Only 14.6% of U.S. total retail is shopped online in 2022, which on the one hand is lower than the pandemic height, but on the other hand, ecommerce sales are projected to reach a staggering 22% share of retail sales in 2025. Ecommerce is evolving rapidly, and it’s the future we have to grasp and use to our advantage.
This article provides a brief overview of ecommerce and its major strengths, the most significant comparison points to traditional retail, as well as failure rates of startups and ecommerce businesses in the U.S.
Why is ecommerce getting so popular?
Ecommerce has become increasingly important in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has led to a surge in online shopping and a shift towards digital business models. In the United States, the share of ecommerce in total retail spiked to 16.1% between the first and second quarter of 2020 from 11.8% in the first quarter of 2020. As a result, businesses that invested in ecommerce were better equipped to weather the challenges of the pandemic and adapt to changing consumer behaviors.
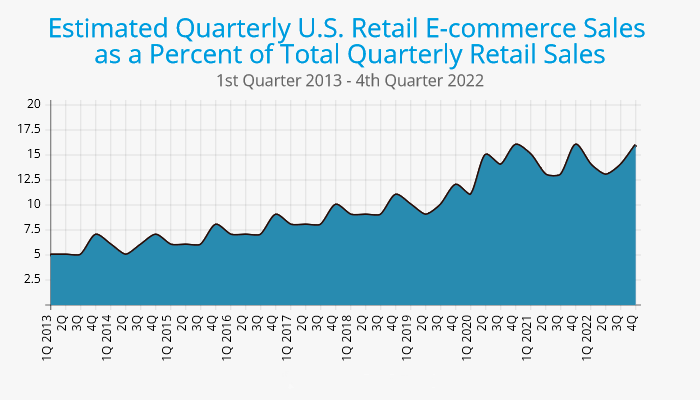
Retail ecommerce sales worldwide are projected to reach about 8.1 trillion dollars by 2026, which is going to be close to a quarter of total global retail sales. Online marketplaces still hold the leading position for the largest share of online purchases, with Amazon taking the 3rd place after Chinese competitors Tmall and Taobao in terms of gross merchandise value. Retail ecommerce revenue in the U.S. is projected to more than triple in the span of 10 years (2017-2027).
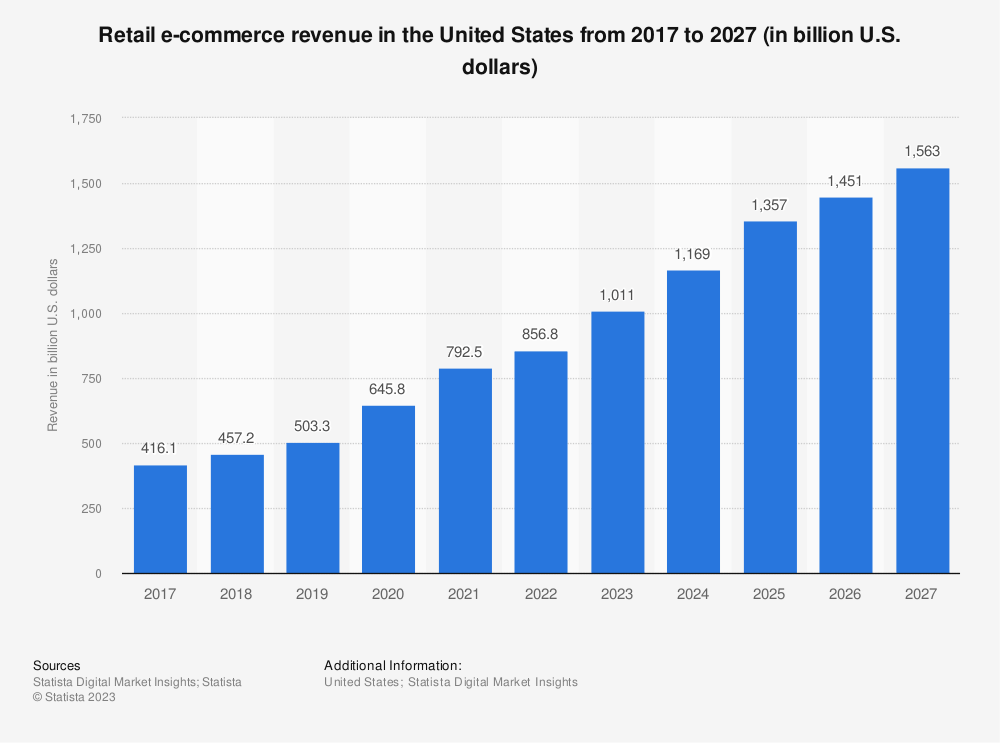
This bit of ecommerce statistics only proves the uncovering potential of the industry.
