Tax obligations can be tricky, especially when reporting income for individuals who aren’t traditional employees. The rules can be confusing, and the paperwork can get overwhelming. So, is there a solution for freelancers or landlords?
Yes. The IRS uses specific forms to ensure that payments for businesses or individuals are accurately tracked and reported. The most commonly used forms are the 1099-MISC and 1099-NEC. But how do you choose the right one, and what are the main differences?
Keep reading the guide, and we’ll help you learn more about 1099-MISC and 1099-NEC!
Key takeaways:
- 1099-MISC is used to report various types of miscellaneous income, such as rent, royalties, and prizes.
- 1099-NEC is used to report nonemployee compensation, which includes payments of $600 or more made to independent contractors.
- Both 1099-MISC and 1099-NEC forms can be submitted electronically or by email.
- Missing the deadlines can result in penalties varying from $60 to $330 per information return.
Contents:
1. Should I use 1099-MISC or 1099-NEC?
2. What is a 1099-MISC used for?
3. What is a 1099-NEC used for?
4. Is sending the forms to the IRS the last step?
5. What are the penalties for missing the filing deadline for 1099 forms?
6. FAQs
Should I use 1099-MISC or 1099-NEC?
If you’re asking this question, then you’ve come to the right place.
To start, let’s understand what these forms are. Both the 1099-MISC and 1099-NEC are the IRS forms used for reporting income. However, they serve different purposes:
- 1099-MISC is used to report various types of miscellaneous income, such as rent or royalties, paid to individuals.
- 1099-NEC is specifically used to report payments made to non-employees for services.
This, basically, is the main difference between the 1099-MISC and 1099-NEC forms, which should be able to answer your question. But that’s not all. We’ll go into detail about each form, uncovering the true meaning and possible challenges.
Before breaking down 1099-MISC and 1099-NEC, let’s check the table below, showing the main information about the two, so you have a basic understanding of their differences:
| 1099-MISC | 1099-NEC | |
| Not subject to self-employment tax | Most likely subject to self-employment tax | |
| Who should send it? | Businesses or individuals with miscellaneous expenses (for example, rent payments) | Businesses or individuals who paid non-employees for services |
| Who will receive it? | Recipients of miscellaneous income (e.g., landlords, prize winners, attorneys) | Independent contractors, freelancers, and self-employed individuals |
| Limit required for filing | $10 for royalties or broker payments$600 for all others | $600 |
| Deadlines | February 28th (paper)March 31st (electronic) | January 31st |
Note: All 1099-MISC and 1099-NEC filers must have an Employer Identification Number (EIN). If you haven’t previously filed a Form 1099 or other return, you must obtain an EIN and include it on each Form 1099 that you file.
Now, let’s move to a more detailed description of each form, starting with 1099-MISC.
What is a 1099-MISC used for?
As previously mentioned, the 1099-MISC Form is used to report payments like rent, royalties, or prize-winnings that aren’t subject to self-employment tax. Think of the 1099-MISC as a catch-all for different types of miscellaneous income that don’t fit into other categories.
Form 1099-MISC must be prepared and filed by February 28th (for paper filing) or by March 31st (for electronic filing).
Who requires a Form 1099-MISC?
You need to file a Form 1099-MISC if you meet any of the following criteria:
1. You paid at least $10 in royalties or broker payments in lieu of dividends or tax-exempt interest;
2. You paid at least $600 for:
- Rents;
- Awards & prizes;
- Attorney payments;
- Other income payments;
- Health care & medical payments;
- Crop insurance proceeds;
- Fishing boat proceeds;
- Cash spent on fish for resale;
- Payments from a notional principal contract to an individual, estate, or partnership.
The simplest example is if your business paid an individual or LLC at least $600 in rent during the year, you’re required to file a 1099-MISC.
Note: Payments to corporations are generally not reported. However, if you paid a corporation for medical or healthcare services, you must report all such payments on your 1099-MISC Form.
How to file?
The first thing to know is that there are five copies of the 1099-MISC Form you need to fill out:
- Copy A: For the IRS;
- Copy 1: For the state tax department;
- Copy B: For the recipient;
- Copy 2: To be filed with the recipient’s state income tax return, when required;
- Copy C: Your copy for recordkeeping.
