Revenue and income are two critical financial terms often used in accounting and finance to assess a company’s financial health and performance. While they are sometimes used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings and implications for businesses.
Hence, in this article, we’ll show how understanding the differences between revenue and income can help businesses make informed decisions, plan for future growth, and evaluate their overall success.
Revenue vs income: definitions
Revenue and income are two key financial terms. Here’s a brief explanation of each term:
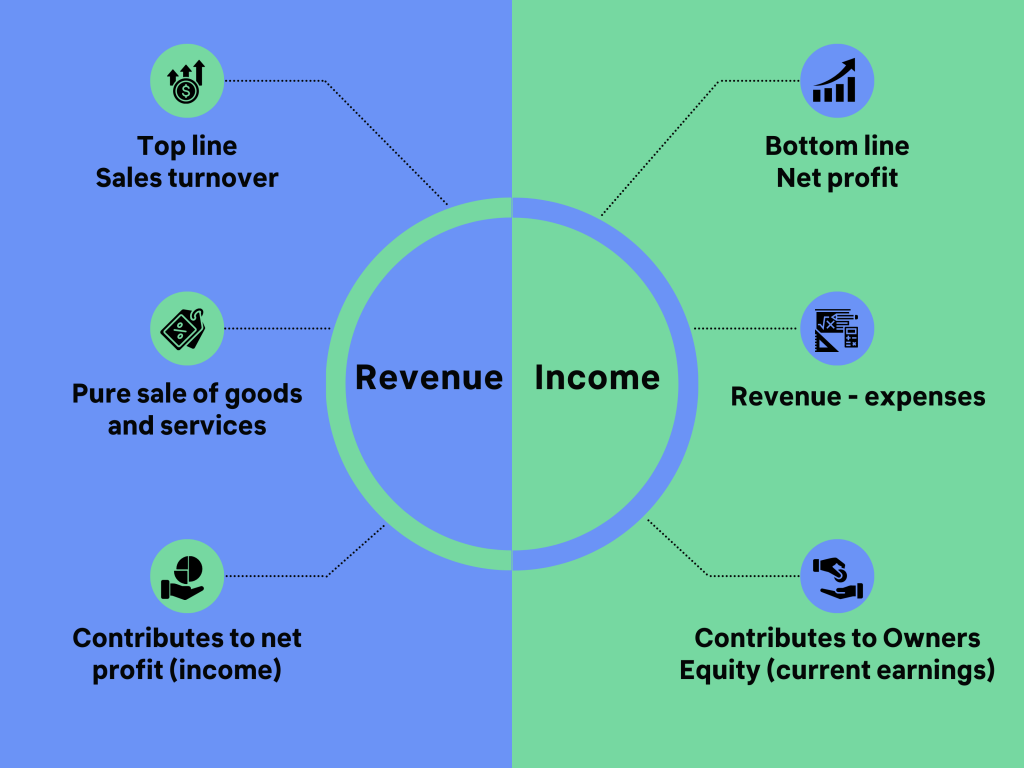
- Revenue, also known as sales or turnover, refers to the total amount of money a company receives from its business activities. This typically includes sales of products and services, as well as other sources like royalties, fees, or investments. Revenue is recorded at the top of an income statement (also known as a profit and loss statement or P&L) and is a gross figure, meaning it is calculated before any expenses or costs are deducted.
- Income usually refers to the company’s net income or profit, which is calculated by subtracting all the expenses and costs from the revenue. Net income is an important financial metric for evaluating a company’s performance and profitability. In an income statement, net income is found at the bottom, after all the expenses, taxes, and other costs have been accounted for.
In the context of personal finance, income refers to the money received by an individual from various sources such as salaries, wages, commissions, investments, rental properties, or other sources.
Are profit and net income the same?
Net income and profit, when discussing the financial health of a business are often used interchangeably, but they can refer to slightly different concepts depending on the context.
Profit is a general term that refers to the financial gain a company or individual makes after deducting all relevant expenses. There are several types of profit, each providing a different level of insight into a company’s financial health including gross profit, operating profit, and net profit.
a. Gross Profit: Gross profit is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from total revenue. This figure shows how much a company makes from its core business operations before considering other expenses, such as taxes, interest, and overhead costs.
b. Operating Profit: Operating profit, also known as operating income, is calculated by subtracting operating expenses (e.g., overhead costs, salaries, rent, and utilities) from gross profit. This figure represents the profit a company generates from its normal business operations, excluding interest and taxes.
c. Net Profit: As mentioned above, net profit is synonymous with net income. This is the final profit a company generates after accounting for all expenses, including interest and taxes.
Net income (or net profit) is a specific type of profit, and it represents the bottom-line figure for a company’s profitability after all expenses have been considered.
How revenue and income feature in business operations
Revenue and income are crucial components of business operations as they help businesses assess their financial health, make informed decisions, and evaluate their overall performance. Here’s how revenue and income feature in various aspects of business operations.
1. Financial statement reporting
Revenue and income are key elements of a company’s financial statements, such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. These statements provide a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health and are used by stakeholders, including investors, lenders, and management, to make decisions related to the business.
2. Performance evaluation
Revenue and income are essential metrics to evaluate a company’s performance over time. By comparing current and historical revenue and income figures, businesses can identify trends, growth rates, and areas where they may need to improve.
3. Budgeting and forecasting
Businesses use revenue and income projections to create budgets and forecasts, helping them set goals, plan for the future, and allocate resources effectively. Accurate revenue and income forecasting can help businesses anticipate potential challenges and opportunities, allowing for better decision-making.
4. Pricing strategy
Understanding revenue and income can help businesses develop pricing strategies that maximize profits while remaining competitive in the market. Analyzing the relationship between revenue, costs, and income can help a company determine the optimal price for its products or services.
