Revenue cycle management (RCM) is a critical process for healthcare providers to manage their financial operations effectively. The process involves managing patient care episodes, from appointment scheduling to payment processing, in order to maximize revenue and improve patient satisfaction. Effective RCM requires healthcare providers to optimize their workflows, invest in staff training, and leverage technology to automate and streamline revenue cycle processes.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what RCM is, its goals, key components, benefits, challenges, tools and technology, and best practices.
Disclaimer. This article aims to provide only general information on the topic and introduce you to the concept. This way, it cannot be taken as professional advice. Please, make sure to turn for help to professional accountants and advisors before making any important decision on your business finances.
Contents:
2. RCM example: What is the revenue cycle in healthcare?
3. Revenue cycle management tools and technology
4. The goals of revenue cycle management
5. Benefits of effective revenue cycle management
6. Challenges in revenue cycle management
7. Best practices for revenue cycle management
The revenue cycle
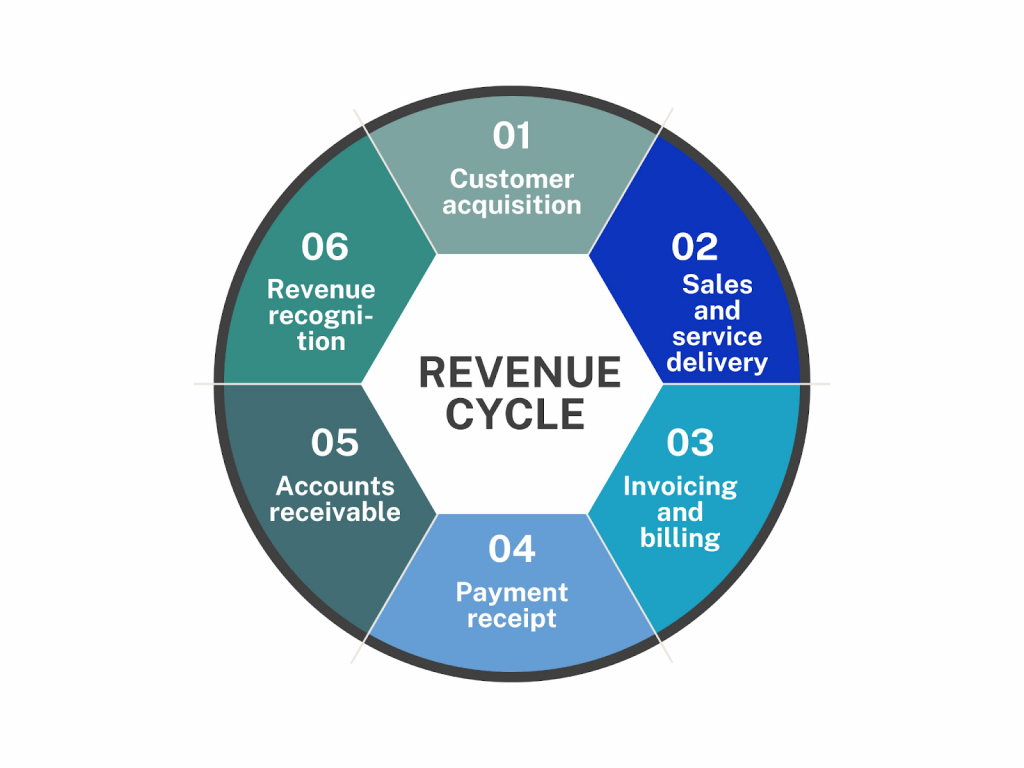
The term “Revenue Cycle” typically refers to the series of events and processes within a business or organization that are related to generating revenue or income. While I provided a detailed explanation of revenue cycle management (RCM) in the context of healthcare in the previous passage, the concept of the revenue cycle can apply to businesses in various industries. Here’s a general overview of “The Revenue Cycle” in a broader business context:
Customer acquisition: The revenue cycle often begins with efforts to acquire customers or clients. This phase may involve marketing and sales activities to attract potential customers to the business.
Sales and service delivery: Once a customer expresses interest or makes a purchase, the business delivers its products or services. This phase includes order processing, fulfillment, and customer service activities.
Invoicing and billing: After the sale or service delivery, the business generates invoices or bills for the products or services provided. Invoices typically include details such as itemized charges, payment terms, and due dates.
