Although “profit” and “profitability “ are two terms that are often used interchangeably, they refer to different accounting concepts. Both profit and profitability are accounting metrics used to analyze a company’s financial success, but there are distinct differences.
This article will examine profit and profitability in detail to understand their differences and how each influences the day-to-day operations of a business.
Contents:
3. Income tax
6. Critical metrics for assessing profitability
7. Key takeaways: Profitability vs. profit
8. Strategies for improving profit and profitability
9. Most profitable companies in 2025
10. Most profitable business opportunities in 2025
Understanding profit
Profit is the money all businesses get after taking into account all of their business expenses. It doesn’t matter if it’s a lemonade stand in your neighborhood or a multi-million dollar publicly traded company; both of these companies aim to earn money. Therefore, a business’s performance is based on its profit in its various forms.
There exist three significant types of profit – gross profit, operating profit, and net profit. Each profit type provides business analysts with in-depth information about a company’s performance, particularly when comparing their business to their competitors.

Components of profit
Companies calculate profit by considering revenue, expenses, and, most importantly, net income. Here’s a detailed look into each of them.
Revenue
Revenue, also known as income, is the money a company earns within a period of time from operational activities such as selling products or obtaining credit. If a company selling $25 pairs of jeans sells 100 units of them in three months, then their quarterly income is $2500.
We can group revenue into two types:
- Operating revenue: sales from a company’s core business;
- Non-operating revenue: derived from secondary sources.
So, if that same jean-selling company made $2500, they made $2500 in operating revenue. But if they sublet a floor of their factory, they’d also earn non-operating passive income (revenue).
Expenses
Expense is the opposite of revenue. It’s the amount of money that an individual or a business spends in order to do something. If we stick to the jean-selling company example, the cost of materials to make the jeans and the money to pay employees to make the jeans would be classified as the company’s expenses.
There are two main types of expenses:
- Operating expenses: the expenses related to the company’s regular activities, like the cost of goods sold, administrative fees, office supplies, direct labor, and rent.
These are the expenses that are incurred from normal, day-to-day activities.
Companies always try to manage their operating expenses to guarantee that they maximize profits. They usually do this by keeping expenses at a minimum.
- Non-operating expenses: they’re not directly related to the business’s core operations. Common examples include interest charges and other costs associated with borrowing money.
These are expenses that happen outside of a company’s day-to-day activities. These costs may occur from restructuring, reorganizing, interest charges, or debt.
Examples of expenses include but aren’t limited to rent, utilities (electricity, water, etc.), wages, salaries, maintenance, depreciation, insurance, and other costs. Expenses are usually regular payments that are necessary to operate a business.
Net income
Net income, also called net profit, is the last component of profit. Net income is the money a company has left after subtracting expenses and financial losses from its income and profits in one accounting period.
Net income is one of the main factors determining the profitability of a business. It shows how effectively a company can balance its operating costs with the money they earn.

Income tax
In the U.S.A., the current corporate tax rate on profits is 21%, reduced from 35% since the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. The corporate income tax is the third-largest source of federal revenue. However, it’s significantly smaller than the individual income tax and payroll taxes.
Defining profitability
Now that we’ve covered profit, its main components, and how it’s taxed in the U.S.A., let’s move on to profitability. In essence, profitability refers to the extent to which a company earns a profit.
Profitability is a metric of how effective a company is. Profitability is the thing that tells key stakeholders if a company can sustain its competitive position in the market and continue to grow.

Determining profitability
Many factors come into play when determining the profitability of any company. Here are some of the most critical factors that affect a company’s profitability.
Expenses
Expenses can really harm a company’s profits. A company can never be profitable if it regularly spends large amounts of money on products and services that don’t bring in profit. That’s why many companies periodically review their expense sheets to determine where costs can be minimized or eliminated.
Demand
Customer demand is a vital factor in how successful a company is. No matter how good your product or service may be, if customers aren’t looking for it, your company won’t make it. Knowing what consumers want and producing those products and services can help companies achieve profits. The more sales a company makes, the more profitable it becomes.
Productivity
Just like in our personal lives, our productivity determines our success. Productivity can help keep companies afloat. However, it doesn’t mean you have to spend more to be more profitable. In fact, it could be the opposite. Businesses can accomplish this by improving their daily operations and increasing manufacturing.
Competition
Competition is arguably the only factor of profitability that a company can’t control. If there are many companies within the same niche industry, they’ll always be competing, and the one whose products or services are better or cheaper will win in terms of profits.
Critical metrics for assessing profitability
Here are the metrics essential stakeholders, like managers, analysts, and investors, use to determine if a business can earn income relative to its revenue, assets, and expenses.
Profit margin ratio
The profit margin measures a company’s profitability as a percentage of the total revenue it keeps as a profit. In simple terms, the profit margin describes the percentage of total sales that a company retains as a profit. Profit margins come in various forms, such as gross and net profit margins.

