setting up and maintaining the integration might require technical assistance.
Dependency on Amazon’s ecosystem
Using Amazon Pay ties a merchant somewhat to Amazon’s ecosystem. Any changes Amazon makes to its policies, fees, or system could directly impact the merchants providing Amazon Pay as their payment option.
Competition with Amazon
Some businesses may be hesitant to use Amazon Pay, considering Amazon as a competitor in the retail space.
Limited physical store use
Unlike some other digital wallets, Amazon Pay is primarily designed for online payments. Its utility in physical stores is limited compared to services like Apple Pay or Google Pay, which support contactless payments.
Potential for account issues
Since Amazon Pay uses Amazon account credentials, any issues with a customer’s Amazon account (like suspension or security concerns) could directly affect their ability to use Amazon Pay.
These drawbacks do not necessarily overshadow the benefits of Amazon Pay. Still, they are important considerations for both users and merchants when deciding on the most suitable payment options for their needs.
Comparison with other digital wallets
Comparing Amazon Pay with other digital wallets involves looking at various aspects such as user experience, security, fees, merchant acceptance, and additional features. Let’s consider some of the popular digital wallets for comparison: PayPal, Google Pay, and Apple Pay.
Learn more about Amazon and Visa gift cards.
User experience
| Amazon Pay | Offers a seamless experience for existing Amazon customers, allowing them to use their stored Amazon account details. |
| PayPal | Known for its wide acceptance and ease of use. Allows payments from PayPal balances, bank accounts, or cards. |
| Google Pay | Integrates well with other Google services and Android devices, offering a convenient tap-to-pay feature on phones. |
| Apple Pay | Provides a smooth payment experience, especially on Apple devices, focusing on quick tap-to-pay functionality. |
Security
| Amazon Pay | Uses Amazon’s robust security systems, including fraud protection. |
| PayPal | Offers strong security measures and a well-established dispute resolution system for payments. |
| Google Pay | Benefits from Google’s security infrastructure, including virtual account numbers for transactions. |
| Apple Pay | Emphasizes security with biometric authentication (Touch ID or Face ID) and tokenization of card numbers. |
Fees
| Amazon Pay | Charges transaction fees, similar to most digital wallets, with specific rates varying by region. |
| PayPal | Known for its transaction fees, including for international payments and currency conversion. |
| Google Pay | Generally does not charge fees for transactions but may incur charges depending on the funding source. |
| Apple Pay | No charges to consumers, but merchants pay transaction fees. |
Merchant acceptance
| Amazon Pay | Online merchants widely accept these payments, especially those targeting Amazon’s customer base. |
| PayPal | PayPal payments are widely accepted online and increasingly in physical stores. |
| Google Pay | These payments are accepted by many online and offline merchants, especially where NFC payments are available. |
| Apple Pay | Broad acceptance of such payments in stores and online, particularly where contactless payments are the norm. |
Additional features
| Amazon Pay | Ties in with Amazon’s ecosystem, offering benefits like using Amazon gift cards. |
| PayPal | Offers credit services, the ability to hold and manage multiple currencies, and a strong presence in peer-to-peer payments. |
| Google Pay | Integrates with other Google services and offers rewards on transactions. |
| Apple Pay | Seamlessly integrates with Apple’s ecosystem, with features like Apple Cash for peer-to-peer payments. |
International reach
| Amazon Pay | Such payments are available in numerous countries but less pervasive than some competitors. |
| PayPal | Extremely popular globally, with a presence in many countries. |
| Google Pay | Availability varies, with a strong presence in regions where Android and iOS devices, respectively, are widely used. |
| Apple Pay | Availability varies, with strong presence in regions where Android and iOS devices, respectively, are widely used. |
In summary, each digital wallet has its strengths: Amazon Pay leverages Amazon’s user base and trust, PayPal is known for its versatility and global acceptance, Google Pay integrates with Google’s ecosystem and is convenient for Android users, and Apple Pay offers a seamless experience for Apple device users with a focus on security. The best choice depends on individual needs, the device ecosystem, and the type of transactions being made.
Conclusion
Amazon Pay presents itself as a highly efficient and user-friendly digital payment solution, drawing on the vast user base and technological prowess of Amazon. Its workflow is designed to prioritize convenience, security, and speed, allowing customers to make purchases on third-party websites using their Amazon account details. This not only streamlines the checkout process but also instills a sense of trust and reliability, leveraging Amazon’s established reputation.
For merchants, integrating Amazon Pay into their online platforms can lead to an enhanced customer experience, potentially increasing conversion rates and customer loyalty due to its ease and security. The system’s robust security measures and fraud protection provide a layer of safety for buyers and sellers, making it a reliable choice in the ever-expanding digital payment landscape.






