Understanding their financial standing can be a formidable challenge for many enterprises. As companies strive to make informed decisions and secure their fiscal stability, one invaluable tool comes to the forefront: the Break Even Point (BEP). Picture this as a financial compass, guiding businesses through the complexities of cost and revenue.
In this exploration, we delve into the significance of BEP, unraveling its role in overcoming financial challenges and charting a course for sustainable success.
Key takeaways
- The break even point (BEP) is where a business covers all its costs but makes neither profit nor loss, acting as a financial milestone indicating stability.
- Break even analysis helps businesses understand the minimum level of activity needed to avoid losses and make informed decisions about pricing and production.
- Understanding and applying the break even point strategically guides businesses in pricing, production, risk assessment, and long-term planning, fostering sustained success and resilience.
Level up your accounting with smart automation! Integrate financial data from all your sales channels in your accounting to have always accurate records ready for reporting, analysis, and taxation. See it in action with a 15-day free trial or spare a spot at our weekly public demo to have your questions answered.
Definition of break even point (BEP)
The break even point (BEP) is a critical financial metric that represents the level of sales or production at which a business’s total revenues exactly equal its total costs, resulting in neither profit nor loss. In other words, it is the point at which a company covers all its fixed and variable costs, and beyond which it begins to generate a profit.
At the break even point, the net income is zero, indicating that the business has recouped all its expenses. It serves as a vital reference for businesses to assess financial viability, make informed decisions about pricing and production levels, and understand the threshold at which profitability begins.
Overview of break even analysis
Break even analysis is a financial assessment tool used by businesses to determine the point at which total revenues equal total costs, resulting in neither profit nor loss. This analytical technique helps businesses understand the relationship between fixed costs, variable costs, and revenue, enabling them to identify the level of sales or production needed to cover all expenses.
The primary objective of break even analysis is to provide insights into the minimum level of business activity required to avoid losses and achieve a state of financial equilibrium. By examining the cost structure and pricing strategies, businesses can make informed decisions regarding product pricing, production volumes, and overall financial strategy. Break Even Analysis is a valuable component of financial planning and decision-making, aiding businesses in setting realistic goals and assessing the potential impact of various scenarios on their financial performance.
Components of break even analysis
To unravel the dynamics of Break Even Analysis, let’s dissect its key components.
Fixed costs
Fixed Costs form the bedrock of any business operation, representing constant expenditures that don’t fluctuate with production levels. Unveiling these fixed costs provides clarity on the financial groundwork. Illustrative examples, from rent to insurance, shed light on the tangible aspects of fixed costs.
Variable costs
Variable costs, on the other hand, are the shape-shifters of business expenses. They fluctuate with production volume, and understanding their essence is crucial for strategic decision-making. Real-world instances, such as raw materials or hourly labor, showcase the variability that businesses must navigate.
Total costs
Total costs bring these elements together in a comprehensive formula. Grasping this formula provides a roadmap for practical calculations, offering businesses a tangible method for understanding and managing their financial landscape.
Break even point calculation
Now that we’ve laid the groundwork, let’s dive into the heart of Break Even Analysis—the Break Even Point (BEP) calculation. This mathematical representation of business equilibrium, becomes a powerful tool when applied to real-world scenarios. By strategically maneuvering production levels and pricing strategies, businesses can unlock the potential for financial success.
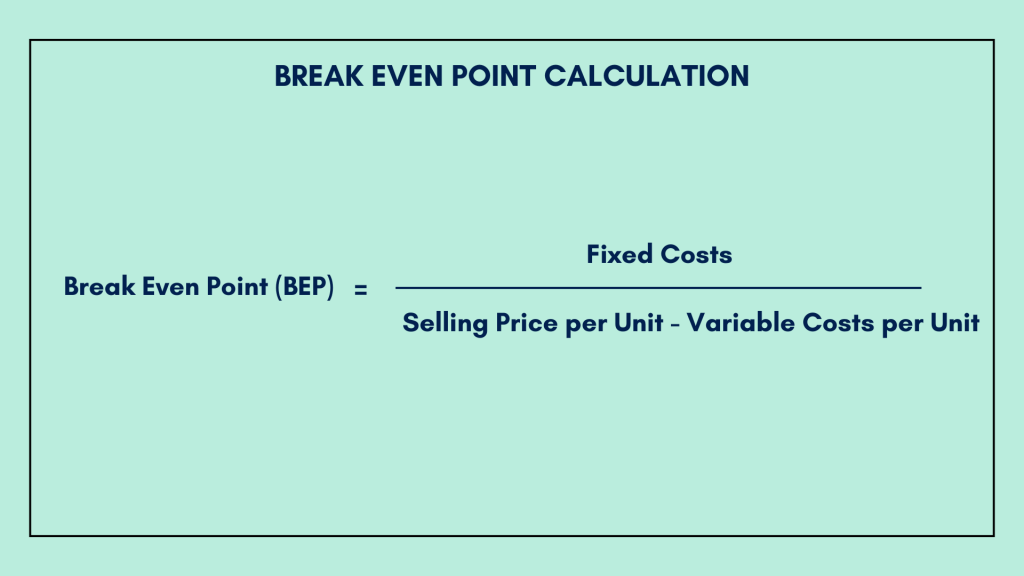
The Break Even Point (BEP) is calculated using a straightforward formula:
Break Even Point (BEP) = Fixed Costs / Selling Price per Unit − Variable Costs per Unit
In this formula:
- Fixed Costs represent all the constant expenses that do not vary with the production or sales volume.
