Today, business finances are as intricate as never before, especially when we speak about online businesses. Handling large volumes of transactions can be complex and information flows rapidly, which impacts the maintenance of financial integrity. This is where forensic accountants step in, armed with a unique set of skills to detect, prevent, and address financial irregularities.
In this article, we’ll delve into what is forensic accounting and uncover the essential role it plays in safeguarding financial systems.
Understanding the concept of forensic accounting
Forensic accounting serves as a vital bridge between finance and investigation. In a nutshell, it’s about applying financial expertise and analytical skills to untangle complex financial situations and uncover potential wrongdoing.
Unlike traditional accounting, which centers on keeping financial records accurate and orderly, forensic accounting dives deep into the numbers to detect irregularities, discrepancies, and signs of fraud. It involves careful financial data analysis, examination of documents, and a keen eye for patterns that might not be immediately apparent.
When does it come to play?
Forensic accountants often work on cases involving financial disputes, fraud investigations, and legal proceedings. They use their skills to reconstruct events, quantify damages, and provide expert testimony in court. Behind their work is a multidisciplinary approach that blends financial knowledge, investigative techniques, and legal understanding, allowing them to piece together puzzles that could have significant legal and financial implications.
Financial accountants are specialists at unraveling financial and compliance puzzles for businesses, so they also come to help when companies fail (or nrglect) at properly bookkeeping and accounting for their business finances and need to figure out where their numbers don’t add up.
Maintaining accurate accounting records is a cornerstone of financial success for any business. Precise and up-to-date accounting ensures the seamless reconciliation of accounts and paves the way for accurate financial reporting, stress-free tax reporting, and effective decision-making. By keeping a vigilant eye on financial transactions, businesses can avoid errors, discrepancies, and the need for intervention by forensic accountants.
Synder, tailored for online businesses of any size, allies them in their pursuit of accuracy. By automating and streamlining accounting processes, Synder minimizes the chances of human error and data inconsistencies. With features like automated data synchronization, expense categorization, and real-time tracking of transactions, Synder ensures that financial records remain precise and consistent. Synder gives businesses reliable tools to manage their finances accurately, empowering them to focus on growth and strategic initiatives while reducing the likelihood of encountering financial discrepancies.
If you believe Synder might be a solution for your business, feel free to book your seat at our free webinar to have your questions answered or sign up for a free trial to explore Synder yourself.
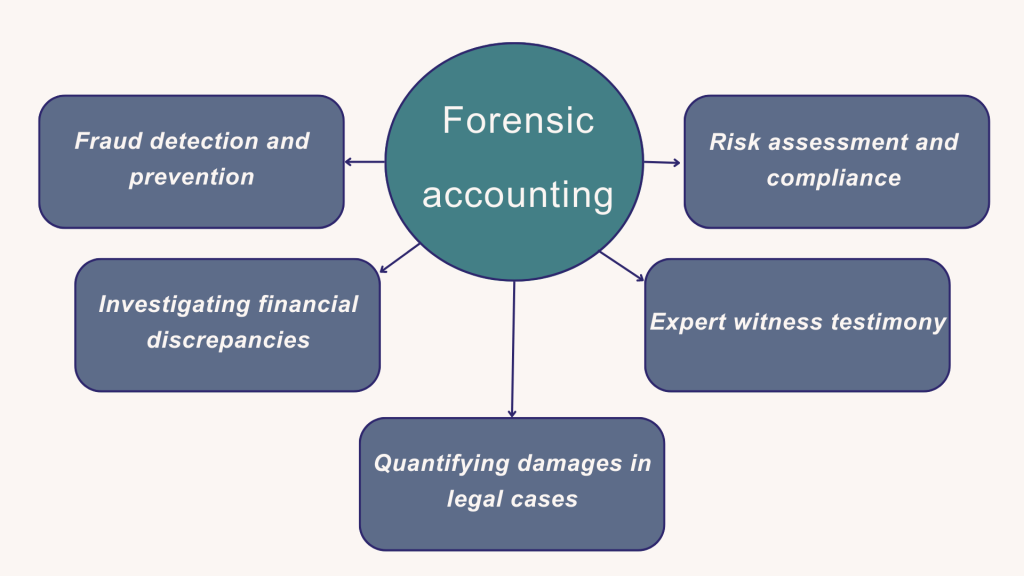
Key responsibilities of a forensic accountant
Let’s look at the typical responsibilities of a forensic accountant in more detail.