Payment receipt: Customers make payments to settle their invoices or bills. Payment methods can vary and may include cash, check, credit card, electronic funds transfer, or other forms of payment.
Accounts receivable: The business tracks outstanding invoices and monitors accounts receivable. This includes following up on overdue payments and managing payment arrangements.
Revenue recognition: Revenue is recognized in the financial records of the business when the goods are delivered or services are performed, and it is reasonably certain that payment will be received.
Learn how to maximize revenue recognition and explore the intricacies of the Periodic Inventory System.
Financial reporting: The business maintains financial records and prepares financial statements, including income statements and balance sheets, which provide an overview of revenue, expenses, and overall financial performance.
Analysis and planning: Regular analysis of financial data helps businesses identify trends, assess the effectiveness of their revenue generation strategies, and make informed decisions to optimize the revenue cycle.
Compliance and taxation: Businesses must ensure compliance with tax regulations and reporting requirements related to revenue. This includes calculating and remitting taxes owed on revenue, such as sales tax or income tax.
Revenue growth strategies: Businesses often engage in strategic planning to explore ways to grow their revenue. This can involve expanding into new markets, launching new products or services, or enhancing customer retention efforts.
Customer relationship management: Maintaining positive relationships with customers is crucial for repeat business and referrals. Good customer service and ongoing communication can impact the revenue cycle by fostering customer loyalty.
Cash flow management: Efficiently managing cash flow is essential to ensure that the business has enough liquidity to cover expenses and invest in growth opportunities.
You might want to read about cash flow management tips for ecommerce businesses.
The specific steps and details of the revenue cycle can vary significantly depending on the type of business or industry. However, the overarching goal of the revenue cycle is to generate income, manage it effectively, and support the financial health and growth of the organization. Effective management of the revenue cycle is a fundamental aspect of business operations and financial success.
RCM example: What is the revenue cycle in healthcare?
A typical RCM example is healthcare revenue management, which we’re going to touch upon further on.
Revenue cycle management in healthcare refers to the process of managing the financial aspects of a healthcare organization’s interactions with patients and insurance companies to optimize revenue generation and ensure accurate and timely payment for services rendered. It encompasses a series of administrative and clinical functions that begin when a patient makes an appointment and end when the healthcare provider receives full payment for their services. The primary goal of RCM is to streamline and improve the financial operations of healthcare organizations while maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements. Here are the key components of the revenue cycle management process:
Patient scheduling
The revenue cycle begins with the scheduling of patient appointments. Accurate patient information and insurance details are collected during this phase.
Registration and check-In
Patients arrive for their appointments and complete the registration process, providing personal and insurance information. Staff verify insurance eligibility and collect any copayments or deductibles due at the time of service.
Coding and documentation
Healthcare providers document the services provided to the patient, and medical coders assign appropriate diagnosis and procedure codes. Proper coding is crucial for accurate billing and reimbursement.
Charge capture
The charges for services rendered are captured electronically or on paper. This includes information about the services provided, codes assigned, and associated costs.
Claim submission
Claims are generated based on the charges, coding, and patient information. These claims are submitted to the patient’s insurance company for payment. This can be done electronically (eClaims) or via paper submission.
Claim adjudication
The insurance company reviews the submitted claims, checks for accuracy, and determines the amount they will pay based on the patient’s coverage and the provider’s contract with the insurer. This process can involve multiple stages of review and may result in claim denials or adjustments.
Payment posting
Once the insurance company processes a claim, the healthcare provider receives an Explanation of Benefits (EOB) or Electronic Remittance Advice (ERA), which details the payment or denial. Payments are posted to the patient’s account, and any remaining balances are billed to the patient.
Accounts receivable management
Healthcare organizations actively manage outstanding accounts receivable, follow up on unpaid or denied claims, and address any billing disputes with insurance companies or patients.
Patient billing
Patients get a bill for the remaining balances after insurance has paid. Healthcare providers may offer payment plans or financial assistance options to help patients settle their bills.
Payment collection
Payments are collected from patients through various means, including cash, check, credit card, or electronic funds transfer.
Denial management
If a claim is denied, providers investigate the reason and may resubmit the claim with corrections or appeal the denial if it was incorrect.
