Planning an acquisition of a business or undergoing the merger process? Get ready to face tons of challenges connected with assets, liabilities, and ownership interests. But there’s a way to avoid these challenges with ease – implementing ASC 805.
Understanding ASC 805 will be useful not only to an accountant, auditor or financial analyst, but also to everyone involved in the business merger process. So let’s explore ASC 805 and its role in business combinations.
Contents:
3. Accounting for ASC 805: Acquisition method
4. How automation software helps with meeting ASC 805 requirements
5. ASC 805 and tax implications
Key takeaways
- ASC 805 guides companies through mergers by providing clear financial instructions.
- Understanding ASC 805 is crucial for professionals involved in mergers to manage complexities effectively.
- ASC 805 outlines key principles, including the recognition, measurement, and disclosure requirements.
What is ASC 805?
ASC 805 is a set of rules created by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) that helps companies understand how to handle financial issues when merging or acquiring another business. It sets out the steps to recognize and measure the assets, liabilities and any non-controlling interests involved in the acquisition. Essentially, it provides guidance on how companies should account for these transactions in their financial statements.
What are business combinations?
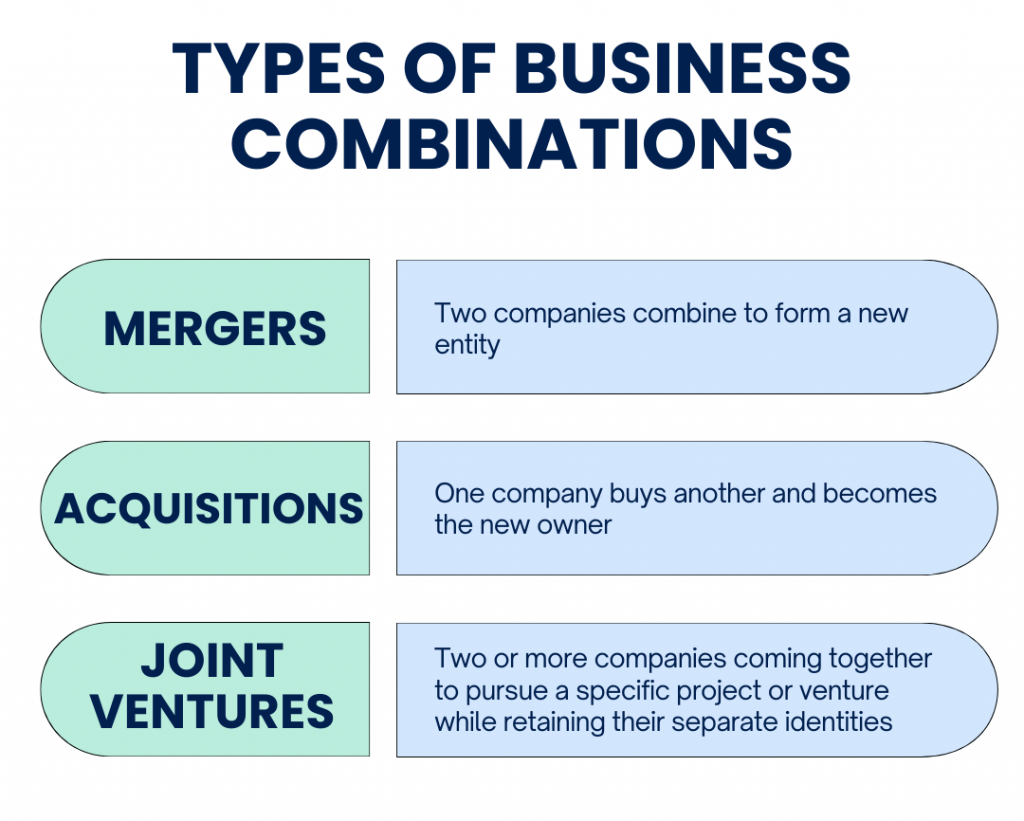
Business combinations occur when one company takes control of another business through activities like:
- Mergers: Two companies combine to form a new entity. An example is the merger between Disney and Pixar in 2006, where Disney acquired Pixar and integrated it into its operations to strengthen its animation capabilities.
