Enhanced due diligence (EDD), a concept gaining increasing relevance in the global business landscape, presents a significant approach to manage and mitigate business and compliance risks. Understanding EDD is critical for businesses of all scales in an era defined by regulatory scrutiny and a persistent need for transparency. This article explores the world of EDD – its basics, importance, components, and implementation.
Check our article about financial due diligence for more information.
This article is a general overview and does not cover all aspects of enhanced due diligence. For a detailed understanding and application, consultation with a professional expert in this field is recommended.
Understanding the basics of enhanced due diligence
Conceptual framework of EDD
Enhanced Due Diligence is a comprehensive process of assessing and mitigating risk factors, particularly in high risk and complex business relationships. It goes beyond surface-level information, delving into intricate details to establish a clear and comprehensive understanding of potential risks and the underlying entities.
Relationship between EDD and standard due diligence
At a fundamental level, both standard due diligence and enhanced due diligence are part of a company’s risk management process. They both serve the purpose of investigating and understanding potential risks associated with business relationships, particularly those involving clients and customers. This process ensures the integrity of financial systems and helps protect businesses from being used to facilitate illicit activities like money laundering or fraud.
Standard due diligence, or customer due diligence (CDD), is the basic level of due diligence every company should perform on all its clients. This process typically includes gathering and analyzing client information to verify their identities and assess the overall risk they present. Information gathered during CDD might include a client’s full name, address, date of birth, and source of funds. Businesses use this information to form a preliminary understanding of the client and their associated risk level.
However, standard due diligence can sometimes be insufficient, especially in situations with a higher risk profile. Here’s where enhanced due diligence comes into play.
EDD goes beyond the scope of standard due diligence. It involves conducting a more thorough investigation into clients deemed high risk, such as those involved in large transactions, operating in high risk jurisdictions, or associated with politically exposed persons (PEPs). EDD aims to gain a deeper understanding of the customer’s activities and relationships, providing a comprehensive risk profile.
While both standard and enhanced due diligence play vital roles in risk management, EDD provides a deeper and more comprehensive view of the potential risks a business relationship may pose. In a regulatory environment where businesses are expected to take a risk-based approach, understanding the difference between the two and knowing when to apply EDD can help businesses maintain regulatory compliance and protect their reputation.
When is enhanced due diligence required?
Enhanced due diligence is required when a business relationship or transaction has been identified as higher risk. This could be due to various factors that present a greater potential for illegal activities, such as money laundering or terrorist financing.
Here are some situations when enhanced due diligence is generally required:
Dealing with politically exposed persons (PEPs)
PEP is an individual who holds a prominent public position or function, which can potentially make them vulnerable to corruption. This can also extend to their family members or close associates. Because of their status, transactions involving PEPs often require EDD to prevent potential misuse of funds, bribery, or corruption.
High-risk business relationships or transactions
These could be transactions of high value, complex, or unusually large transactions, or patterns of transactions that have no apparent economic or lawful purpose.
Private banking and anonymous transactions
Due to their very nature, private banking sectors and anonymous transactions often require EDD due to a higher level of inherent risk.
Non-face-to-face business relationships
These types of relationships might increase the risk of fraud, money laundering, or terrorist financing and thus typically necessitate EDD.
Correspondent banking relationships
In correspondent banking relationships, the correspondent bank is required to perform EDD on the respondent bank to manage risks effectively.
The importance of enhanced due diligence
Here are some key reasons why EDD is essential:
Risk management
EDD is a crucial part of a company’s risk management strategy. By conducting in-depth checks and balances on high-risk customers or business relationships, companies can identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks, such as financial fraud, corruption, or involvement in illegal activities.
Regulatory compliance
Regulatory bodies around the world, such as the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) in the United States and the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) globally, require businesses to conduct EDD as part of their Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) obligations. Failure to perform adequate EDD can result in heavy fines, sanctions, and legal implications.
Reputation management
Inadequate due diligence can lead to an association with money laundering, fraud, or corruption, which can severely damage a company’s reputation. Conducting EDD helps organizations maintain their reputation by demonstrating a commitment to ethical business practices and robust risk management.
Avoidance of financial loss
Effective enhanced due diligence can identify red flags that indicate a potential financial loss. This may include links to fraudulent activities or association with politically exposed persons (PEPs) who may present higher risks.
