Journal entries are a part of QuickBooks accounting software, allowing users to record transactions accurately and maintain financial records effectively. However, errors can occur, or adjustments are needed, necessitating the deletion of journal entries.
In this article, we’ll explore the ins and outs of journal entries in QuickBooks and provide a guide on deleting them when necessary.
Key takeaways
- Journal entries in QuickBooks are crucial for accurately recording and maintaining financial transactions, ensuring compliance with accounting standards and providing valuable insights for business decisions.
- Creating journal entries in QuickBooks involves logging details of various transactions, such as sales, expenses, payroll, asset acquisitions, loans, and adjustments, which helps in organizing financial data effectively.
- Deleting journal entries should be done carefully to correct errors, remove duplicates, or adjust voided transactions, while ensuring data integrity, maintaining an audit trail, and considering consultation with an accountant if necessary.
Understanding journal entries in QuickBooks
For starters, let’s break down some basics and speak about journal entries in general to understand the consept and their role in accounting.
What are journal entries?
In accounting, a journal entry is a formal record of financial transactions. It’s like a detailed note that shows when a transaction occurred, which accounts were affected, and the amounts involved. Journal entries help businesses keep track of their money movements accurately and in order.
Creating a journal entry in QuickBooks is like telling the software what happened in a transaction. You provide all the necessary details and put it under the right account so QuickBooks can accurately reflect your business’s financial picture.
Level up your QuickBooks experience with smart automation! Integrate financial data from all your sales channels in QuickBooks to have always accurate records ready for reporting, analysis, and taxation. See it in action with a 15-day free trial or spare a spot at our weekly public demo to have your questions answered.
Why are journal entries important?
As mentioned, journal entries are the records of your transactions in accounting, making your books accurate, helping you comply with laws, and providing an organized view of your financial data for analysis, taxation, audits, you name it.
Making it accurate
Journal entries ensure that your financial records are accurate and up-to-date. They capture every financial transaction, big or small, which helps you understand where your money is coming from and where it’s going.
Making you compliant
Keeping accurate financial records isn’t just good practice. It’s often a legal requirement. Journal entries, at this point, help you comply with tax regulations and other financial reporting standards.
Making good decisions
Clear and detailed journal entries set a foundation for valuable insights into your business’s financial health. It helps you make informed decisions about spending, investments, and future planning.
Making it transparent for auditing
Sometimes, your business faces audits from tax authorities. Or else you need to show your financial records to investors or lenders. Journal entries serve as evidence of your financial activities. They demonstrate your transparency and accountability.
Creating journal entries in QuickBooks
As mentioned, businesses generate various transactions in their day-to-day routine. These transactions fall into different types of journal entries to reflect them in accounting.
Types of journal entires based on various transactions
Let’s look at the types of transactions that typically require journal entries.
#1 – Sales and revenue transactions
When a business sells goods or services to customers, it generates revenue. Recording sales transactions in the journal helps track the income earned by the business.
Journal entries for sales typically involve debiting accounts receivable or cash for the amount received and crediting sales revenue accounts.
#2 – Purchase and expense transactions
Businesses often purchase goods or services necessary for their operations. These expenses need to be recorded accurately to track the money going out of the business.
Journal entries for purchases and expenses involve debiting expense accounts for the amount spent and crediting accounts payable or cash accounts.
#3 – Payroll transactions
Payroll transactions involve the payment of wages and salaries to employees. These transactions include various components such as gross wages, taxes withheld, and benefits.
Journal entries for payroll transactions may include debiting wage expense accounts and crediting cash or accounts payable accounts.
#4 – Asset acquisitions and depreciation
When a business acquires assets like equipment, property, or vehicles, it records the transaction to reflect the asset’s value.
Journal entries for asset acquisitions involve debiting the relevant asset account and crediting accounts payable or cash accounts. Additionally, periodic journal entries for depreciation expense allocate the cost of assets over their useful lives.
Read more about What asset cannot be depreciated in accounting.
#5 – Loan and interest payments
Businesses often take out loans to finance operations or purchase assets. Recording loan transactions helps track the principal amounts borrowed and interest payments.
Journal entries for loan transactions include debiting cash or the loan account for the amount received and crediting liabilities for the amount owed. Interest payments involve debiting interest expense accounts and crediting cash accounts.
#6 – Adjusting entries
Adjusting entries are necessary to ensure that financial statements accurately reflect the business’s financial position and performance at the end of an accounting period.
These entries may include recording accrued expenses, prepaid expenses, accrued revenue, and depreciation.
How to create a journal entry in QuickBooks?
It’ll be pretty safe to say that QuickBooks, at its core, is a digital version of an accounting book. So, creating journal entries is pretty much the same process, only it’s faster and more convenient. Here’s how it works.
