The concept of billable expenses plays a crucial role in accounting and finance management. It forms the basis of transparent financial interactions between service providers and clients, ensuring that the costs associated with delivering a service are accurately accounted for and reimbursed.
This article looks at the fundamentals of billable expenses, shedding light on what they entail and how they contribute to the overall financial health of an enterprise.
Exploring billable expenses
Let’s first break down billable expenses.
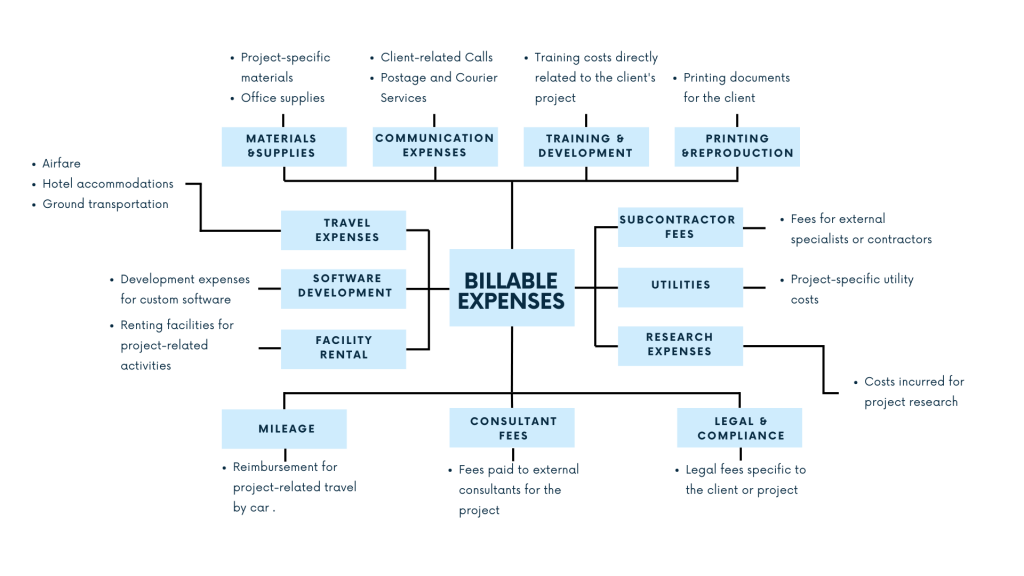
By definition, billable expenses are costs or expenditures that a business incurs on behalf of a client or project and can be charged back to the client. Such expenses are directly associated with the work performed for a specific client or project. Usually, a business and a client agree upon them at and before signing a contract or agreement. Billable expenses may include travel costs, materials, subcontractor fees, or any other direct costs of providing a service or delivering a product to a client.
Billable means a business bills clients for these expenses to recover the direct costs of fulfilling their needs.
Shouldering certain expenses to a client is a strategic financial move businesses often employ for several reasons, ensuring that the direct costs of fulfilling a client’s needs are recovered and influencing the account holding strategy. Designating specific costs as client billable helps companies optimize their financial structure and enhance overall profitability.
An example of billable expenses for a product / service delivery
I think a real-life example might better explain how billable expenses work.
Imagine someone hiring a consulting firm to provide strategic advice on a project. While delivering the service, the consulting firm spends some money, as it’s necessary to fulfill their job for this client’s project. What can be the cases? Let’s have a look.
- Travel expenses
Consultants travel to the client’s location for meetings, workshops, or other project-related activities. So, the costs associated with airfare, hotel accommodations, meals, and transportation can be considered billable expenses. - Materials and supplies
The consulting firm purchases specific materials, software licenses, or other supplies, particularly for the client’s project. These costs are also called billable and can be billed to the client. - Subcontractor fees
The consulting firm hires subcontractors or third-party specialists to contribute to the project. The firm can pass on the fees paid to these subcontractors to the client as billable expenses. - Equipment rental
- The consulting firm needs to rent specialized equipment or facilities for the project. The rental costs, at this point, can be regarded as billable.
In each such case, the consulting firm would track these expenses separately (from their business expenses) and include them in the client invoice. The client, in turn, is expected to reimburse the consulting firm for these billable expenses in addition to the fees for the consulting services.