Operational efficiency
EDD can improve operational efficiency by providing a clear understanding of the potential risks involved with a customer or transaction. This enables organizations to make informed business decisions, manage risks effectively, and allocate resources more efficiently.
Investor confidence
Investors and shareholders have increased confidence in companies that adopt strong risk management practices, including EDD. Demonstrating a commitment to EDD can enhance investor relations and potentially lead to greater investment.
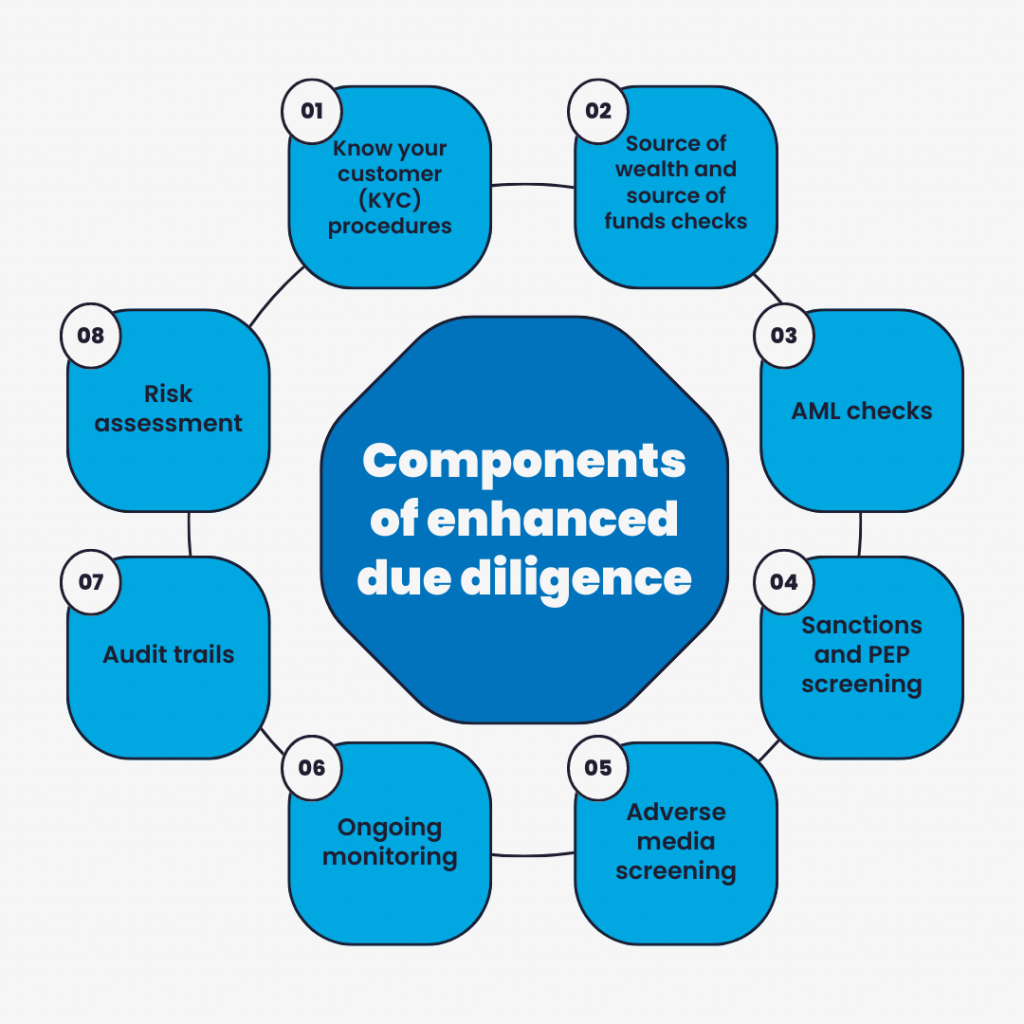
Components of enhanced due diligence
Know your customer (KYC) procedures
EDD extends the scope of KYC by gathering more detailed information about high-risk customers. This can include a comprehensive understanding of the customer’s business, ownership structure, and the purpose and nature of the transaction or relationship.