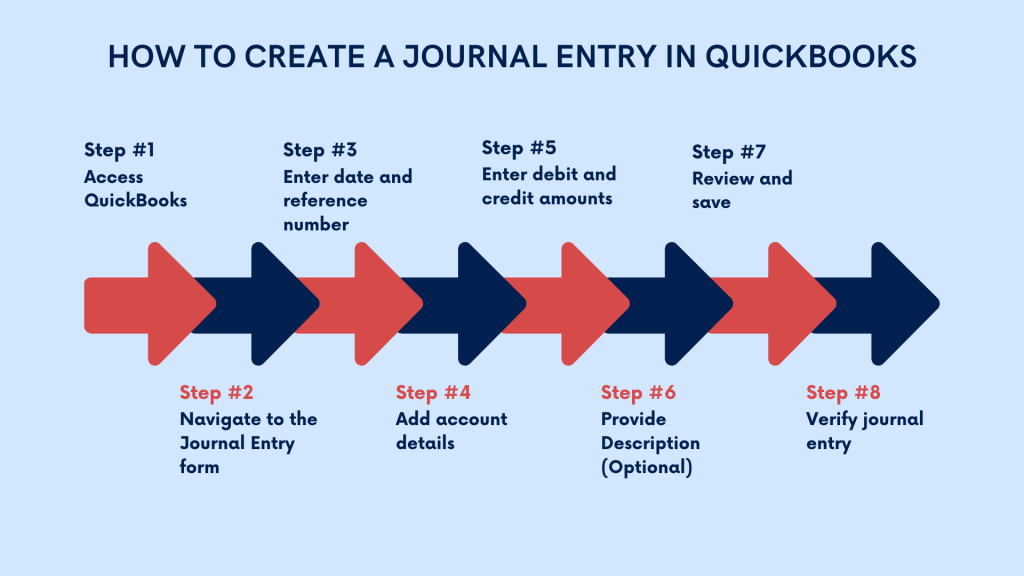
- Access QuickBooks
Log in to your QuickBooks account and ensure you have the necessary permissions to create journal entries. - Navigate to the Journal Entry form
Depending on your QuickBooks version, locate the “Create” menu or the “+” sign at the top of the screen. From the dropdown menu, select “Journal Entry” under the “Other” section. - Enter date and reference number
In the journal entry form, enter the date of the transaction. This should reflect the date the transaction occurred. Assign a reference number or description to the journal entry for easy identification and reference in the future. - Add account details
Identify the accounts affected by the transaction. QuickBooks allows you to select both debit and credit accounts for each entry. Choose the appropriate account from the dropdown menu under the “Account” column. - Enter debit and credit amounts
Determine whether the account is to be debited or credited based on the nature of the transaction. Enter the corresponding debit or credit amount in the designated columns for each account. - Provide Description (Optional)
Include a brief description or memo to provide additional context or details about the transaction. This description can help other users understand the purpose of the journal entry. - Review and save
Double-check the entries to ensure accuracy and proper balancing between debits and credits. Once verified, click the “Save” or “Save and Close” button to record the journal entry in QuickBooks. - Verify journal entry
After saving the journal entry, review the transaction history or journal entry report to confirm that it has been recorded correctly. Ensure that the journal entry aligns with the business’s financial records and accounting principles.
When should users consider deleting journal entries in QuickBooks?
Deleting journal entries should be approached with caution and reserved for specific circumstances. Here are some scenarios when users might consider deleting journal entries in QuickBooks:
#1 – Error correction
Users may need to delete journal entries if they’ve made a mistake during data entry or if the entry contains inaccuracies that need correction. Examples include entering incorrect amounts, selecting the wrong accounts, or duplicating entries inadvertently.
# 2- Reversal of duplicate entries
Duplicate journal entries can distort financial reports and lead to confusion. Users should delete duplicate entries to maintain accurate records and prevent misinterpretation of financial data.
#3 – Unnecessary entries
If users identify journal entries that are no longer relevant or necessary for financial reporting, they may consider deleting them to declutter their records and streamline their accounting processes.
#4 – Adjustment for voided transactions
When voiding a transaction, users may need to delete the corresponding journal entry to ensure that the financial records accurately reflect the voided transaction and its impact on account balances.
In summary, users should consider deleting journal entries in QuickBooks primarily to rectify errors, remove duplicates, eliminate unnecessary entries, or adjust for voided transactions.
What are the steps to delete a journal entry in QuickBooks?