- Acquisitions: One company buys another and becomes the new owner. It’s like when Facebook acquired Instagram in 2012 to expand its social media portfolio and reach a larger audience.
- Joint ventures: Two or more companies coming together to pursue a specific project or venture while retaining their separate identities. For instance, the partnership between Toyota and Mazda to build a new manufacturing plant in the United States, where both companies collaborate to share resources and expertise in the automotive industry.
These combinations can happen for various reasons, like expanding into new markets or achieving cost savings through synergies. They’re significant events that require careful consideration and proper accounting treatment to accurately reflect their impact on financial statements and performance.
Importance of ASC 805 in business combination
ASC 805 is important for business combinations because it gives companies a structured way to manage the financial side of a merger or acquisition. This helps everyone involved, including investors and regulators, understand the financial implications of these transactions.
Following ASC 805 promotes transparency and consistency, which builds trust among stakeholders.
Key principles of ASC 805
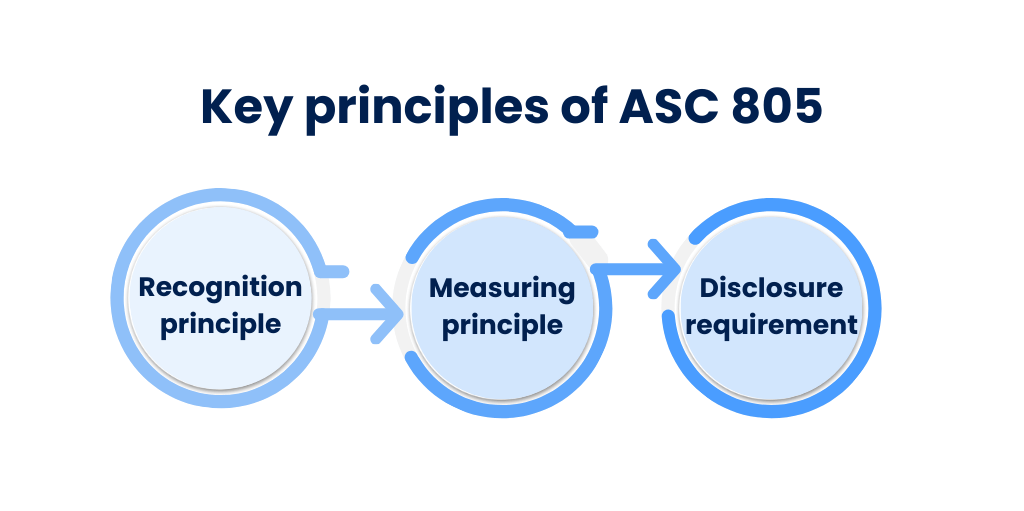
Recognition principle
- This principle guides companies in documenting assets, liabilities, and non-controlling interests acquired during a business combination.
- It emphasizes accurately measuring these items at their fair value when the acquisition happens.
Think of it like putting together a puzzle during a merger or acquisition. ASC 805 ensures that every part is carefully documented.
Measuring principle
- ASC 805’s measuring principle helps companies determine the value of assets acquired in a business combination.
- It suggests using fair value, which is the amount received from selling an asset or paying off a liability in a typical market deal, for assessment.
In simple terms, companies need to accurately assess the value of what they’re getting when they team up with another entity.
Disclosure requirement
- ASC 805 requires companies to make disclosures to promote transparency and understanding of how a business combination affects their finances.
- These disclosures provide important details about the combination, such as the companies involved, timing, financial division, and potential risks or benefits.
It’s like pulling back the curtain to show stakeholders what’s really going on behind the scenes of a merger or acquisition.
Accounting for ASC 805: Acquisition method
When businesses merge or are acquired, they need to follow specific accounting rules, and the most common accounting method used worldwide is the acquisition method.
