Customer due diligence (CDD) is a phrase that has been increasingly reverberating through the boardrooms of global businesses. At its core, CDD is a process that organizations employ to ensure they understand their customers, their operations, and the risks they pose. As companies navigate a world of ever-increasing regulation and scrutiny, it’s more important than ever that they carry out proper customer due diligence. This article delves into the concept, importance, implementation, and challenges in customer due diligence.
This article is a general overview and does not cover all aspects of customer due diligence. For a detailed understanding and application, consultation with a professional expert in this field is recommended.
Due diligence: Understanding the concept of customer due diligence (CDD)
CDD, a concept that originated from the need to prevent financial crime, has evolved into an integral component of organization operations and compliance. It is governed by a stringent regulatory framework designed to deter financial crimes like money laundering, terrorism financing, fraud, and corruption. This framework, driven by international bodies like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), outlines the key components of CDD: identifying and verifying the customer’s identity, understanding the nature of the customer’s activities, and conducting ongoing monitoring of the business relationship.
Customer due diligence (CDD) vs enhanced due diligence (EDD)
CDD and EDD are both key components of a comprehensive approach to prevent financial crimes. They are practices used by financial institutions and other regulated businesses to assess risk and ensure compliance. However, they differ in their purpose, scope, and when they are applied.
Customer due diligence (CDD)
This is a basic level of due diligence every financial institution performs on a customer before establishing a business relationship. The process involves:
- Identifying the customer and verifying their identity using reliable, independent source documents, data or information.
- Identifying the beneficial owner, if any, and taking reasonable measures to verify their identity.
- Understanding the nature and purpose of the business relationship to develop a risk profile for the customer.
Enhanced due diligence (EDD)
This is a more detailed version of CDD and is performed on high-risk customers. These are customers who, due to their nature of business, geographic location, transaction patterns, or other factors, pose a higher risk for potential money laundering or other illicit activities.
EDD goes beyond CDD by gathering additional information to understand customer behavior better and mitigate associated risks. This can involve deeper scrutiny of the customer’s financial transactions, more extensive background checks, reviewing the source of funds, and ongoing monitoring.
In summary, CDD is a basic level of investigation performed for all customers, while EDD is a more comprehensive, in-depth process used for high-risk customers. The specific practices involved in CDD and EDD can vary depending on the jurisdiction, regulatory requirements, and the internal policies of the institution.
Read our article about enhanced due diligence to learn more details.
Due diligence: The importance of customer due diligence in business
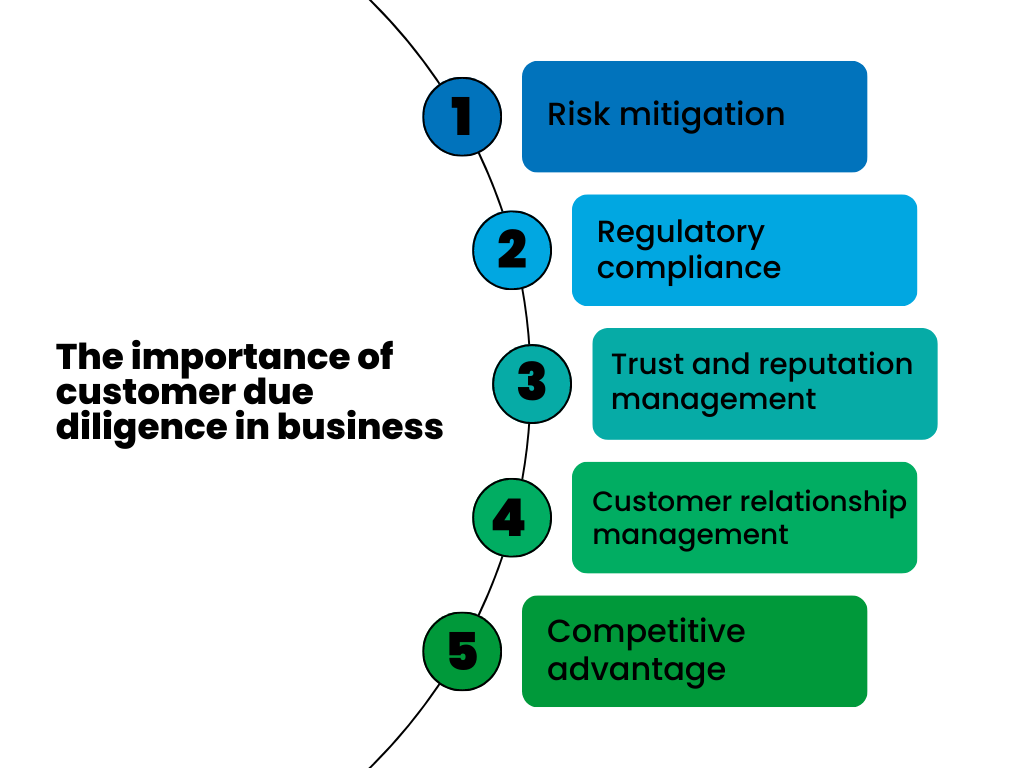
Risk mitigation
CDD helps businesses identify and mitigate various risks, including financial, legal, and reputational risks. By understanding who their customers are and what activities they’re involved in, businesses can better assess potential risks and take preventative actions.