Fraud detection and prevention
Forensic accountants operate as careful financial detectives, equipped with a keen eye for detail. Their primary role is to carefully comb through financial records, analyzing transactions and data. This process involves identifying anomalies, patterns, and inconsistencies that could be red flags for potential fraud.
By scrutinizing financial statements, ledgers, and transaction records, they unveil discrepancies that might otherwise go unnoticed. This approach enables them to expose a range of fraudulent activities, from embezzlement and asset misappropriation to the manipulation of financial statements for personal gain or to deceive stakeholders.
Investigating financial discrepancies
Numbers that don’t align often indicate more than just mathematical errors. Forensic accountants are skilled at deciphering the stories behind these discrepancies. A forensic accountant analyzes financial data and other information regarding an investigation, carefully tracing the flow of money to detect irregularities that might signify foul play. This process involves carefully comparing records, analyzing transaction trails, and seeking out inconsistencies that could point to fraudulent activities.
When dealing with suspected financial misconduct, forensic accountants embark on a trail-blazing journey to gather evidence, often collaborating closely with law enforcement agencies. Their ability to reconstruct financial events is crucial in bringing hidden irregularities to light, aiding in the pursuit of justice.
Quantifying damages in legal cases
One of the distinctive skills that forensic accountants possess is the ability to put a financial value on damages. In legal disputes, they become financial quantifiers, calculating economic losses, determining lost profits, and assessing the overall value of businesses affected by disputes.
This role is particularly significant in courtrooms, where forensic accountants present their findings in an understandable manner. Their task involves translating complex financial information into clear, comprehensible language that judges, juries, and legal professionals can grasp. This bridging of the financial-linguistic gap is crucial in helping legal proceedings comprehend the monetary implications of cases, contributing to fair and informed judgments.
Expert witness testimony
Communicating complex financial concepts effectively is no small feat, especially in a legal context. Forensic accountants excel as interpreters, converting intricate financial jargon into plain, understandable language.
As expert witnesses, they assist judges, juries, and legal professionals in comprehending the financial intricacies of a case. Their role involves explaining how financial transactions, discrepancies, and irregularities relate to legal claims or disputes. This ensures that financial evidence is presented accurately, enabling a more informed legal decision-making process.
Risk assessment and compliance
Forensic accountants play a proactive role in ensuring financial integrity. Beyond detection and investigation, they engage in risk assessment and compliance endeavors. By evaluating an organization’s financial systems, policies, and controls, they identify vulnerabilities that could potentially be exploited for financial misconduct.
This assessment informs the design and implementation of internal controls, policies, and procedures that minimize the risk of future financial irregularities. By taking preventive measures, forensic accountants contribute to the establishment of a robust financial environment that upholds transparency, accountability, and ethical conduct.
Forensic accounting tools and techniques
With all the above in mind, it’s pretty obvious that the job forensic accountants do involve the application of specialized knowledge and investigative skills possessed by CPAs. But that’s not it. They also utilize certain techniques and protocols to deal with analysis and investigation, and it’s quite unlikely that they do their job, like, manually. So, let’s sneak a peek into the forensic accounting toolset.
- Data analysis and forensic technology
Forensic accountants employ sophisticated data analytics tools to detect unusual patterns, trends, and outliers in financial data. They also leverage technology to retrieve and analyze electronic evidence, such as emails and electronic transactions. - Interviewing and interrogation skills
Beyond numbers, effective communication is crucial. Forensic accountants conduct interviews and interrogations, gathering information from individuals involved in financial matters. - Document examination
Forgery and altered records are common tactics in financial fraud. Forensic accountants meticulously examine documents to detect signs of manipulation, utilizing handwriting analysis and document authentication techniques.
Choosing the certified forensic accounting career: forensic accounting qualifications and training
Embarking on a career in accounting can be an exciting journey, and within the realm of numbers and financial analysis, one intriguing path is that of a forensic accountant. This role combines financial expertise with investigative prowess to uncover financial discrepancies and potentially fraudulent activities. If you’re considering delving into the world of forensic accounting, understanding the qualifications and training required is essential.
Formal education – setting up the foundation of expertise
The journey into forensic accounting often begins with a solid educational foundation. A bachelor’s degree in accounting, finance, or a related field serves as the starting point. Building upon this, pursuing a master’s degree in forensic accounting or a similar specialization can provide in-depth knowledge of financial investigation techniques, fraud prevention strategies, and legal aspects that play a crucial role in this field.