Return on assets (ROA)
Return on assets expresses a company’s profitability compared to its total assets. Basically, it highlights how well a company can generate a profit relative to its asset base.
Divide the company’s net income by its total assets to calculate ROA. A high ROA tells us that a company is more efficient and productive at managing its balance sheet to generate profits, while a low ROA shows that there’s room for improvement.

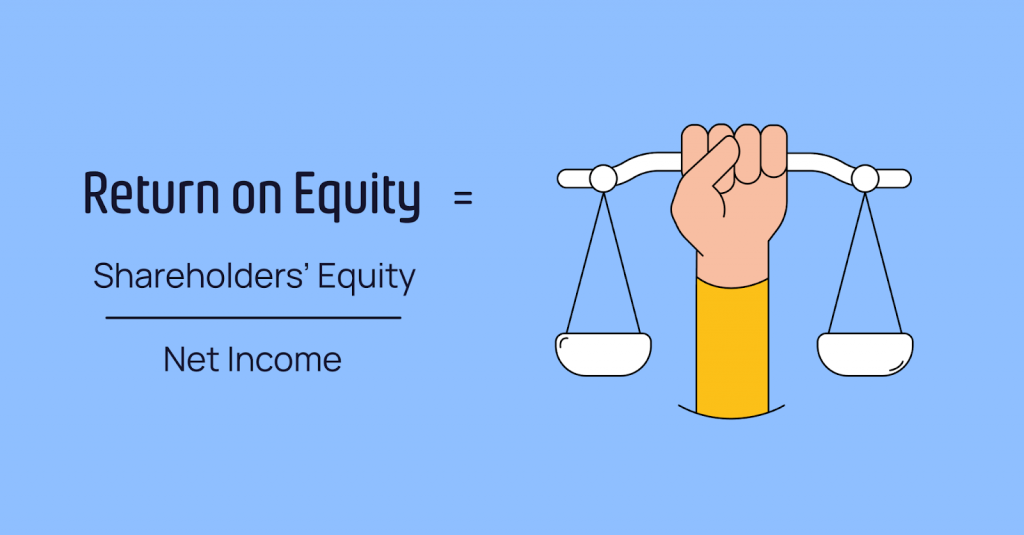
Return on equity (ROE)
Return on equity allows stakeholders to understand how profitable a company is based on its ability to earn a profit. Like with the ROA, a high return on equity indicates that a company’s management works efficiently, generating adequate income and growth through its equity financing.
A company’s return on equity is calculated by dividing net income by shareholders’ equity. Since the shareholders’ equity equals the company’s assets minus its debt, the return on equity is considered the return on net assets.
Key takeaways: Profitability vs. profit
- Profitability: a financial metric that companies use to determine how successful they are. This is a relative measurement and is normally expressed as a ratio.
Profitability is determined by looking at a company’s expenses, the demand for its product of service, how productive the company is, and how competitive is the market that the company is in. - Profit: an absolute measurement of all the money businesses receive after taking into account all of their business expenses.
Profit is made up of components such as the company’s revenue, its total expenses, and its net income.
Strategies for improving profit and profitability
Most companies aim to improve their efficiency and profitability in today’s ever-more competitive market.
If businesses want to boost both their profit and profitability, they can employ a number of strategies that focus on maximizing revenue, minimizing expenses, and maximizing operational efficiency.
Cost reduction techniques
Businesses should meticulously analyze expenses throughout all of their daily operations. This way, the business can figure out areas of inefficiency and try out methods to minimize unnecessary expenses.
Companies can achieve this by renegotiating contracts with suppliers for better terms, streamlining production processes to eliminate waste, or adopting new technologies to reduce labor costs.
Moreover, performing regular audits to identify and eliminate redundant expenses can significantly improve the bottom line while enhancing a company’s overall profitability.
Revenue enhancement strategies
Another strategy for increasing profit and profitability lies in revenue enhancement strategies. These strategies involve researching chances to increase sales and revenue streams without proportionately increasing expenses.
Companies can do this by diversifying their product or service offerings to cater to evolving consumer demands, as well as venturing into new markets or demographics or launching targeted marketing campaigns to attract new customers and retain the old ones.
What’s more, fostering customer loyalty through high-quality service, personalized experiences, and rewards programs might lead to repeat business and higher customer lifetime value, thereby bolstering overall profitability.
Efficiency improvements
Last but not least, optimizing operational efficiency is of vital importance for improving the profit and profitability of a business. By identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and redundancies within day-to-day processes, companies can streamline operations and dedicate resources better.
This could mean investing in technology solutions that better workflow automation, trying out lean methodologies to minimize waste and maximize productivity, or enabling your workers with training and resources to perform their roles more efficiently.
Most profitable companies in 2025
After talking about profitability in theory, let’s look at the companies that are successfully maintaining their profitability in practice. Here are the top five most profitable companies in the world in 2025, ranked by earnings:
