For small business owners, accurately calculating total revenue is essential for making informed decisions and achieving financial success. But with so many factors to consider, it can be overwhelming to determine the right approach. That’s where this ultimate guide comes in useful – packed with tips and tricks to help you navigate the world of revenue calculation like a pro.
From understanding the basics of revenue calculation to some useful tips, this article covers everything you need to know to stay on top of your finances. So, if you’re ready to take control of your revenue and unlock the full potential of your business, let’s dive in!
Contents:
1. The basics of revenue calculation
3. How to calculate total revenue: Examples with ecommerce and SaaS businesses
4. Common mistakes to avoid when calculating revenue
5. How to increase total revenue
Key takeaways:
- Total revenue is the total amount of money a business generates before any expenses are deducted.
- Revenue is categorized into operating revenue, from core business activities, and non-operating revenue, from activities not central to the business’s primary operations.
- Total revenue is calculated by multiplying the number of units sold by the price per unit.
- Common mistakes in revenue calculation, such as mixing up revenue types and poor record-keeping, can lead to inaccurate revenue figures
.
The basics of revenue calculation: What is the total revenue of a business?
Total revenue refers to the complete amount of money generated by the company’s activities before any expenses are deducted. It’s a key financial metric, representing the gross income obtained from sales of goods or services and possibly other sources (rental income, investment income, or royalties, depending on the company’s business model). Total revenue is usually reported for a specific period, such as a month, quarter, or year.
Different types of revenue
There are two main types of revenue: operating revenue and non-operating revenue.
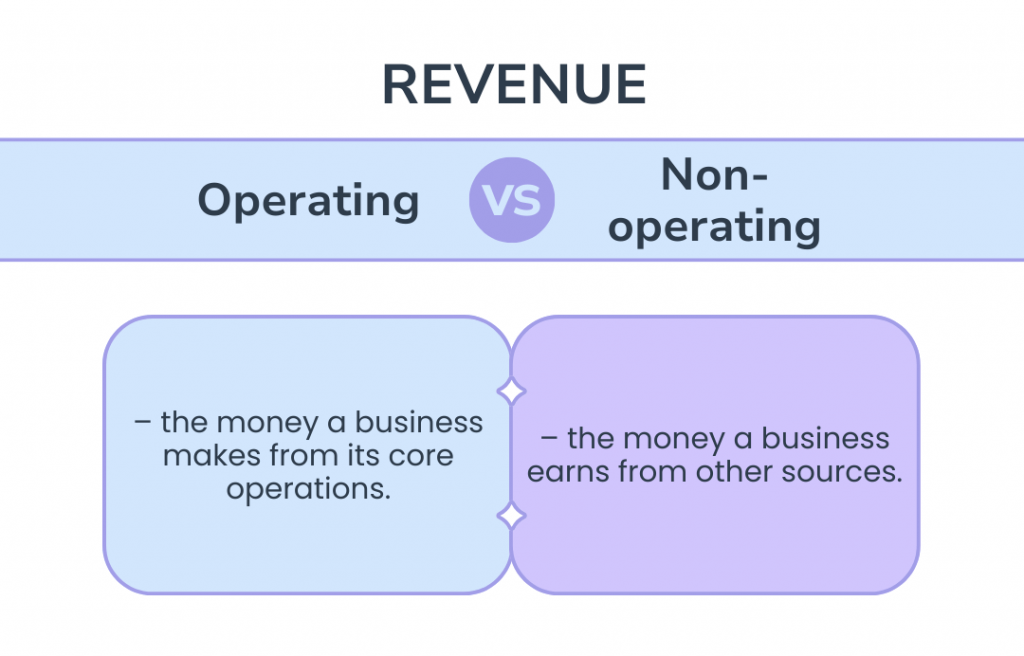
Operating revenue
This type of revenue is generated from a company’s core business activities.
- For a manufacturing company, operating revenue comes from selling the products it manufactures.
- For a service provider, it’s the income earned by providing services.
Operating revenue is a key indicator of a business’s efficiency and its potential for long-term sustainability. It reflects the primary activities that the business is designed to carry out.
Non-operating revenue
This includes income from activities that are not related to the primary operations of the business. Examples of non-operating revenue include interest earned on investments, profits from the sale of assets, rental income from property, or royalties.
Non-operating revenue can be less predictable than operating revenue.
→ Want to know more about COGS? Read our expert article ‘How to Calculate Cost of Goods Sold’.