Social work – collaborating for clarity
Effective forensic accountants are more than just financial analysts. They are collaborators, often working closely with legal teams, law enforcement, and other stakeholders to uncover financial irregularities. This collaborative aspect can be likened to a form of social work, where effective communication, teamwork, and the ability to navigate intricate relationships are key.
Acquiring professional certifications – AICPA and CFE credentials
Gaining recognition as a qualified forensic accountant involves obtaining professional credentials that validate your expertise. The Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE) offers the Certified Fraud Examiner (CFE) credential, a mark of excellence in the field. This certification underscores your commitment to fraud prevention and detection. It demonstrates that you possess the knowledge and skills required to identify fraudulent activities and effectively contribute to legal investigations.
Additionally, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) provides specialized training and resources in forensic accounting, enhancing your professional competence and broadening your skill set.
Practical experience – bridging the gap
While formal education provides the foundation, practical experience solidifies your competence. Gaining hands-on exposure through internships, entry-level positions, or collaborations with experienced professionals sharpens your investigative skills and deepens your understanding of real-world financial scenarios. Social work, communication, and collaboration skills also come into play, as forensic accountants often work closely with legal teams, law enforcement agencies, and other stakeholders in uncovering financial discrepancies.
Real-life forensic accounting examples
Interested in how forensic accounting applies in real life? Let’s dive into the history of financial fraud and see how forensic accountants helped get through the hassle and find out the truth. You might’ve heard about some of these financial scandals that lead to millions of dollars lost, as well as reputations and trust. If not for forensic accountants that managed to discover and disclose financial misconduct on time, the consequences could be much worse, affecting even more people.
Waste Management accounting scandal (1998)
In the late 1990s, the Waste Management scandal rocked the business world as one of the earliest and most significant instances of corporate accounting fraud. Waste Management, a waste disposal company, was involved in a scheme to artificially inflate its earnings and present a healthier financial picture to shareholders and regulators. The company resorted to improper accounting practices that falsely enhanced its financial performance, leading to substantial repercussions for its stakeholders.
Forensic accountants, armed with their analytical skills and financial expertise, delved into the company’s financial statements and records. Their scrutiny revealed a series of irregularities that included the improper capitalization of expenses and the manipulation of reserves. These deceptive tactics effectively masked the true financial health of the company, painting a picture of profitability that was far from accurate. The work of forensic accountants was pivotal in uncovering the fraudulent activities that had misled investors and regulators.
Enron scandal (2001)
The Enron scandal stands as a watershed moment in the world of corporate fraud. Once a renowned energy company, Enron’s meteoric rise was marred by a web of deceit that involved intricate financial manipulation. Forensic accountants took center stage in exposing the layers of falsehood that had been carefully crafted within the company.
At the heart of the scandal were off-balance-sheet transactions, a mechanism used to hide debt and artificially boost profits. These transactions allowed Enron to present a much rosier financial picture than reality dictated. The meticulous analysis conducted by forensic accountants unveiled the complex web of partnerships and shell companies Enron had established to carry out these deceptive practices. Through careful examination of financial statements, ledgers, and transactions, forensic accountants pieced together the puzzle of financial deception.
The impact of their work was profound. Their relentless pursuit of truth shattered the facade of Enron’s success and exposed the stark reality of its financial woes. As the truth emerged, investor confidence crumbled, and the company’s stock price plummeted. The revelations triggered a chain reaction that led to Enron’s bankruptcy, causing significant financial losses for shareholders, employees, and pension funds. The Enron scandal showcased the vital role of forensic accountants in unearthing complex financial fraud, ultimately serving as a cautionary tale about the importance of transparency, accountability, and ethical financial practices.
HealthSouth fraud (2003)
In one of the largest accounting scandals in the healthcare industry, HealthSouth, a prominent healthcare services provider, found itself entangled in a web of deception. The company orchestrated a massive accounting fraud that artificially inflated its earnings by billions of dollars, leading investors and regulators astray.
Forensic accountants took center stage in uncovering this intricate scheme. Armed with their analytical acumen, they meticulously sifted through a labyrinth of documents, transactions, and ledgers. Their goal was to trace the financial footprints left behind by the fraudulent activities. Their examination uncovered a trail of fictitious entries and fabricated invoices that had been cleverly designed to distort the company’s financial reality.