How the acquisition method of accounting works
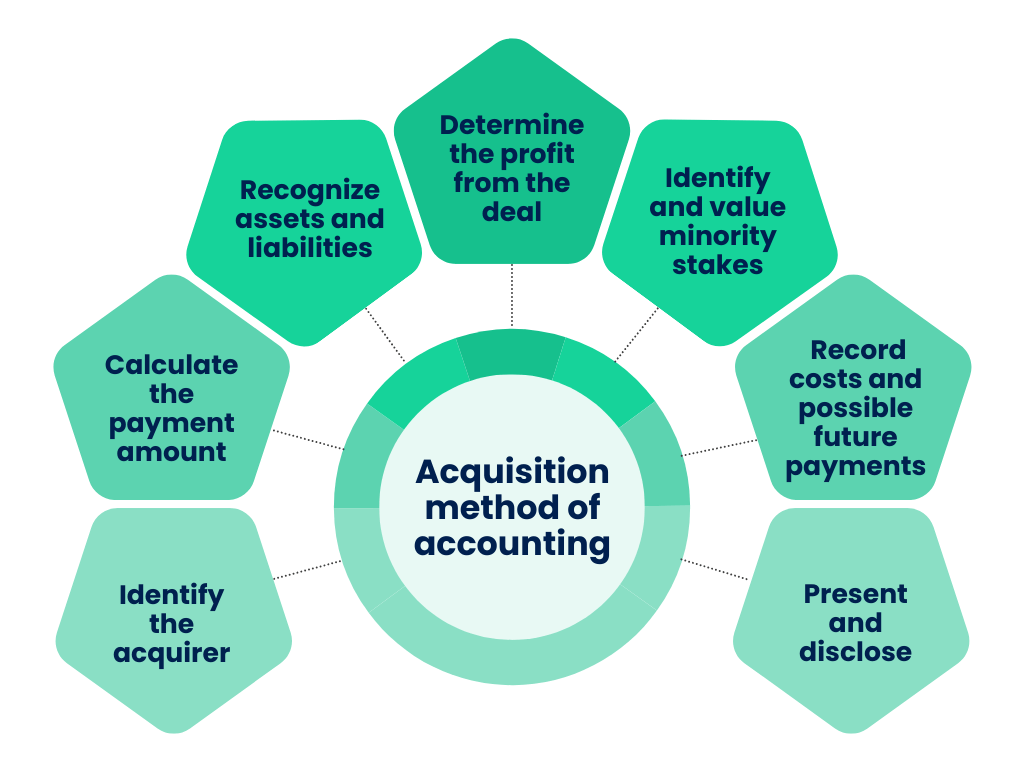
1. Identify the acquirer
When deciding which company takes charge in a business combination, it’s key to look at who has the power to make financial and operational decisions for the acquired company.
2. Calculate the payment amount
Figuring out the total value of liabilities and equity in a business combination involves considering all the resources, debts, and ownership interests included in the deal. This assessment occurs on the acquisition date when control officially shifts from one party to another.
3. Recognize assets and liabilities
As of the acquisition date, the acquired assets need to be documented at their fair value. This includes both tangible (such as buildings and equipment) and intangible assets (such as patents and trademarks), as well as any known or potential liabilities.
4. Determine the profit from the deal
When the amount paid is more than the value of the assets obtained, it leads to goodwill, which symbolizes the anticipated benefits from the combination in the future. Conversely, if the value of the assets obtained is higher than the payment made, it’s considered a gain from a bargain purchase.
To put it simply:
- Goodwill: The amount paid > the value of the assets obtained
- Gain from a bargain purchase: The amount paid < the value of the assets obtained
5. Identify and value minority stakes
If the acquiring company doesn’t own the entire business, it records the non-controlling interests at their fair values on the acquisition date.
6. Record costs and possible future payments
Any costs directly related to the combination are recorded right away. Also, contingent payments, like potential future expenses, are first evaluated at their fair value. These evaluations are then updated as necessary to account for changes in estimates over time.