Deleting journal entries in QuickBooks involves a straightforward process. Follow these steps to delete a journal entry:
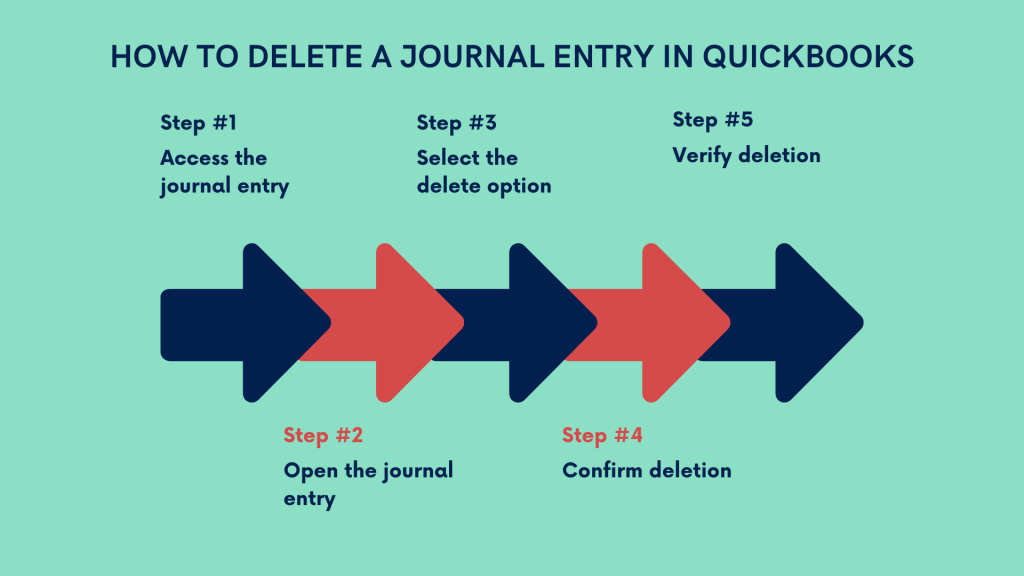
- Access the journal entry
Log in to your QuickBooks account and navigate to the journal entry you want to delete. - Open the journal entry
Click on the journal entry to open it and view the details. - Select the delete option
Look for the option to delete the journal entry. In QuickBooks Online, you can typically find the delete option in the top-right corner of the entry screen. - Confirm deletion
QuickBooks will prompt you to confirm the deletion of the journal entry. Review the details to ensure you’re deleting the correct entry, and confirm the deletion when prompted. - Verify deletion
After deleting the journal entry, verify that it has been successfully removed from your records by reviewing the transaction history or journal entry report.
Following these steps ensures that users can effectively delete journal entries in QuickBooks when necessary.
What to consider before deleting a journal entry?
Before proceeding with the deletion of a journal entry in QuickBooks, users should consider the following precautions and considerations:
Data integrity
Ensure that deleting the journal entry will not compromise the integrity or accuracy of your financial records.
Review the entry carefully to understand its impact on account balances and financial statements.
Backup data
Before deleting any journal entry, consider creating a backup of your QuickBooks data to safeguard against accidental data loss or deletion.
Audit trail
QuickBooks maintains an audit trail of all transactions, including deleted journal entries. Users should be aware that deleted entries may still be accessible through the audit trail for auditing and historical purposes.
Consultation with accountant
If uncertain about whether to delete a journal entry, consider consulting with a qualified accountant or financial advisor for guidance and expertise.
By considering these precautions and considerations, users can make informed decisions regarding the deletion of journal entries in QuickBooks while mitigating potential risks.
Consequences of deleting journal entries in QuickBooks, and how to mitigate risks?
Deleting journal entries in QuickBooks can have several potential consequences, and users should take steps to mitigate associated risks:
Data inaccuracy
Deleting journal entries without proper consideration can lead to inaccuracies in financial reports and distortions in account balances.
To mitigate this risk, carefully review entries before deletion and consider alternative solutions such as adjusting entries or voiding transactions where appropriate.
Audit trail integrity
Deleting journal entries removes them from the active records but retains them in the audit trail for historical tracking and auditing purposes.
Users should be aware that deleted entries may still be accessible through the audit trail and should maintain the integrity of the audit trail by deleting entries judiciously.
Loss of historical data
Deleting journal entries removes them permanently from the active records, potentially resulting in the loss of valuable historical data.
To mitigate this risk, consider archiving deleted entries or maintaining backup copies of financial records for historical reference and compliance purposes.
Documentation
Document the reasons for deleting journal entries and any associated decisions or considerations to maintain transparency and accountability in financial management.
Maintain clear documentation of all financial transactions, adjustments, and deletions to facilitate auditing and regulatory compliance.
Bottom line
Understanding journal entries in QuickBooks is essential for maintaining accurate financial records and ensuring compliance with accounting standards. While journal entries are a powerful tool for recording transactions, errors may occasionally occur, necessitating their deletion. Establishing and following the proper procedures and exercising caution can help users confidently manage and delete journal entries in QuickBooks when necessary, ensuring the integrity and accuracy of their financial data.
Continue reading: How to import invoices into QuickBooks
Share your thoughts
What’s your experience managing journal entries in QuickBooks? Would you mind sharing? We’d love to hear from you in the comments section below!