Expenses: understanding billable and non-billable
Distinguishing between billable and non-billable expenses boils down to understanding whether an extra cost happens because of your work on a specific client or project.
If your expenses are connected with meeting a client’s needs or fulfilling a project, they are likely billable. Think of travel costs (mentioned above) or materials used for a particular client’s work. You can specify such expenses in client agreements and, later on, bill your clients to compensate for the resources you spent.
Non-billable expenses are a different story. They are the general operational costs necessary for day-to-day business operations, like rent or salaries for staff not directly tied to client projects. These costs aren’t invoiced to clients but are fundamental for the overall business.
So, here’s a rule of thumb in understanding which expenses to consider billable and negotiate with clients. Would you have this extra spending if it hadn’t been for fulfilling your client’s project? If the answer is no, you are likely dealing with billable expenses.
What is billable expense income?
In a nutshell, billable expense income is the money a business or individual earns by charging others for expenses incurred, i.e., billable expenses. As a business spends money on some client’s progect-related stuff, they need to record an expense on the books and then, when invoicing their client for the latter, they should record corresponding income on the financial statements. This income is specific to compensating out-of-pocket spending on delivering a service or product.
Let’s look at it in the same example as above.
A consulting firm incurs travel expenses while working on a client’s project. They bill the client for these expenses in addition to the fees for the consulting services. The amount charged to the client for these billable expenses contributes to the overall billable expense income.
Why should a company track billable expense income?
Properly tracking and accounting for billable expense income is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records and assessing the profitability of client projects.
Let’s break it down.
- Accurate financial reporting
Properly tracking billable expense income ensures accurate financial reporting. It allows businesses to correctly predict the costs associated with client projects, providing a clear picture of overall profitability. - Client invoicing
Tracking billable expenses is essential for invoicing clients accurately. It helps businesses recover direct costs incurred on behalf of clients, ensuring that the client reimburses those expenses outlined in the agreement. - Profitability analysis
By monitoring billable expense income, businesses can assess the profitability of individual projects. This insight is valuable for making informed decisions about pricing, resource allocation, and the financial viability of certain project types.
Managing billable expense income: best practices
Tracking billable expense income might be challenging. Following certain best practices might help businesses in managing billable more efficiently. Let’s look at those in more detail.
- Use a dedicated system
A robust accounting or project management system might help accurately track billable expenses and income. Many software solutions provide features particularly designed for this purpose. - Detailed invoicing
Clearly outline billable expenses on client invoices. A breakdown of each expense category might ensure transparency and facilitate client understanding. - Client agreements
You might want to establish clear terms in client agreements regarding what expenses are billable. It can help avoid misunderstandings and ensure that clients know about the specific costs they will be responsible for reimbursing. - Regular reconciliation
Periodically reconciling the billed expenses with the actual costs incurred might help identify discrepancies and ensure you account for all billable expenses properly. - Documentation
Keep thorough documentation of all billable expenses, including receipts and invoices. This documentation serves as evidence in case of client queries, audits, or internal reviews.
One should bear in mind that diligently tracking billable expense income might help businesses maintain financial transparency, enhance client relationships, and make informed decisions to optimize overall profitability.
How billable expense income impacts a business’s tax returns
Some might believe that, with billable expense income, you make your business liable to pay a higher tax. It’s not totally correct, but billable expense income can have implications for a company’s tax returns, and understanding these dynamics is crucial for accurate financial management. Here are several ways in which billable expense income may impact a company’s tax returns:
- Taxable income and deductions
- Billable expense income is typically considered part of a company’s gross income. However, it’s offset by the corresponding deductible expenses associated with providing services or products. The relationship between billable income and deductible expenses influences the net effect on taxable income.
- Expense deductions
- Businesses can usually deduct legitimate expenses, including billable expenses, from their taxable income. This deduction helps reduce the overall tax liability. Therefore, the proper billable expense documentation and categorization are critical for maximizing deductions.
- Client reimbursements
- If clients reimburse businesses for billable expenses the reimbursement is generally considered income. However, since the corresponding expenses were already deducted, the net effect on taxable income is often minimal.