7. Present and disclose
In financial statements, the acquiring company separates acquired assets, taken-on liabilities, and non-controlling interests. They also offer more information to stakeholders about the nature of the business combination and how it affects finances.
Making M&A accounting easier: How automation software helps with meeting ASC 805 requirements
Getting ready for a company merger means making sure your accounting and financial reports are detailed and right. Automation software is very helpful for making these reports better, especially when dealing with the tricky requirements of ASC 805.
How does Synder make accounting easier?
Think about using a modern tool like Synder, which not only makes it easy to match & reconcile data with a single click from popular payment systems like Stripe and PayPal to accounting software such as QuickBooks Online/Desktop, Sage Intacct, and Xero but also keeps a close eye on the cost of goods sold (COGS) tracking for a full view of finances. After linking up data easily and capturing all necessary information, Synder then focuses on giving deep financial insights with Synder Insights.
Synder Insights is a product that makes Synder more than just a tool for moving data around. It looks closely into transactions, giving businesses a clear picture of their money situation across different areas. The tool makes detailed reports on sales, earnings, cost of goods sold (COGS), and how well individual products or services are doing.
For companies about to merge, the information Synder provides is very useful. It creates detailed reports showing profit margins, pointing out which products are doing well and which aren’t across all selling places, and keeping track of fees and costs.
This careful look at finances creates a strong base for accurately valuing assets and debts, helping make smart strategic choices. It takes over the detailed checking process needed for mergers under ASC 805 rules smoother, helping companies merge more easily.
Optimize your business processes and explore Synder features with a free trial. And to gain more insights and tips, attend informative Synder’s Weekly Public Demo.
ASC 805 and tax implications
ASC 805, which focuses on business combinations in financial reporting, also affects taxation, especially regarding deferred taxes and estimated allowances.
Deferred tax issues
When two companies team up or one buys the other, their financial records may not sync perfectly for taxes. This creates what’s called deferred tax assets, predicting future tax impacts.
- If a company spends more than it can currently deduct from taxes, it might pay less in taxes later when it can use those deductions, creating a deferred tax asset.
- On the other hand, if a company earns income but hasn’t paid taxes on it yet, it results in a deferred tax liability because taxes will be owed on that income later.
ASC 805 steps in during mergers or acquisitions, requiring companies to examine these deferred tax assets and liabilities tied to the acquired company. They must acknowledge them on their financial statements and assess how they’ll impact future tax payments. Moreover, they need to adjust these assessments based on expected future tax rates when resolving these differences.
Estimated allowances
When companies merge or are acquired, there might be uncertain future costs or obligations, like ongoing legal battles or warranty claims. According to ASC 805, these potential costs need to be estimated and included in the financial statements when the merger happens.
This involves predicting expenses such as:
- Legal fees
- Warranty claims
- Restructuring costs for the combined company
These estimates aren’t fixed forever. Companies must regularly review and update them as new information becomes available or circumstances change. This ensures that the financial statements provide a more accurate picture of the potential future impacts of the merger.
Conclusion
ASC 805 is the most important accounting standard for companies involved in mergers and acquisitions. It provides clear instructions on how to handle financial issues during these transactions, ensuring transparent and accurate reporting. By following ASC 805, companies can improve the clarity, reliability and accountability of their finances during mergers. It can simplify the work of both accountants and business owners.
FAQs
What are the criteria for ASC 805?
ASC 805 says that when a business is acquired, its inventory should be valued at its fair price on the acquisition date, as per ASC 820 rules. Usually, the new owner will count the inventory as worth more than what the previous owner did before the acquisition.
When was ASC 805 issued?
On October 28, 2021, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) released Accounting Standards Update No. 2021-08, which focuses on how companies should account for contract assets and liabilities arising from contracts with customers in business combinations, according to Topic 805.
What is the difference between ASC 805 and IFRS?
ASC 805 requires adjustments to be made for the future, changing amounts in the current period when an issue is identified. In contrast, IFRS 3 requires adjustments to be made looking back, revising past periods through a process called “recasting”.