With a precise attention to detail, forensic accountants unraveled the threads of this complex scheme. They pinpointed instances of improper financial reporting that had systematically misrepresented HealthSouth’s financial health. As their analysis progressed, the true extent of the fraud became clear, revealing an orchestrated effort to inflate earnings and give a false impression of the company’s financial prowess.
Ultimately, the revelations brought about a reckoning for HealthSouth. The forensic accountants’ work provided the evidence needed to substantiate claims of financial misconduct, paving the way for legal action and regulatory intervention.
WorldCom accounting mischief (2002)
In one of the most significant corporate scandals of its time, WorldCom, a telecommunications giant, was exposed for engaging in massive accounting fraud. Forensic accountants took center stage as they meticulously dissected the company’s financial statements. Through a methodical analysis, they unveiled a series of improper accounting entries that had the effect of inflating reported profits while obscuring actual expenses.
Read morea about double-entry in accounting.
At the heart of the deception were entries that shifted regular operating costs, such as line maintenance expenses, into capital expenditure accounts. By doing so, the company artificially boosted its bottom line and created the illusion of financial health. This intricate manipulation of financial data spanned billions of dollars, painting a deceptive picture to investors and regulators alike.
The WorldCom case served as a stark reminder of the critical role forensic accountants play in safeguarding financial transparency and accuracy.
Bernie Madoff ponzi scheme (2008)
Bernie Madoff’s Ponzi scheme stands as one of the most staggering financial frauds ever witnessed. Madoff lured investors with the promise of remarkably high returns, all while maintaining an elaborate illusion. Forensic accountants, armed with their analytical acumen, embarked on an arduous journey to unravel the intricate web of deceit.
As financial detectives, these experts meticulously traced the convoluted flow of funds within Madoff’s labyrinthine financial empire. Every transaction, every record was subjected to careful scrutiny. Their methodical analysis revealed glaring inconsistencies and irregularities that raised serious suspicions. Uncovering this fraudulent tapestry was like putting together a puzzle with deceptive pieces. Through their relentless efforts, forensic accountants managed to peel away the layers of deception, exposing a colossal Ponzi scheme that had duped investors of billions of dollars.
The impact of their work was blasting. Their findings not only shattered the facade of Madoff’s purported investment success but also paved the way for his eventual arrest and subsequent conviction. The case sent shockwaves through the financial world, serving as a stark reminder of the importance of forensic accounting in safeguarding investors and preserving the integrity of the financial landscape.
Lehman Brothers bankruptcy (2008)
The collapse of Lehman Brothers marked a pivotal moment in the global financial crisis, sending shockwaves through the financial industry. As one of the largest investment banks, Lehman Brothers’ bankruptcy exposed the vulnerabilities within the financial system.
Forensic accountants played a crucial role in investigating the circumstances leading to the collapse. They delved into the company’s intricate financial transactions, meticulously analyzing complex financial instruments and derivative products. Their work went beyond the surface-level numbers, aiming to unveil the underlying truth behind Lehman’s financial health.
Through careful scrutiny of the financial statements and records, forensic accountants uncovered questionable accounting practices. These practices involved creative accounting techniques that allowed the firm to present a more favorable financial position than was accurate. They identified the manipulation of certain financial instruments to mask the true extent of liabilities and risks.
The forensic accountants’ findings shed light on the company’s deteriorating financial condition, revealing the significant impact of these practices on Lehman Brothers’ downfall. This revelation contributed to a deeper understanding of the financial crisis and highlighted the need for greater transparency and accountability in the financial industry.
Bottom line
As you can see, forensic accountants are financial watchdogs, upholding the integrity of financial systems. By mixing the accounting and analytical skills to investigate financial transactions of a person or business, they uncover hidden truths within numbers, presenting them in courts and boardrooms alike. In a world where transparency and accountability are paramount, their expertise shines brightly, ensuring that financial discrepancies are exposed and justice prevails. As financial landscapes grow more intricate, the demand for skilled forensic accountants continues to rise, highlighting the crucial role they play in maintaining the sanctity of modern finance.
Want to learn more? Read about articles about How far back can IRS audit and What is GAAP in accounting.







Forensic accounting is the application of accounting principles and investigative skills to examine financial information for evidence of fraud or other wrongdoing. Forensic accountants use their skills to gather and analyze evidence, identify financial irregularities, and develop expert opinions. I really appreciate the insights you provided in your blog. Thank you for sharing this valuable information.
Thanks, Tarhib! Appreciate your comment.