5. Cost management
By analyzing revenue and income, businesses can identify areas where they may need to reduce costs or improve efficiency to increase profitability. This can involve renegotiating contracts with suppliers, streamlining operations, or implementing cost-saving technologies.
6. Financing decisions
A company’s revenue and income play a significant role in attracting investors and securing loans. Strong revenue and income figures indicate a healthy and profitable business, making it more likely to receive financing from banks or investors.
7. Tax planning
Revenue and income directly impact a company’s tax obligations. By understanding their revenue and income figures, businesses can engage in tax planning strategies to minimize their tax liabilities while remaining compliant with tax regulations.
8. Benchmarking
Revenue and income can be used as benchmarks to compare a company’s performance against industry peers or competitors. This helps businesses identify areas where they may be underperforming or excelling and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Bottom line
In summary, revenue and income are fundamental to business operations as well as accounting, providing valuable insights into a company’s financial health, performance, and growth potential. Understanding these metrics helps businesses make informed decisions and plan for long-term success.
What business can learn from net income metric?
Businesses can learn valuable insights from the income metric, specifically net income, which is the amount remaining after all expenses, taxes, and costs are subtracted from the revenue. Analyzing net income can help a company understand its profitability, efficiency, and overall financial performance. Here are some key insights businesses can glean from the income metric.
1. Profitability
Net income is a primary indicator of a company’s profitability. A positive net income means the business is generating profits, while a negative net income indicates losses. Businesses can use this metric to gauge their success, monitor their progress, and make informed decisions about strategy and growth.
2. Efficiency
Comparing net income to revenue helps businesses determine their efficiency in converting sales into profits. A higher net income relative to revenue indicates a more efficient operation, whereas a lower net income may signal inefficiencies in cost management, pricing, or operations.
3. Financial health
A consistent or growing net income is a sign of a healthy business, as it demonstrates the company’s ability to generate profits, cover expenses, and reinvest in growth. On the other hand, declining or negative net income may indicate financial difficulties or poor performance, warranting further investigation and corrective action.
4. Performance evaluation
By analyzing company income over time or comparing it to industry benchmarks, businesses can evaluate their performance and identify trends, strengths, and weaknesses. This information can be used to adjust strategies, set goals, and allocate resources effectively.
5. Investor attractiveness
A strong net income can make a business more attractive to investors, as it indicates a higher likelihood of generating returns on investment. A company with a healthy net income may find it easier to secure financing, attract equity investments, or go public through an initial public offering (IPO).
6. Cost management
Net income helps businesses identify areas where they may need to improve cost management, such as reducing operating expenses, renegotiating supplier contracts, or optimizing pricing strategies. By addressing these issues, businesses can enhance their profitability and financial performance.
7. Decision-making
A thorough understanding of net income can inform a wide range of business decisions, from expansion and investment to mergers and acquisitions. By considering the potential impact on net income, businesses can make more informed choices that support their long-term objectives.
What business can learn from revenue value?
Analyzing the revenue metric can provide valuable insights into various aspects of a business’s operations, market position, and growth potential. Here’s what businesses can learn from the company revenue.
1. Sales performance
Revenue is a direct reflection of a company’s sales performance. By monitoring revenue over time, businesses can identify trends, seasonality, and the effectiveness of their sales and marketing efforts. This can help them adjust their strategies to boost sales and revenue.
2. Market demand
Revenue can give businesses an indication of market demand for their products or services. An increase in revenue may signify growing demand, while a decline could suggest a decrease in demand or increased competition. Understanding market demand helps businesses adjust their offerings, pricing strategies, and marketing efforts.
3. Market share
By comparing their revenue to that of competitors or the overall industry, businesses can estimate their market share. This can help them understand their position within the market and identify areas where they may need to improve or expand their market share.
4. Growth potential
Revenue growth is a key indicator of a company’s growth potential. Consistent revenue growth may suggest a sustainable business model, strong market position, or effective sales and marketing strategies. This information can be used to inform decisions about expansion, investments, and long-term planning.
5. Pricing strategy
Analyzing revenue in relation to sales volume can help businesses evaluate their pricing strategy. If revenue is growing at a slower rate than sales volume, it may indicate that the company’s pricing is too low, or it is offering excessive discounts. Conversely, if revenue growth outpaces sales volume growth, it could signal an effective pricing strategy or strong demand for the company’s products or services.
6. Customer retention and acquisition
Changes in revenue can provide insights into customer retention and acquisition efforts. An increase in revenue may indicate that the business is successfully acquiring new customers or retaining existing ones, while a decrease could signify customer attrition or reduced spending from existing customers.
7. Product or service mix
Analyzing revenue by product or service category can help businesses understand which offerings are most popular and profitable. This information can be used to refine product or service offerings, allocate resources more effectively, and prioritize marketing efforts.
8. Cash flow management
Revenue is a crucial component of cash flow management, as it directly affects a company’s ability to cover expenses, make investments, and meet financial obligations. Monitoring revenue can help businesses anticipate potential cash flow challenges and take appropriate action to maintain financial stability.
Learn more about e-commerce sales revenue.
Revenue and income: closing thoughts
Revenue and income are both essential financial metrics that provide valuable insights into a company’s financial health and performance. By analyzing and understanding both revenue and income, businesses can make strategic decisions, manage resources effectively, and monitor their performance to ensure long-term success.

%20(1).png)





Thanks for sharing your valuable insights on revenue v/s income! Revenue is the total amount generated from sales, while income is what’s left after deducting all costs. Keep sharing.
Distinguishing between revenue and income is crucial for financial clarity. Revenue reflects total earnings before expenses, while income is what remains after costs. Understanding this disparity aids businesses in effective financial management and growth planning.
Thank you Mellisa for your comment!