Regulatory compliance
In many industries, particularly in financial services, regulations mandate the performance of due diligence on customers. This is intended to prevent crimes such as money laundering, fraud, and financing of terrorism. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, including fines and sanctions, which could have significant financial and reputational impacts.
Trust and reputation management
Conducting proper CDD can enhance a business’s reputation by demonstrating its integrity and taking its responsibilities seriously. This can improve relationships with stakeholders, including customers, employees, investors, and regulators, fostering trust and facilitating business growth.
Customer relationship management
Through the CDD process, businesses can gain a better understanding of their customers’ needs and behaviors. This information can be leveraged to improve product offerings, personalize marketing efforts, and enhance overall customer experience, all of which can contribute to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Competitive advantage
In today’s highly competitive business environment, having robust CDD processes in place can provide a competitive edge. It signals to customers, competitors, and the market at large that a business is dedicated to maintaining high ethical standards and is committed to conducting its operations responsibly.
Learn more about financial due diligence and due diligence checklist.
Steps in implementing customer due diligence (CDD)
CDD is a multi-step process that requires careful planning and execution.
Customer identification
The first step in the CDD process is to identify the customer. This requires gathering key information about the customer, such as their name, address, contact details, and, in some cases, information about their employment or source of funds. The specific information needed may vary based on jurisdiction and industry.
Customer verification
Once the identification information is collected, it needs to be verified. Identity verification usually involves cross-checking the provided details with reliable, independent source documents, data or information. For businesses, this might involve validating a potential corporate client’s registration details with the relevant business registry.
Understanding the nature and purpose of the business relationship
The next step is to understand the nature and purpose of the proposed business relationship. This involves understanding why the customer requires the services, the anticipated level of activity, and the nature of the transactions involved. This helps the business to assess the risk associated with the customer and to identify any potential red flags.
Risk assessment
Based on the collected information, a risk assessment is conducted. This involves determining the potential risk the customer may pose to the business, typically categorized as low, medium, or high risk. Factors that might influence this risk rating include the customer’s location, their occupation, the nature of their business, the type of services they’re requesting, and their overall financial behavior.
Ongoing monitoring
Once the business relationship has been established, it’s essential to continually monitor the customer’s activities to ensure they remain in line with what was originally understood about the customer. This might involve tracking transactions, keeping customer information up-to-date, and re-assessing the customer’s risk level as necessary.
Record keeping
Finally, it’s essential to keep comprehensive records of all the CDD processes. These records should include customer information, risk assessments, and any actions taken in response to potential issues. Such documentation can be crucial for demonstrating compliance with relevant regulations.
Remember, the specific steps and procedures in the CDD process can vary depending on the jurisdiction, the nature of the business, and the regulatory framework the business is operating under. Always consult with a legal or compliance professional to ensure your CDD procedures are compliant with all relevant laws and regulations.
Due diligence: challenges in implementing CDD
Implementing a comprehensive customer due diligence program is crucial for businesses, but it can come with its own set of challenges. Here are some of the most common ones:
Resource intensive
Effective CDD procedures require significant resources, including time, personnel, and technology. Depending on the size and nature of the business, this could involve hiring additional staff, investing in new software, and dedicating significant amounts of time to maintaining and updating customer information.
Technological constraints
Many businesses struggle with outdated or inadequate technology that makes it difficult to gather, store, and analyze customer data efficiently. Advanced technologies are often required to handle the large amounts of data involved in CDD and to carry out necessary analytics.
Regulatory complexity and changes
The regulatory landscape surrounding CDD is complex and constantly changing. Businesses need to stay updated with changes in laws, regulations, and best practices in all jurisdictions in which they operate. This can be particularly challenging for businesses with a global presence.
Data privacy and protection
With the collection and analysis of customer data comes the responsibility to protect that data. Companies must ensure they comply with all relevant data protection regulations, which can vary widely by region. Failure to adequately protect customer data can result in penalties and damage to the company’s reputation.
Customer cooperation
Sometimes, customers might be reluctant to provide the necessary information for CDD, either because they view the process as intrusive or because it requires them to provide sensitive information. Getting customers to understand and cooperate with CDD processes can be a challenge.
Inaccurate or incomplete information
Customers may provide inaccurate or incomplete information, either unintentionally or deliberately. This can lead to incorrect risk assessments and potential compliance issues.
By being aware of these challenges, businesses can proactively seek solutions and strategies to address them, thereby ensuring their CDD processes are both effective and compliant.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while the journey of implementing and maintaining effective CDD processes may be demanding, it is indeed a worthwhile investment. Businesses that successfully navigate this path stand to gain improved risk management, enhanced customer relationships, and, ultimately, sustained business growth. As we forge ahead into an increasingly interconnected business environment, the significance of customer due diligence will only continue to magnify, further emphasizing its vital role in the corporate world.
This article is a general overview and does not cover all aspects of customer due diligence. For a detailed understanding and application, consultation with a professional expert in this field is recommended.

%20(1).png)





Effective customer due diligence (CDD) is an important component of enhancing business processes and mitigating risk