What you need to file
Let’s take a look at the fields in the example of Copy A of a Form 1099-MISC.
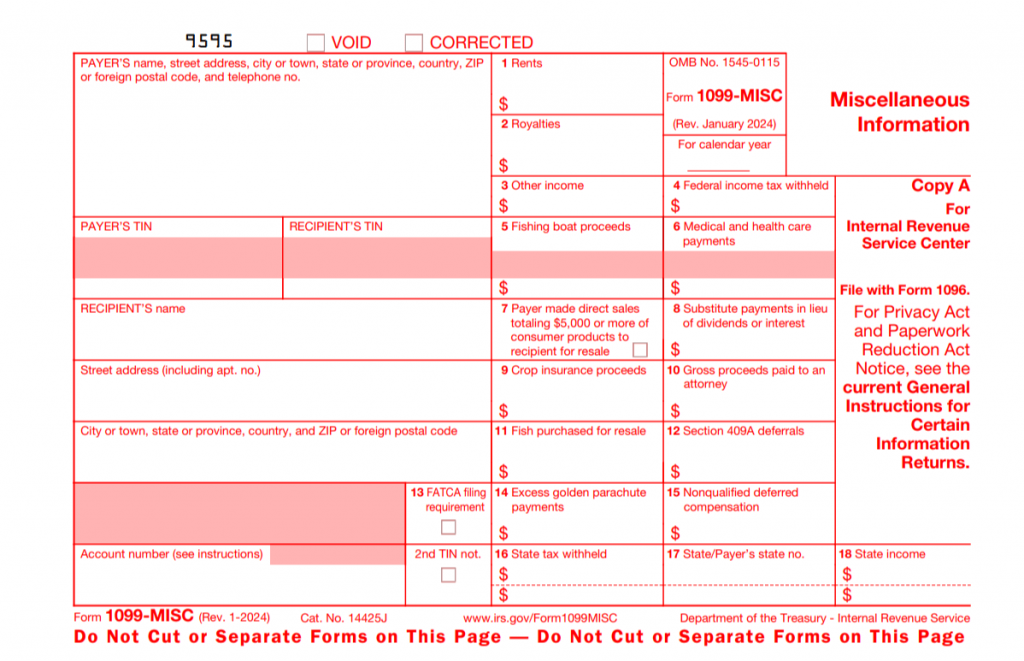
This sample of Copy A of a Form 1099-MISC is for informational purposes only. It shouldn’t be copied and filed with the IRS.
At first glance, the 1099-MISC Form can be divided into three main sections:
- Payer’s information;
- Recipient’s information;
- Boxes.
For the first two sections, you’ll need to file the following information:
| Payer’s information | Recipient’s information |
| Name; Street address, city or town, state or province, country; ZIP or foreign postal code; Telephone number; Tax Identification Number or SSN. | Name; Full address; ZIP or foreign postal code; Telephone number; Tax Identification Number or SSN. |
Note: To ensure accuracy, collect the recipient’s information by sending the recipient a Form W-9.
→ Learn the difference between W-9 and 1099 Forms.
The section with the boxes includes 18 fields to fill out the amounts paid to the recipient in various categories. Typically, you’ll use only 3 or 4 of these boxes, depending on the types of payments made.
What do you do when all the fields are filled out?
Once all the information is gathered and filled, you can submit the 1099-MISC Form in two ways:
- Electronically: with the IRS’ FIRE (Filing Information Returns Electronically) system or from an accounting software with payroll integrations, for example, QuickBooks Payroll;
- Manually.

→ Learn more about Form 1096 and how to file it.
Note: If you need more time to file, you can request an extension by sending paper Form 8809 to the IRS by January 31st. This form must be mailed; it can’t be filed online.
Now, moving to the next form – 1099-NEC.
Stay updated on the latest news in the accounting and bookkeeping world! Sign up for our weekly newsletter to receive the newest articles on the hottest trends.
What is a 1099-NEC used for?