- Selling Price per Unit is the amount for which a single unit of a product or service is sold.
- Variable Costs per Unit are the costs that vary with each unit produced or sold.
This formula gives the quantity of units that need to be produced and sold for total revenue to equal total costs, resulting in neither profit nor loss. It’s a valuable tool for businesses to determine the minimum level of activity required to avoid losses and start making a profit.
Graphical representation enhances our understanding further. Visualizing the Break Even Chart transforms complex financial data into actionable insights. Interpreting this chart becomes a skill, offering a bird’s-eye view of the business’s financial landscape and paving the way for informed decision-making.
Significance of break even point
Understanding the Break Even Point is the gateway to strategic decision-making. In the realm of business decision-making, BEP serves as a guiding star. Navigating through the intricacies of pricing strategies, businesses leverage their Break Even Point to strike a balance between profitability and market competitiveness.
Risk Assessment takes center stage as businesses utilize Break Even Analysis to evaluate their financial fortitude. By understanding the Break Even Point’s role in risk assessment, enterprises gain the foresight to weather market uncertainties and ensure their viability.
Factors influencing break even point
The Break Even Point is not set in stone; it dances to the tune of external factors.
- Market conditions play a crucial role in this dance. Fluctuations in market demand impact the Break Even Point, requiring businesses to adapt swiftly to changing consumer needs. Navigating the Competitive Landscape further underscores the dynamic nature of BEP, as businesses strategically position themselves for success amid industry rivals.
- Operational efficiency emerges as a key influencer. By enhancing efficiency through Break Even Analysis, businesses optimize processes and minimize costs. Delving into cost-saving measures, from efficient resource allocation to streamlined production processes, allows enterprises to proactively manage their Break Even Point.
Break even analysis and business planning
Integration into business plans becomes the natural evolution of break even analysis. Embedding this financial tool into the fabric of business plans empowers enterprises to make informed decisions.
Financial forecasts gain precision, and long-term strategic planning takes on a new level of sophistication as businesses align their goals with their Break Even Point.
Continuous monitoring becomes the mantra for success. Adapting to market changes through ongoing Break Even Analysis ensures that businesses remain agile in the face of economic shifts. This continuous monitoring becomes the bedrock of informed decision-making, offering updated insights into the Break Even Point and guiding strategic choices.
Tools for break even analysis
- Spreadsheet models serve as the technological backbone for Break Even Analysis. Excel Templates streamline the process, making complex calculations accessible to businesses of all sizes. Software Applications take it a step further, simplifying Break Even Point calculations and providing a user-friendly interface for financial analysis.
- Online calculators offer accessibility and ease of use, allowing businesses to perform quick Break Even Point calculations on the go. However, understanding the limitations and considerations of these tools is crucial for accurate financial planning.
Conclusion
In business, understanding the break even point and break even analysis emerges as a cornerstone for financial success. As we recap the journey through fixed and variable costs, break even point calculation, and the tools that facilitate this analysis, we encourage businesses to embrace these concepts wholeheartedly.
Unlocking financial success begins with the mastery of break even analysis. The transformative potential of understanding and strategically applying the break even point cannot be overstated. As you navigate your business journey, delve deeper into the intricacies of Break Even Analysis, for within lies the key to sustained success and fiscal resilience.
Continue reading: Learn the difference between product and period costs.
Share your thoughts
Let us know what you think about break even point. Do you rely on it managing your business? Share your thoughts in the comments section below.