- Saudi Aramco ($247.43 billion in earnings) – the Saudi Arabian national petroleum and natural gas company. The company brings in huge profits for the Saudis – mainly because Arabian oil is incredibly cheap to pump out of the ground;
- Apple ($117.66 billion in earnings) – an American hardware and software developer and technology company that develops and sells consumer electronics as well as operating systems and application software. Their profit margin size depends on their premium prices, ability to create high-quality, innovative products, and diversification of revenue streams;
- Berkshire Hathaway ($100.30 billion in earnings) – an American holding company whose conglomerate includes over 80 companies with activities spanning a wide range of business areas. The company’s success can be attributed to the fact that it owns many insurance companies, which generates a lot of cash that Berkshire Hathaway can invest in long-term assets;
- Microsoft ($95.02 billion in earnings) – an American company that develops and distributes software and services. Microsoft’s profits lie in their main function – Microsoft provides cloud resources and a wide range of software to many businesses worldwide;
- Alphabet (Google) ($78.78 billion in earnings) – an American holding company of the former Google LLC, which continues to exist as a subsidiary. Alphabet’s success depends on the ad market, as advertising revenue makes up 76% of Alphabet’s total revenue;
Most profitable business opportunities in 2025
Starting a new business won’t ever come with a guarantee for profit or profitability, but there are some business ideas that experts believe will thrive in the future, ensuring that you enjoy large profit margins.
Here are some of the most profitable business opportunities in 2025, according to Forbes:
A cupcake business
According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the cake market is estimated to be worth around $83.07 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach $97.85 billion by 2029. That is a CAGR growth of 3.33% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
Sports memorabilia
Market Decipher, a market research and consultancy firm, produced a report estimating that the sports memorabilia market is currently valued at $26.1 billion. It’s expected to reach $227.2 billion by 2032, up from $26.1 billion in 2021. This would mean that it’s growing at a CAGR of 21.8% from 2022 to 2032.
A bridal shop
According to Maximize Market Research, a market research and business consulting firm, the bridal wear industry was worth $11.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow to $17.4 billion in 2029. That’s a CAGR growth of 6.6% from 2022 to 2029.
Food truck business
According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the food truck industry is worth $4.15 billion in 2024 and is estimated to reach $6.87 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 6.5% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
The party rental industry
The party supply rental services provide all the necessary resources for a particular party or event, like seating, decorations, audio equipment, etc.
The party rental market size was estimated at $14.20 billion in 2023 and $16.30 billion in 2024. The industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of 14.90% to reach USD 37.54 billion by 2030.
Key takeaways
In conclusion, while profit and profitability are both equally important accounting metrics for a business, they showcase different aspects of the business’s success.
Profit is the money a company makes by selling its products or services, and profitability is the company’s ability to generate profit from the money it receives.
Profitability is determined by a company’s overall expenses, demand for their product or service, productivity of the employees, and competition within a given industry. When assessing the profitability of a company, metrics like the profit margin, return on assets, and return on equity are the most important.
It’s important to know profit and profitability for a business because they provide crucial insights into its financial health, performance, and overall success.