We’ve already mentioned that Form 1099-NEC is used for reporting nonemployee compensation that’s most likely to be subject to self-employment tax. It’s specifically designed for payments made to independent contractors – this form helps the IRS track their total earnings and collect the correct amount of taxes.
Form 1099-NEC must be reported and filed annually by January 31st.
Who requires a Form 1099-NEC?
U.S. businesses use the 1099-NEC Form to report payments of more than $600 in a calendar year to self-employed individuals who provide services but aren’t permanent employees. Such independent contractors include:
- Freelancers;
- Self-employed service providers operating as individuals or small businesses (attorneys, CPAs, tax professionals, etc.).
A simple example: You run an online shop and hire a CPA for a consultation before tax season. You pay $1,200 for their services, which is more than $600, so now you’re required to file a Form 1099-NEC to report the nonemployee compensation to the IRS.
Note: When hiring employees globally, U.S. companies should use Form W-8BEN. This form establishes the international contractors status as non-U.S. citizens and determines the necessary tax reporting and withholding requirements for the entity providing their income.
How to file?
The filing process for the 1099-NEC is similar to that of the 1099-MISC. As a payer, you need to follow these steps:
- Gather information;
- File the form;
- Send it.
And just like with the 1099-MISC:
- Copy A goes to the IRS;
- Copy B is sent to the contractor.
What you need to file
Let’s refer to the IRS site for a sample of the 1099-NEC Form. Similar to the 1099-MISC sample, this example is for informational purposes only. This sample CANNOT be printed or filed.
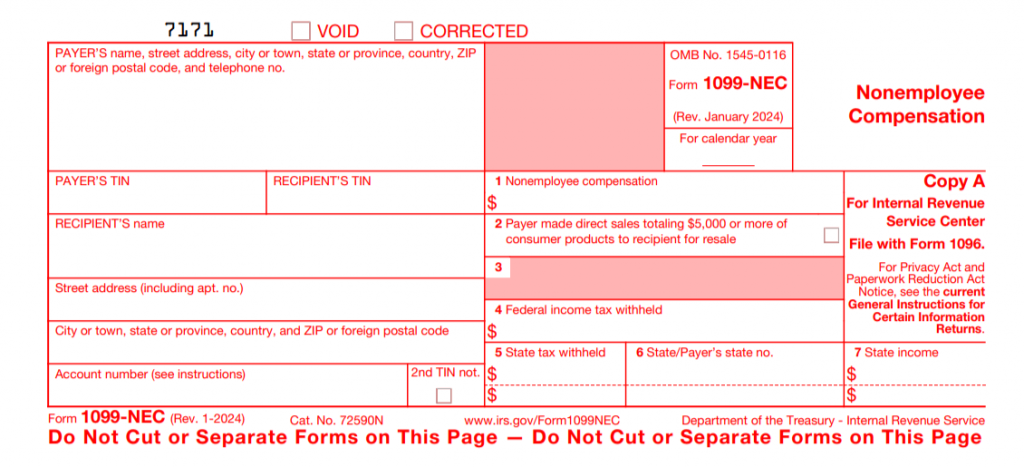
Here, you can see the familiar “payer’s” and “recipient’s” sections, along with boxes. Luckily, there are only 7 of them.
Before filing, as a company reporting nonemployee compensation on Form 1099-NEC, you’re to collect a Form W-9 from each contractor you paid over $600 during the previous year.
The information needed for the 1099-NEC Form includes:
- Payer’s name, address, phone number, and Tax Identification Number (TIN);
- Recipient’s name, address, and TIN (taken from a Form W-9);
- State identification number;
- Nonemployee compensation exceeding $600.
Note: In most cases, the only box that’ll apply to you is Box 1: Nonemployee compensation.
Once all the necessary fields are completed, the form can be submitted to the IRS either by e-file (through the IRS’s FIRE system) or by mail.
Want to know how to manage all your records and tackle tax season with confidence? Discover how Synder can assist you with bookkeeping and accounting tasks by visiting a Weekly Public Demo or starting a 15-day free trial. No credit card required. Access historical transactions from over 30 supported platforms.