If you think for a moment about the growing popularity of ecommerce, simple reasons to explain it would spring to mind in no time:
- Ecommerce is convenient as it provides shopping opportunities from any place at any time, making it a popular choice for consumers.
- Ecommerce is cost-effective as it allows businesses to save on the cost of physical store space, employees, and other overheads.
- Ecommerce provides increased reach, which enables businesses to reach a wider audience, both locally and globally, thereby increasing their customer base.
- Ecommerce is all about personalization of the shopping experience for customers, leading to better customer engagement and loyalty.
- Ecommerce provides businesses with valuable data insights into customer behavior, preferences, and purchasing patterns, which can help them make informed decisions and improve their offerings.
How is ecommerce different from traditional retail?
We believe that although the ecommerce market has stemmed from being a mere counterpart of brick-and-mortar retail and evolved into a whole new shopping ecosystem, it’s far from the pinnacle of digital transformation that is yet to come. The ecommerce landscape today has its established rules and key players, and yet it’s open to innovation from startups and adjustment to the current economic situation. Although ecommerce is a part of retail and is classified by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics as “nonstore retail”, it has its peculiar features that distinguish it from a traditional retail business, including:
1. Online presence
An ecommerce business operates entirely online, whereas a retail business operates from a physical store or multiple physical locations.
2. Global reach
Ecommerce businesses have a global reach, which means they can cater to customers worldwide, while traditional retail businesses are limited to a local or regional market.
3. Reduced overhead costs
Ecommerce businesses have lower overhead costs compared to traditional retail businesses since they don’t need to invest in physical infrastructure, inventory storage, and staff in a physical store.
4. Personalized experience
Ecommerce businesses can offer a personalized shopping experience to customers through targeted advertising, product recommendations, and personalized communication.
5. Data-driven decisions
Ecommerce businesses rely heavily on data analytics and metrics to make informed decisions about their products, pricing, and marketing strategies. This ecommerce accounting process is vital for tracking performance and optimizing operations.
6. Flexibility
Ecommerce businesses have the flexibility to adjust their product offerings, pricing, and promotions in real-time to meet changing market demands and consumer preferences.
7. Customer reviews
Ecommerce businesses often rely on customer reviews and ratings to build trust and credibility with potential customers.
8. Mobile optimization
Ecommerce businesses must optimize their website and online shopping experience for mobile devices, since a growing number of customers prefer to shop online using their smartphones and tablets.
Overall, an ecommerce business model offers several advantages over traditional retail businesses, including reduced overhead costs, global reach, personalized shopping experiences, and data-driven decision-making. However, it also presents unique challenges and requires a different approach to business operations and customer engagement. The retail accounting practices for ecommerce need to adapt to these online transaction environments to ensure accuracy and compliance.
It would be fair to say that physical or traditional retail does have its undeniable advantages over ecommerce.
1. Tangible experience
Physical retail is about a more tangible and sensory experience that online shopping cannot match. It allows customers to see, smell, feel and touch products they are going to buy.
2. Personal interaction
Traditional retail allows customers to interact with the store staff and receive personalized assistance and recommendations, which can create a more enjoyable and engaging shopping experience.
3. Immediate satisfaction
Receiving purchases immediately, without having to wait for delivery, guarantees immediate satisfaction.
4. No shipping costs
Traditional retail eliminates the need for shipping costs, which can add to the overall cost of online purchases.
Stating that ecommerce is going to replace traditional sales any time soon seems like an overstatement. We believe that traditional sales and ecommerce are going to be complementary in the future.
Success or failure
Starting and maintaining an ecommerce business can be quite a task, and getting the valuable information before the crisis can’t be overestimated. Keeping track of every SKU number in inventory management is crucial for ecommerce success, ensuring products are always available for customers. We believe that it’s wise to get some reliable information about ecommerce business, its stages and possible hurdles along the way, and equip yourself with numbers from day 1, which will help you to make data-driven decisions.According to the recent report of the U.S. Bureau of Labor, 48.4% of businesses that were launched in 2017 survived in 2022, which means that only half of businesses survived till their 5th year. 20.9% of new startups failed in their 1st year (2018) and 31%-in their 2nd year (2019). So it’s about 50/50, survive or die in the span of 5 years. These numbers prove that it’s better to be prepared than just hope that the odds are in your favor and look for unicorns with your head in the clouds. And speaking of unicorns… It’s a well-known fact that only 1% of the startups become unicorns valued at $1B+.