Source of wealth and source of funds checks
These checks involve determining the origin of the customer’s overall wealth and the specific funds involved in the transaction. This can help detect potential cases of money laundering or corruption.
Anti-money laundering (AML) checks
Anti-money laundering checks are an integral part of EDD, with more extensive checks conducted for high risk customers. This might involve more detailed scrutiny of their transactions to detect any patterns that could suggest money laundering.
Sanctions and PEP screening
Enhanced due diligence includes checking whether the customer is on any international sanctions lists or if they are a Politically Exposed Person (PEP). These checks are crucial as transactions involving such individuals or entities present a higher risk.
Adverse media screening
Adverse media involves checking for any negative news coverage related to the customer. Adverse media can provide valuable information about potential risks associated with the customer.
Ongoing monitoring
EDD is not a one-time procedure. It requires continuous monitoring of high risk customers and their transactions to detect any change in risk level. This allows for timely action to be taken if any suspicious activities are identified.
Audit trails
Keeping a thorough record of the due diligence process is crucial for enhanced due diligence. This helps demonstrate compliance with regulatory authorities and can be useful in case of any future investigations.
Risk assessment
Based on the information gathered, a risk assessment is carried out to determine the level of risk associated with the customer. The level of risk can determine the extent of due diligence required in the future.
Implementing enhanced due diligence in business operations
Developing an EDD framework
Implementing EDD begins with the development of a robust EDD framework that clearly defines procedures, roles, responsibilities, and reporting mechanisms. It should be tailor-made to the organization’s nature, size, and risk profile.
Incorporating technology in EDD
Technology plays a significant role in enhanced due diligence. AI and machine learning can automate routine tasks, flag suspicious activities, and analyze large volumes of data, thus streamlining EDD processes and enhancing their effectiveness.
Role of employee training and awareness
Employee training and awareness are crucial in implementing EDD. Businesses should invest in regular training programs to ensure their employees understand EDD processes and their importance.
Enhanced due diligence software solutions: How to find the right one
With the increasing regulatory pressures and complexity of business operations, utilizing software solutions for enhanced due diligence can greatly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your compliance efforts. Such software automates several aspects of the due diligence process, reducing manual labor, minimizing errors, and ensuring more accurate and reliable results.
Here are some key features and benefits of EDD software:
Automation of data collection
EDD software can automatically gather and organize data from various sources. This includes personal identification information, financial records, corporate documentation, and more. Automation reduces the time spent on data collection and enhances the accuracy of the collected information.
Risk assessment
Enhanced due diligence software uses complex algorithms to assess risk levels based on the collected data. It can automatically flag high risk clients or transactions, facilitating quicker decision-making.
AML compliance
EDD software helps businesses comply with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations by identifying suspicious activities that may suggest money laundering.
Ongoing monitoring and alerts
EDD software offers continuous monitoring of clients and transactions, adjusting risk scores as new data becomes available. This feature can alert your business to changes that might impact a client’s risk level.
Audit trails
EDD software provides comprehensive audit trails, documenting every step of the due diligence process. This is crucial for demonstrating regulatory compliance and for use in potential future investigations.
It’s important to choose an enhanced due diligence software solution that fits the unique needs and risk profile of your business. Remember, while EDD software can significantly streamline the due diligence process, it does not eliminate the need for expert analysis and human judgement. Therefore, it should be used in conjunction with a comprehensive compliance strategy that includes experienced compliance professionals.
Conclusion
In the digital era, the integration of software solutions in the enhanced due diligence process can enhance efficiency, streamline data management, and provide critical insights in real time. However, technology is not a panacea, and the role of informed human judgment remains paramount to interpreting complex scenarios and making nuanced decisions. The future of EDD looks promising, with advances in technology offering more refined tools for risk analysis and decision-making. Yet, businesses must remain vigilant and adaptable to evolving regulatory landscapes and emerging risks. Through robust EDD practices, companies can foster a culture of compliance, protect their reputation, and contribute to the global fight against financial crime. Ultimately, a commitment to enhanced due diligence is not just a legal obligation but an investment in the sustainable and ethical growth of a business.
This article is a general overview and does not cover all aspects of enhanced due diligence. For a detailed understanding and application, consultation with a professional expert in this field is recommended.

%20(1).png)