It’s no surprise that we live in a world where every dollar counts and transparency is key. But how to control an endless cash flow? Obviously, with the standards and rules.
Today, we’ll talk about Cost Accounting Standards (CAS) – the rules established by the U.S. government that ensure fair and consistent financial practices. Join us as we explore how CAS works, why it’s essential for anyone involved in federal contracts, and how it impacts accounting practice.
Key takeaway:
- Cost Accounting Standards are developed and revised by CASB.
- For the time being, Cost Accounting Standards consist of 19 standards.
- There are two types of CAS coverage: full and modified.
Contents:
1. CASB and CAS: Definition and purpose
2. How many standards are there in cost accounting?
3. What is a Cost Accounting Standards threshold?
4. What is a CAS Disclosure Statement in accounting practice?
5. The difference between CAS, GAAP and FAR
CASB and CAS: Definition and purpose
Cost Accounting Standards Board
If you think the Cost Accounting Standards Board sounds fancy, you’re on the right track.
The Cost Accounting Standards Board (CASB) is an independent board established within the Office of Federal Procurement Policy (OFPP), which is part of the U.S. Office of Management and Budget.
The CASB is responsible for developing and revising Cost Accounting Standards, which provide detailed guidelines for contractors on how to measure, allocate, and report costs. We’ll talk about them in more detail a bit later.
The board consists of five members, including:
- The Administrator of the OFPP, who serves as the Chair of the CASB;
- Two members from federal agencies, appointed by the Administrator;
- Two members from the private sector, also appointed by the Administrator.
Cost Accounting Standards
Now, let’s focus on the main topic of this guide.
Cost Accounting Standards are a set of 19 standards and rules established to achieve uniformity in cost accounting and reporting.
To put it simply, CAS is set to ensure companies working with the U.S. government handle their costs systematically. A so-called guidebook that provides instructions on how to track and report expenses for government contracts.
CAS covers a variety of costs, such as
- Depreciation;
- Pension plans;
- Personal compensation;
- Indirect costs and other areas of cost accounting.
Note: Cost accounting standards only apply to contracts, not contractors or agencies.
→ Find out more about cost accounting.
How many standards are there in cost accounting?
As we’ve already mentioned, the 19 Cost Accounting Standards cover a wide range of topics related to cost accounting practice. Each standard covers a specific area, so let’s break them down into 6 categories.
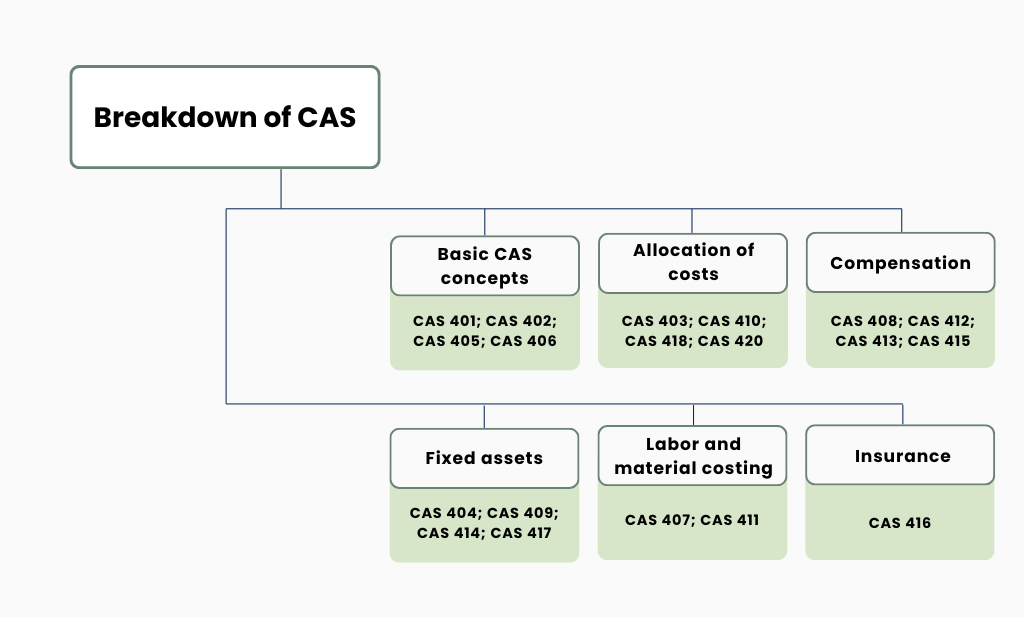
1. Basic CAS concepts
These are subject to modified coverage.