Financial reporting and analysis
Regular financial reporting and analysis are conducted to monitor revenue performance, identify trends, and make strategic decisions to improve the revenue cycle.
On the whole, effective revenue cycle management is essential for the financial stability of healthcare organizations, as it helps maximize revenue, reduce denials and delays in reimbursement, and ensure compliance with healthcare regulations. It requires collaboration among various departments, including front-office staff, clinical staff, billing and coding teams, and finance professionals.
Revenue cycle management tools and technology
There are several tools and technology solutions available for healthcare providers to improve their revenue cycle management processes.
- Electronic health records (EHRs) provide a centralized platform for managing patient information, appointments, and billing information.
- Revenue cycle management software provides tools for managing charge capture, coding and billing, claims management, and denial management. EHR revenue cycle management solutions provide the best of both worlds.
- Predictive analytics solutions provide insights into revenue cycle trends and identify opportunities for improvement.
A good example of a robust analytics solution is Synder Insights. It offers comprehensive real-time data, eliminating the need for additional tools or sources. Exploring the Synder use case about American Hospitality supply, can provide insights into how specific software solutions can be effectively applied in various scenarios to enhance RCM efficiency and accuracy.
It caters to both accounting professionals and business owners as an integral part of their service or operations. With just a few clicks, reports are automatically generated using the data the tool extracts from your ecommerce platforms and sales channels, furnishing you with all the insights on key business metrics necessary for thorough data analysis. Synder Insights empowers you to:
1. Access all the essential reports, accompanied by explanations of their significance, why they matter, and, most importantly, how they can facilitate your business growth.
2. Transform your business decision-making into a data-driven process.
Learn how to scale your business with Synder Insights during a 15-day free trial or reserve a spot at the weekly demo session.
The goals of revenue cycle management
Revenue cycle management involves a set of goals and objectives aimed at optimizing the financial processes associated with generating revenue. The primary goals of RCM are to ensure that a business or healthcare organization can maximize revenue, minimize delays in reimbursement, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements. Here are the key goals of revenue cycle management:
Maximize revenue
The fundamental goal of RCM is to maximize the revenue generated by a business or healthcare organization. This involves accurately capturing all billable services, ensuring that claims are submitted promptly, and collecting payments efficiently.
Accelerate cash flow
RCM aims to expedite the flow of cash into the organization. This includes reducing the time it takes to process claims, receive payments, and post them to accounts. Faster cash flow helps improve the organization’s financial stability.
Minimize claim denials
One of the challenges in revenue cycle management is to reduce claim denials by payers (such as insurance companies). Effective RCM strategies focus on proper coding, documentation, and claims submission to minimize denials and rejections.
Enhance accuracy and compliance
RCM seeks to ensure the accuracy of billing and coding practices to prevent errors that can lead to overpayments, underpayments, or legal issues. Compliance with the industry’s regulations and billing guidelines is crucial to avoid fines and penalties.
Reduce operating costs
Efficient revenue cycle management can help reduce administrative costs associated with billing, collections, and accounts receivable management. Automation and streamlined processes can contribute to cost savings.
Optimize staff productivity
Effective RCM involves optimizing the productivity of staff members involved in the revenue cycle, including billing and coding professionals, administrative staff, and customer service representatives.
Increase data analytics and reporting
RCM relies on data analytics to track key performance indicators (KPIs) related to revenue, claims, denials, and collections. These insights enable organizations to make data-driven decisions to improve revenue cycle performance.
Enhance financial planning
Accurate and timely revenue data allows organizations to engage in better financial planning and budgeting. It helps in forecasting revenue, managing expenses, and making informed investment decisions.
Support strategic growth
RCM plays a crucial role in supporting the strategic growth of organizations and businesses. By optimizing revenue generation and financial operations, organizations can invest in expansion, new services, and improved customer care.
Maintain regulatory compliance
Organizations must adhere to complex regulatory requirements in the United States. RCM ensures compliance with these regulations to avoid legal issues.
Reduce bad debt
RCM strategies aim to minimize bad debt, which occurs when payers fail to make payments for services rendered. This includes setting up payment plans, offering financial assistance, and pursuing collections when necessary.