- Profitability and tax liability
- Billable expense income contributes to the overall profitability of a company. Higher profits may lead to increased tax liability. Therefore, businesses must carefully assess the balance between billable income and deductible expenses to manage their taxable income effectively.
- Tax credits and incentives
- Some jurisdictions offer tax credits or incentives for specific business activities. Depending on the nature of the billable expenses, a company may qualify for certain credits or incentives, further impacting its tax returns.
- Tax planning opportunities
- Strategic tax planning involves optimizing a company’s tax position by leveraging available deductions and credits. Businesses can strategically manage billable expenses to align with tax planning objectives, such as minimizing taxable income and maximizing deductions.
- Accounting methods
- The accounting methods one uses for recognizing billable expenses and income can also impact tax returns. Accrual accounting and cash accounting, for example, may have different timing effects on when to recognize income and expenses for tax purposes.
As you can see, the impact of billable expense income on tax returns is contingent on various factors, including expense deductions, client reimbursements, and overall profitability. Diligent accounting practices, accurate documentation, and strategic tax planning are essential for navigating the complexities of tax implications associated with billable expense income. Businesses should consider consulting with tax professionals to ensure compliance and optimize their tax position.
How accounting software handles billable expense income tracking and management
As mentioned above, the accuracy of billable expenses and billable expense income tracking is an important aspect that impacts a company’s finance management. At this point, accounting software implementation is a transformative step for businesses seeking to streamline billable expense income tracking and management. Beyond enhancing accuracy and efficiency, this technology fosters financial transparency, contributing to overall business success in today’s fast-paced economic landscape.
Here’s a closer look at how accounting software transforms this critical aspect of financial management.
- Accurate expense recording
Accounting software can integrate with multiple payment systems to help businesses accurately record and categorize expenses (as account billable, for example). By distinguishing between billable and non-billable items, organizations gain a nuanced understanding of the costs associated with specific clients or projects. - Automated client invoicing
Generating client invoices becomes a breeze with accounting software. The software automates the inclusion of detailed breakdowns of billable expenses, mitigating the risk of manual errors. It can offer users various templates for invoicing, so they can select and use an appropriate invoice template to form a consistent invoicing process for their small business. Moreover, it efficiently handles the closure of pending invoices upon payment processing, streamlining the entire financial workflow. This automation not only enhances accuracy but also fosters transparency in financial transactions. - Customized client agreement compliance
Tailoring the software to align with client agreements is a key strength. It includes configuring the system to track specific billable expenses and ensuring adherence to agreed-upon rates or reimbursement terms. Such customization enhances precision and cultivates client trust. - Real-time monitoring
Real-time monitoring of billable expense income is a game-changer. Businesses can view their project-related income and expenses in real-time, facilitating informed decisions regarding project profitability and resource allocation. - Insightful financial reporting
Robust financial reporting features might provide insights into billable expense income trends over specific periods. Businesses can generate reports to analyze patterns, assess project profitability, and make well-informed financial decisions. - Trustworthy audit trails
The software maintains a trustworthy audit trail of all financial transactions, including billable expenses. This careful record-keeping is valuable for internal reviews and external audits and ensures compliance with rigorous accounting standards. - Access anytime, anywhere
Many accounting software solutions operate on a cloud-based infrastructure, offering businesses the advantage of remote access to financial data. This feature is particularly beneficial for organizations with distributed teams or those requiring on-the-go access for efficient billable expense tracking and management.
Final word
To make long story short, billable expenses facilitate a flawless exchange between service providers and clients.
Understanding billable expense dynamics boils down to a straightforward question: does the expense tie directly to a specific client or project? If yes, it’s a marked billable expense, fundamental for navigating financial success.
Carefully recording billable expense income is crucial for precise financial reporting, enabling accurate client invoicing and insightful profitability analysis. As billable expense management can be challenging, businesses might harnsee some common best practices and accounting software. This technological ally can record billable and non-billable expences and propperly categorizes them. It automates all these processes, eliminating the risk of errors, offering real-time monitoring, insightful reporting, and a trustworthy audit trail.
As businesses step into this era of financial management, the integration of accounting software becomes a guiding beacon, simplifying the intricate path to success in the dynamic economic landscape.