| CAS 401 | Consistency in Estimating, Accumulating, and Reporting Costs |
| CAS 402 | Consistency in Allocating Costs Incurred for the Same Purpose |
| CAS 405 | Accounting for Unallowable Costs |
| CAS 406 | Cost Accounting Period |
2. Allocation of costs
| CAS 403 | Allocation of Home Office Expenses to Segments |
| CAS 410 | Allocation of Business Unit General and Administrative Expenses to Final Cost Objectives |
| CAS 418 | Allocation of Direct and Indirect Costs |
| CAS 420 | Accounting for Independent Research and Development Costs and Bid and Proposal Costs (IR&D and B&P) |
3. Compensation
| CAS 408 | Accounting for Costs of Compensated Personal Absence |
| CAS 412 | Composition and Measurement of Pension Cost |
| CAS 413 | Adjustment and Allocation of Pension Cost |
| CAS 415 | Accounting for the Cost of Deferred Compensation |
4. Fixed assets
| CAS 404 | Capitalization of Tangible Assets |
| CAS 409 | Depreciation of Tangible Capital Assets |
| CAS 414 | Cost of Money as an Element of the Cost of Facilities Capital |
| CAS 417 | Cost of Money as an Element of the Cost of Capital Assets Under Construction |
5. Labor and material costing
| CAS 407 | Use of Standard Costs for Direct Material and Direct Labor |
| CAS 411 | Accounting for Acquisition Costs of Material |
6. Insurance
| CAS 416 | Accounting for Insurance Costs |
Note: CAS 419 is reserved for future use or potential new standards.
Keep your accounting records under control by storing them in one source of truth with Synder Sync capabilities. Learn how a smart accounting software solution can enhance your workflow by visiting a Weekly Public Demo or test the features yourself by signing up for a 15-day free trial.
What is a Cost Accounting Standards threshold?
It refers to the specific monetary thresholds that determine whether a government contractor or subcontractor must comply with the CAS requirements.
The requirements of Cost Accounting Standards apply to all negotiated contracts that exceed the threshold of $2 million unless there’s an exemption. Typically, a contract award of $7.5 million or more serves as a trigger contract that establishes CAS coverage unless, again, an exemption applies.
There are two types of Cost Accounting Standards coverage:
- Full CAS coverage;
- Modified CAS coverage.
Full coverage
Full coverage requires compliance with all 19 Cost Accounting Standards.
It applies to contractors who received negotiated contracts and subcontracts with $50 million or more in CAS-covered awards in their most recent cost accounting period.
Modified coverage
Modified coverage requires compliance with a subset of Cost Accounting Standards (typically CAS 401, CAS 402, CAS 405, and CAS 406).
It applies to contractors that receive negotiated contracts and subcontracts of $7.5 million or more but less than $50 million in CAS-covered awards in their most recent cost accounting period.
Exemptions from CAS coverage
- Contracts/subcontracts under the $7.5 million;
- Sealed bid contract;
- Contract/subcontract with a small business;
- Contract/subcontract with foreign governments, their agents, or instrumentalities*;
- Contract/subcontract price is set by law or regulation;
- Contracts/subcontracts for commercial items (FAR 12.207);
- Firm fixed price contract/subcontract awarded on the basis of adequate price competition without submission of certified cost or pricing data.
* – The exemption doesn’t extend to contracts/subcontracts with foreign concerns that are subject to CAS 401 or 402.
What is a CAS Disclosure Statement in accounting practice?
A CASB Disclosure Statement is a form where a U.S. government contractor outlines its cost accounting practice. This disclosure is required to demonstrate Cost Accounting Standards compliance for the duration of its active CAS-covered awards.