In short, the goals of revenue cycle management encompass various aspects of financial optimization, efficiency, compliance, and patient satisfaction. Effective RCM practices help organizations achieve financial stability, support growth initiatives, and provide quality care while maintaining transparency and compliance with relevant regulations.
Benefits of effective revenue cycle management
Effective RCM offers numerous benefits to businesses and organizations across various industries. Whether in healthcare, retail, manufacturing, or any other sector, optimizing the RCM process can positively impact financial health, operational efficiency, and overall business success. Here are some of the key benefits of effective revenue cycle management:
- Improved cash flow: Efficient RCM processes accelerate the collection of payments, reducing the time between providing goods or services and receiving payment. This results in a more consistent and stable cash flow, enabling organizations to meet financial obligations and invest in growth opportunities.
- Maximized revenue: By accurately capturing and billing for all products or services provided, organizations can maximize their revenue potential. Effective RCM ensures that no revenue goes unaccounted for or is lost due to billing errors or oversights.
- Reduced operating costs: Streamlined RCM processes can lead to cost savings through automation and efficiency improvements. Fewer manual tasks and errors mean reduced labor costs and lower expenses associated with accounts receivable management.
- Enhanced financial stability: Effective RCM provides financial predictability and stability by reducing revenue fluctuations and minimizing the risk of financial crises or cash flow shortages.
- Minimized debt: RCM strategies, including credit management and timely collections, help minimize bad debt. Businesses can better assess customer creditworthiness, set appropriate credit limits, and pursue collections efforts when necessary.
- Risk mitigation: Effective RCM ensures that organizations comply with industry regulations and legal requirements, reducing the risk of fines, penalties, or legal disputes related to revenue generation and billing practices.
- Improved customer satisfaction: Transparent and efficient billing and payment processes can enhance the customer experience. Clear communication about charges, payment options, and billing inquiries contributes to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Optimized resource allocation: With better visibility into cash flow and revenue trends, organizations can allocate resources more effectively. This includes strategic investment in growth opportunities and operational improvements.
- Data-driven decision-making: RCM relies on data analytics and reporting to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs). This data-driven approach helps organizations make informed decisions, identify trends, and implement strategies to enhance the revenue cycle.
- Strategic growth: Improved financial stability and enhanced revenue generation can support strategic growth initiatives, such as expanding into new markets, launching new products or services, or acquiring competitors.
- Streamlined processes: Automation and efficiency improvements in the revenue cycle reduce administrative burdens and eliminate bottlenecks in the billing and payment process. This leads to smoother operations and faster revenue realization.
- Stronger provider-payer relationships: In healthcare and similar industries, effective RCM can strengthen relationships with insurance companies and payers. Timely and accurate claims submission and payment can lead to more favorable contract negotiations.
- Enhanced competitive advantage: Businesses with effective RCM processes are better positioned to compete in the market. They can offer competitive pricing and customer-friendly payment options, giving them an edge over rivals.
- Financial transparency: RCM provides organizations with greater transparency into their financial operations, making it easier to identify areas for improvement and implement sound financial management strategies.
- Increased profitability: Ultimately, effective RCM contributes to increased profitability by optimizing revenue generation, reducing costs, and improving the financial health of the organization.
Overall, effective revenue cycle management is essential for organizations across industries to maintain financial stability, maximize revenue, and achieve sustainable growth. By optimizing RCM processes and leveraging data-driven insights, businesses can enhance their overall financial health and competitiveness in the marketplace.
Challenges in revenue cycle management
Revenue cycle management is a complex and multifaceted process that comes with several challenges. These challenges can impact an organization’s ability to optimize its revenue cycle and maintain financial stability. Here are some common challenges in revenue cycle management:
- Changing regulatory environment: Changes in regulations, billing guidelines, and reimbursement policies can make it challenging for organizations to stay compliant and adapt to new requirements.
- Documentation errors: Inaccurate and incomplete documentation can lead to claim denials, delayed payments, or underbilling, which can significantly impact revenue.
- Claim denials and rejections: Payers often deny or reject claims for various reasons, such as coding errors, missing information, or lack of medical necessity. Managing and appealing denials can be time-consuming and costly.
- High administrative costs: The administrative costs associated with billing, collections, and accounts receivable management can be substantial. Reducing these costs while maintaining efficiency is a challenge.
- Data security: Protecting customer information and ensuring compliance with the industry regulations adds complexity to RCM processes.