Is sending the forms to the IRS the last step?
No. After submitting the 1099-MISC and 1099-NEC forms to the IRS, you also need to ensure the following:
#1. Sending copies to the recipient
Send Copy B of the 1099 Form to each contractor. With their consent, you can send the form electronically. If the recipient doesn’t consent to receive the statement electronically, a paper copy will be provided. This allows them to report the income on their tax return.
#2. State filing requirements
Check if your state requires you to file the 1099-NEC or 1099-MISC Form with the state tax department. If so, submit the necessary copies as per your state’s guidelines.
States exempt from 1099 filing include:
- Alaska;
- Florida;
- Illinois;
- Nevada;
- New Hampshire;
- New York;
- South Dakota;
- Tennessee;
- Texas;
- Washington;
- Wyoming.
If you’re a business or independent contractor operating in these states, you don’t need to submit a 1099-MISC or 1099-NEC Form to the state. However, filing requirements can change, so it’s important to check with each state’s tax authority for the latest information.
What are the penalties for missing the filing deadline for 1099 forms?
As stated in the IRS General Instructions for 2024, the amount of the penalty is based on when you file the correct information return.
- $60 per information return if you correctly file within 30 days after it’s due; maximum penalty $664,500 per year ($232,500 for small businesses).
- $130 per information return if you correctly file more than 30 days after the due date but by August 1; maximum penalty $1,993,500 per year ($664,500 for small businesses).
- $330 per information return if you file after August 1 or you don’t file required information returns; maximum penalty $3,987,000 per year ($1,329,000 for small businesses).
→ Learn the peculiarities of cash flow calculation and its formula.
Exceptions to the penalty
The penalty won’t apply to any failure that you can show was due to reasonable cause and not to willful neglect. You must be able to show that the failure in either the 1099-MISC or the 1099-NEC Form happened because of something beyond your control or due to significant mitigating factors. You must also be able to show that you acted responsibly and took steps to prevent the failure.
Summing up: The main difference between 1099-MISC and 1099-NEC
To summarize, the main difference between the two forms is the type of income they report. The 1099-NEC is used specifically for reporting payments to non-employees for services, while the 1099-MISC covers a wider range of miscellaneous income.
The thing is that both forms have their complexities, so bookmark this article and refer back to it whenever needed. We’ll help you remember where to file the amounts paid to a CPA or where to put the attorney’s fees!
Disclaimer: This information is for general informational purposes only and doesn’t constitute legal or tax advice. Please consult your attorney or tax advisor for advice tailored to your specific situation regarding the 1099-MISC or 1099-NEC Form. Only your attorney or tax advisor can ensure that this information—and your understanding of it—applies appropriately to your circumstances. All liability for actions taken or not taken based on this information is expressly disclaimed.
Share your thoughts
Have you faced the challenge of choosing between the 1099-MISC and 1099-NEC? Share your story in the comments section below!
FAQs
Is all 1099-MISC income taxable?
Income from a 1099-MISC form is taxable income, so you should report it on your tax return. If you have any uncertainties, consulting a tax professional can help ensure you meet all reporting requirements.
Can 1099-NEC be reported as MISC income?
No. Filing the wrong 1099 Form, whether you use the 1099-MISC instead of the 1099-NEC or vice versa, can lead to penalties and delays in processing tax returns.
Who must file 1099-NEC?
If you pay $600 or more to non-employees for services, you’re required to file a 1099-NEC to report those payments to the IRS and provide a copy to the recipient.
If you’re an independent contractor or a team receiving Copy B, it’s not your responsibility to file the form.
Do all LLCs get a 1099-MISC or 1099-NEC?
Generally, corporations or LLCs with S Corp or C Corporation tax status don’t receive a 1099-NEC or 1099-MISC Form.
Should attorney fees be on 1099-MISC or NEC?
The attorney fees you pay for services related to your business should be reported in Box 1 of Form 1099-NEC.
What is the outcome of missing the filing deadline?
The IRS imposes penalties for late filing, which can range from $60 to $330 per form, depending on how late the filing is.

%20(1).png)