Gross revenue vs. net revenue
As was said above, total revenue, often referred to as gross revenue or sales, is the entire amount of income generated by a company from its primary operations before any costs or expenses are deducted. Total revenue gives stakeholders a broad view of a company’s sales performance and market demand for its products or services over a specific period.
Net revenue, on the other hand, is the amount of money that remains after subtracting direct costs associated with producing the goods or services sold, known as the cost of goods sold (COGS), from the total revenue. Net revenue can also be adjusted by deducting returns, allowances for damaged or missing goods, and discounts.
Thus, net revenue provides a more accurate picture of the income contributing to the profit. It reflects the efficiency and effectiveness of a business’s operations by showing how much revenue is retained after covering the direct costs of goods and services sold.
The key difference lies in what these figures represent:
- Total revenue is a gross measure that does not account for any costs or deductions.
- Net revenue provides a clearer view of the effective income that contributes to profit after accounting for direct costs and other deductions directly related to sales.
→ Learn more about the difference between Net profit and revenue.
Revenue formula: What is the formula for calculating total revenue?
To calculate total revenue, you need to multiply the number of units sold by the price per unit (product or service). The formula looks as follows:
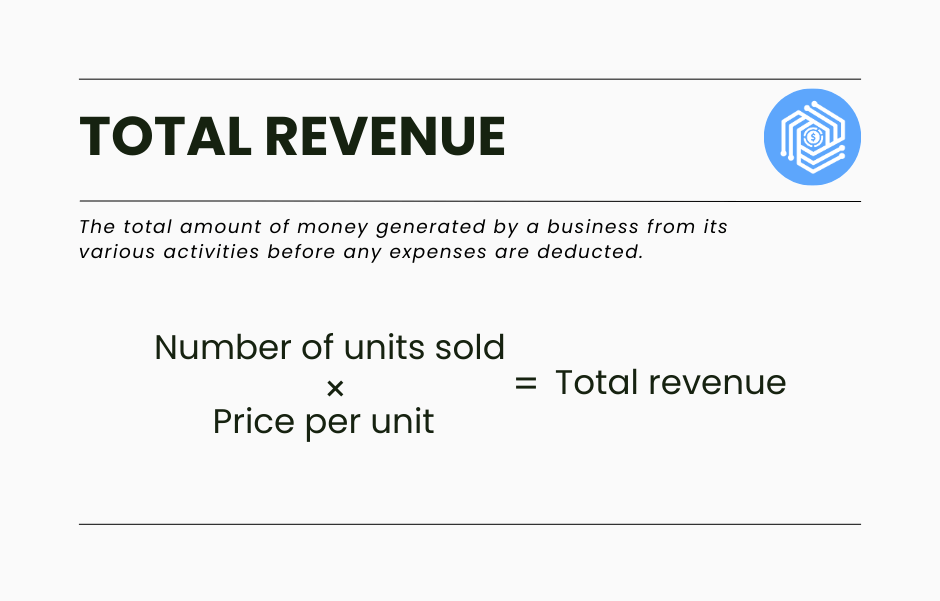
This formula represents the total income generated from the sale of goods or services before any expenses are deducted. Here’s how it breaks down:
- Number of units sold: The total number of units of the product that have been sold during a specific period.
- Price per unit: The selling price of each unit of the product or service.
For businesses with multiple products or services, the total revenue would be the sum of the revenues generated from each product or service line. If a business also earns income from other sources besides the sale of goods or services, such as interest, investments, or property rental, these amounts would be added to the total revenue from sales to get the overall total revenue of the business.