- Technology integration: Implementing and integrating RCM software and technology solutions into existing healthcare systems can be a complex and costly endeavor.
- Staff training and turnover: RCM staff require ongoing training to keep up with changing regulations and technologies. High turnover rates in RCM departments can disrupt operations and lead to errors.
- Lack of standardization: Different payers may have varying requirements for claims submission and payment processes, making it challenging to standardize RCM practices.
- Claim backlogs: A backlog of unprocessed claims can lead to delayed payments and negatively affect cash flow.
- Revenue leakage: Leakage occurs when organizations fail to capture all billable services, leading to lost revenue. Identifying and addressing sources of revenue leakage is an ongoing challenge.
- Outsourcing risks: Some organizations outsource RCM processes to third-party vendors. Ensuring the quality and security of outsourced RCM services can be a concern.
- Market competition: In competitive markets, organizations must balance the need to provide quality service with the pressure to offer competitive pricing, which can affect revenue.
- Interoperability and data exchange: Sharing customer information and financial data across different systems and providers can be difficult due to interoperability challenges.
Addressing these challenges in revenue cycle management requires a combination of strategic planning, technology adoption, staff training, and continuous process improvement. Organizations must stay agile and adaptive to navigate the evolving landscape of revenue cycle management effectively.
Best practices for revenue cycle management
Effective RCM requires service healthcare providers to follow several best practices, including setting clear goals and metrics, optimizing workflows, investing in staff training and development, and leveraging technology solutions.
- Clear goals and metrics help healthcare providers track their progress and adjust their processes accordingly.
- Optimized workflows help healthcare providers improve efficiency and accuracy.
- Investing in staff training and development ensures that healthcare providers have the skills and knowledge needed to effectively manage revenue cycle processes.
- Leveraging technology solutions helps healthcare providers automate and streamline revenue cycle processes, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
Conclusion
In summary, RCM is an essential aspect of healthcare revenue generation, and its importance cannot be overstated. By effectively managing the revenue cycle, healthcare providers can improve their financial performance, provide better patient care, and ensure compliance with regulations, thanks to the accounting for medical practices. It is important for healthcare providers to stay up-to-date with industry trends and best practices to ensure that they are effectively managing their revenue cycle processes and maximizing revenue.
You might also want to check out other articles on revenue:
1. “Payment Orchestration – Merchants’ Secret Recipe for Getting More Revenue”
2. “Net Profit vs Revenue: What is the Difference?”
3. “Maximizing Revenue Recognition Efficiency with Synder: Seamlessly Connect Stripe and QuickBooks”











.png)
This comprehensive article provides an insightful overview of RCM and its significance in healthcare. The revenue cycle management goals are clearly articulated, covering everything from maximizing revenue to supporting strategic growth and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Thank you so much Kris for such a nice feedback!
I like that you talked about having transparency when it comes to the financial operations of an organization with the help of RCM processes which can be useful to improve and implement strategies. I can imagine the benefits of those effects when they are applied to one’s company, especially when they are starting out in the industry they are in. So they have to be invested in as soon as they can outsource those services, since there might be organizations that cannot afford them at the moment when they are just starting out.
Hi Mia, absolutely, you’ve highlighted a key point. Transparency in financial operations through RCM processes is indeed crucial, especially for new companies in their industry. While cost can be a consideration for startups, investing in such services early on can provide significant long-term benefits and set a strong foundation for growth and strategy implementation.
Nice information! Thanks for this article
Your post highlights some crucial aspects of optimizing revenue cycles in healthcare. Managing the revenue cycle efficiently is indeed vital for ensuring that healthcare providers receive timely and accurate payments while minimizing administrative costs. I appreciate the emphasis on leveraging technology to streamline processes and improve accuracy.
Absolutely! Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) is crucial for healthcare organizations to optimize their financial processes. By streamlining billing, collections, and claims management, RCM not only improves cash flow but also enhances patient satisfaction.
Investing in RCM solutions can help identify inefficiencies and reduce the days in accounts receivable. Plus, with the ongoing changes in regulations and payer requirements, effective RCM ensures compliance and minimizes revenue leakage. It’s a game-changer for healthcare providers aiming to balance quality care with financial sustainability!