The Disclosure Statement is typically structured in a standardized format, such as the Form CASB DS-1. It includes detailed sections and questions that guide the contractor in providing comprehensive information about their cash flow. The form is then reviewed and approved by the government.
Contractors should submit a Disclosure Statement if:
- Contractors and subcontractors that receive negotiated contracts of $50 million or more in CAS-covered awards in their most recent cost accounting period;
- Contractors with contracts between $7.5 million and $50 million (if they are subject to modified Cost Accounting Standards coverage).
Note: A Disclosure Statement is not required if:
- the company and its segments didn’t receive $50 million or more in CAS-covered awards during the last cost accounting period;
- the company and its segments received $50 million or more, but the business unit received less than $10 million in CAS-covered awards and less than 30% of segment sales in the prior year.
The difference between CAS, GAAP and FAR
Cost Accounting Standards (CAS), Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), and the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) are three distinct frameworks used in accounting practice and financial management. Each serves a different purpose and applies to different types of organizations and transactions.
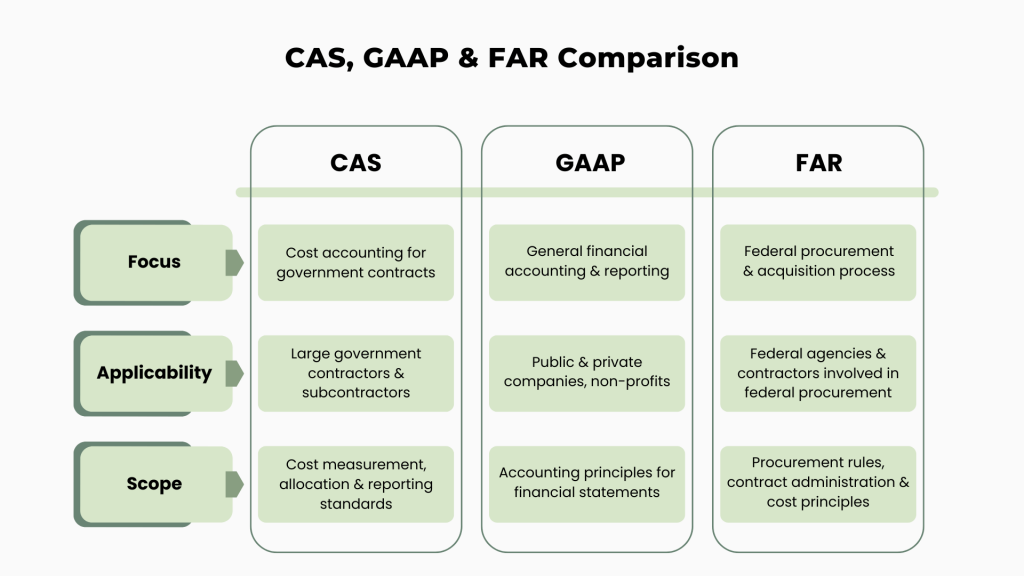
To put it simply:
- CAS is a set of standards designed to ensure consistency in cost accounting for government contractors. It focuses on how government contracts measure, assign, and allocate costs.
- GAAP is a comprehensive set of accounting principles and standards for preparing and presenting financial statements for publicly traded and private companies.
- FAR is a set of rules governing the acquisition process by which the federal government purchases goods and services.
→ Learn how to get business insights from data and how businesses benefit from data analytics.
Conclusion: Cost accounting practice
Understanding and implementing Cost Accounting Standards (CAS) may seem tough at first, but is an important step toward ensuring fairness and transparency in government contracting. By following the requirements, contractors comply with federal regulations and build trust and credibility with their clients and stakeholders through consistent accounting practices.
On the other hand, non-compliance can result in various penalties, including the potential risk of contract loss and the need to directly reimburse the government for any overcharges resulting from non-compliant practices.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and shouldn’t be considered as professional advice. We strongly recommend consulting with a qualified professional or expert to ensure compliance with Cost Accounting Standards and other relevant regulations to maintain proper accounting practices.
Share your thoughts
Did you find this guide on accounting practices helpful? Or perhaps you have your own experiences with cost accounting standards? Leave a comment below, and let’s talk!







.png)