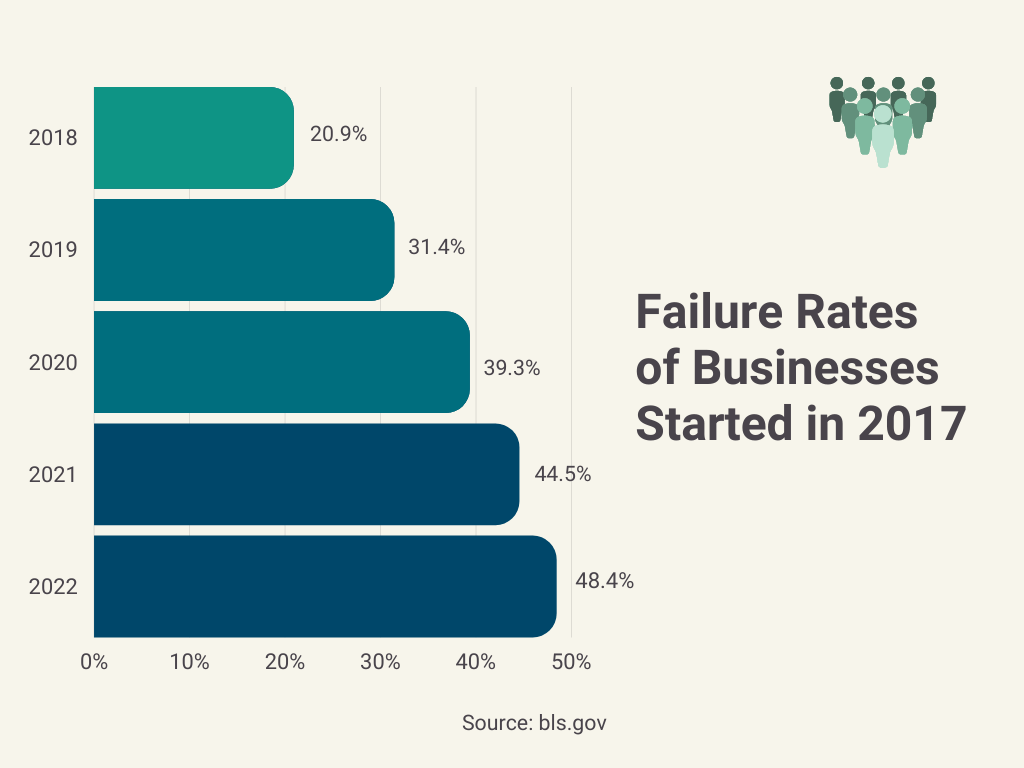
According to some studies, the failure rate of ecommerce businesses is around 80%-90%. One of the reasons the failure rate is so high is that an ecommerce business can be easy to set up, requiring investment of smaller amounts of money in comparison with many other businesses.
In the book “The Business of Platforms: Strategy in the Age of Digital Competition, Innovation, and Power” the authors state that ecommerce platforms fail at an alarming rate. The authors made an attempt to identify as many failed American platforms as possible over the last twenty years. Comparing 209 failures against the 43 successful platforms allowed them to extract some information about why platforms struggle and fail. We have to grasp what the authors understand under “platform” first. Innovation platforms mentioned in the book allow third-party firms to add complementary products and services to a core product or technology, examples being Google Android and Apple iPhone operating systems, Amazon Web Services. Transaction platforms provide the exchange of information, goods, or services like Amazon Marketplace, Airbnb, or Uber.
The most significant findings concerning ecommerce failure rate that were described in the book are:
- Failed platforms live about 4.9 years
- Many platforms collapse within 2–3 years
- Standalone firms have a life cycle of only 3.7 years
Closing thoughts
It’s safe to say that ecommerce is becoming increasingly popular, and its growth is projected to continue. While it offers several advantages over traditional retail, such as reduced overhead costs and global reach, it also presents unique challenges and requires a different approach to business operations and customer engagement. However, traditional retail still has its own strong points, such as a more tangible and sensory experience and immediate satisfaction.
Ecommerce is a sport of achievement, but only when you master your skills in the game you play. Ecommerce skills are some of those assets that can help you stay ahead of the curve and finally win the race.
In the next article we’re going to focus on the ecommerce life cycle, its stages and challenges.











.png)