How to calculate total revenue: Examples with ecommerce and SaaS businesses
Example #1. How to calculate ecommerce revenue
Let’s say an ecommerce company sells three different types of products. Over a month, their sales figures are as follows:
| Product | Units sold | Price per unit |
| A | 500 | $20 |
| B | 300 | $30 |
| C | 200 | $50 |
To calculate the total revenue, we multiply the units sold by the price per unit for each product and then sum up the results:
- Revenue from Product A = 500 units * $20 = $10,000
- Revenue from Product B = 300 units * $30 = $9,000
- Revenue from Product C = 200 units * $50 = $10,000
Total revenue = $10,000 (A) + $9,000 (B) + $10,000 (C) = $29,000
| Product | Units sold | Price per unit | Revenue |
| A | 500 | $20 | $10,000 |
| B | 300 | $30 | $9,000 |
| C | 200 | $50 | $10,000 |
| Total revenue | $29,000 |
Example #2. How to calculate SaaS business revenue
A SaaS company offers three subscription tiers: Basic, Standard, and Premium. The subscriber count and monthly pricing for each tier in a month are as follows:
| Subscription plan | Subscribers | Price per month |
| Basic | 100 | $50 |
| Standard | 200 | $90 |
| Premium | 50 | $200 |
The calculation goes as follows:
- Revenue from Basic plan = 100 subscribers * $50 = $5,000
- Revenue from Standard plan = 200 subscribers * $90 = $18,000
- Revenue from Premium plan = 50 subscribers * $200 = $10,000
Total revenue = $5,000 (Basic) + $18,000 (Standard) + $10,000 (Premium) = $33,000
| Subscription plan | Subscribers | Price per month | Revenue |
| Basic | 100 | $50 | $5,000 |
| Standard | 200 | $90 | $18,000 |
| Premium | 50 | $200 | $10,000 |
| Total revenue | $33,000 |
→ Learn more about SaaS industry trends for 2024.
Common mistakes to avoid when calculating revenue
Calculating total revenue might seem straightforward, but several common mistakes can lead to inaccurate figures. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when calculating total revenue:
- Failing to separate operating revenue from non-operating revenue.
- Not accounting for returns, discounts, or allowances, leading to inflated revenue figures.
- Missing some revenue sources or counting the same revenue more than once due to record-keeping errors.
- Mistaking cash received for revenue in accrual accounting.
- Using incorrect or outdated exchange rates for foreign currency transactions.
- Allocating revenue to incorrect time periods, especially in businesses with subscriptions or long-term contracts.
- Not accounting for the costs associated with sales commissions or bonuses.
- Inadequate record-keeping and failure to verify transactions lead to revenue reporting inaccuracies.
How to increase total revenue
1. Expand your customer base
Utilize data-driven marketing campaigns to identify and target potential new customers. Explore untapped markets by analyzing demographics, interests, and behaviors that align with your product or service offerings. Partnerships with complementary businesses can open new customer channels, and expanding into new geographical areas or online marketplaces can significantly increase your customer reach.
2. Increase sales to existing customers
Implement strategies like cross-selling, where you suggest related products or services to customers at the point of sale, or upselling, where you encourage customers to buy a more expensive version of a product or a premium service. Loyalty programs that offer rewards, discounts, or exclusive benefits can motivate repeat purchases and strengthen customer relationships.
3. Introduce new products or services
Invest in research and development to innovate and create new offerings that meet current or emerging needs in your market. Diversification into new product lines or services can also mitigate risks by spreading income sources and tapping into new customer segments.
4. Optimize pricing strategy
Regularly review and adjust your pricing based on competitive analysis, cost, value delivered, and customer willingness to pay. Consider adopting dynamic pricing models for services or products with fluctuating demand, allowing prices to vary based on market conditions, time, or customer profiles.
5. Leverage technology
Automate repetitive sales tasks to increase efficiency and reduce errors.
However, with so many options available, it’s easy to get lost or miss the tool that will cover your needs. If you’re looking for a comprehensive analytics tool that will connect all your sales channels and payment platforms under one hood, consider giving a try to Synder Insights. Synder Insights will provide you with real time access to the data from all your connected platforms on a single dashboard without the need to go to multiple apps to collect it.
The tool will offer you a set of helpful KPI reports spanning the most important metrics for ecommerce businesses, allowing you to track revenue growth (among others) and identify areas for improvement.
The best part is that you won’t have to spend time gathering data and using complex formulas to determine your KPIs. For example, Synder can calculate the total revenue for you! Just open the corresponding report and filter the data by channel or time period. What’s more, you’ll get insights into your customers’ behavior and product performance—all in one place.
Try a 15-day free trial or book a spot on a Weekly Public Demo to check the tool with our specialist. With Synder, you can get the full picture of your business performance and identify opportunities for growth!
→ Find out how data-driven insights can help you grow your business.
6. Focus on high-margin products
Prioritize the promotion and sale of high-margin items. Analyzing your product mix and focusing marketing and sales efforts on the most profitable items can improve overall revenue and profitability.
Conclusion
Calculating total revenue is essential for the success of any small business. By understanding the basics of revenue calculation, avoiding common mistakes, and using automated analytics tools, business owners can optimize their revenue calculations and make informed decisions about the future of their business.
With the right approach and mindset, you can unlock the full potential of your business and achieve financial success.






.png)
