38% of failed startups attribute their failure to problems with cash flow alone, which is a staggering number leading us to a thought that understanding, predicting and controlling the cash flow is crucial for keeping the business solvent. Cash flow statement is a standard financial statement that helps record and analyze a company’s cash flow and is basically an indicator of how well a company pays its debts and manages its operational expenses. It’s important to pay special attention to two types of business expenses-disbursement and reimbursement, as understanding the difference between the two helps manage a company’s cash flow effectively. This article focuses on disbursement and reimbursement and covers the following points:
Contents:
- Operational cash flow or cash flow from operations (CFO)
- Investment cash flow or cash flow from investing (CFI)
- Financing cash flow or cash flow from financing (CFF)
2. What is disbursement and how does disbursement work?
6. Reimbursement vs disbursement
7. Synder and payment management
Cash flow basics
When talking about disbursement and reimbursement, it’s impossible to ignore the fact that we’re talking about the parts of cash flow, the financial term which basically refers to the movement of cash into or out of an account, a business, or an investment. It makes sense to get into the basics of what cash flow is to have a better understanding of its parts.
Cash received by a company is called cash inflows while the money spent is outflows. One of the signs of good financial health of the company is cash inflows exceeding cash outflows.
According to Investopedia, there are three types of cash flows:
- Operational cash flow
- Investment cash flow
- Financing cash flow
Operational cash flow or cash flow from operations (CFO)
Operational cash is received or spent in the process of a company’s business operations such as production and selling of goods and services. CFO is the key indicator of a company being able to pay its operating expenses. It’s calculated by subtracting operating expenses from the cash received from sales.
Investment cash flow or cash flow from investing (CFI)
Investment cash flow refers to cash that’s received or spent through various investment-related activities such as buying and selling of assets and securities that’ll help scale the business. Research and development can take a huge part of investment cash flow.
Financing cash flow or cash flow from financing (CFF)
Financing cash flow refers to cash received through debt or paid out as debt repayments. Issuing stock, paying dividends, and repurchasing shares counts as part of financing cash flows of a company. CFF is an indicator of how well a company manages its capital structure.
Managing cash flows carefully and setting aside emergency reserves to cushion the possible unexpected expenses is the key to financial stability for businesses and individuals alike.
What is disbursement and how does disbursement work?
Simply said, disbursement means money paid by a business from dedicated funds. Loan delivery to a borrower by a bank, dividend payment to shareholders, money disbursed by an intermediary on behalf of the client, financial aid in the form of a government grant to a startup are all examples of disbursement. Being the part of cash flow, disbursement is a record of day-to-day business expenses.
In accounting terms, a disbursement is a payment in cash or cash equivalents over a specific period of time, which is recorded in the general ledger and cash disbursement journal of a business. If disbursements are higher than revenues, the cash flow is negative, which is an early sign of financial problems. At the same time, disbursements recorded may differ from the actual profit-loss situation if the company is using accrual accounting method, which means that it records expenses when they occur and not paid out and income when it’s earned, not received.
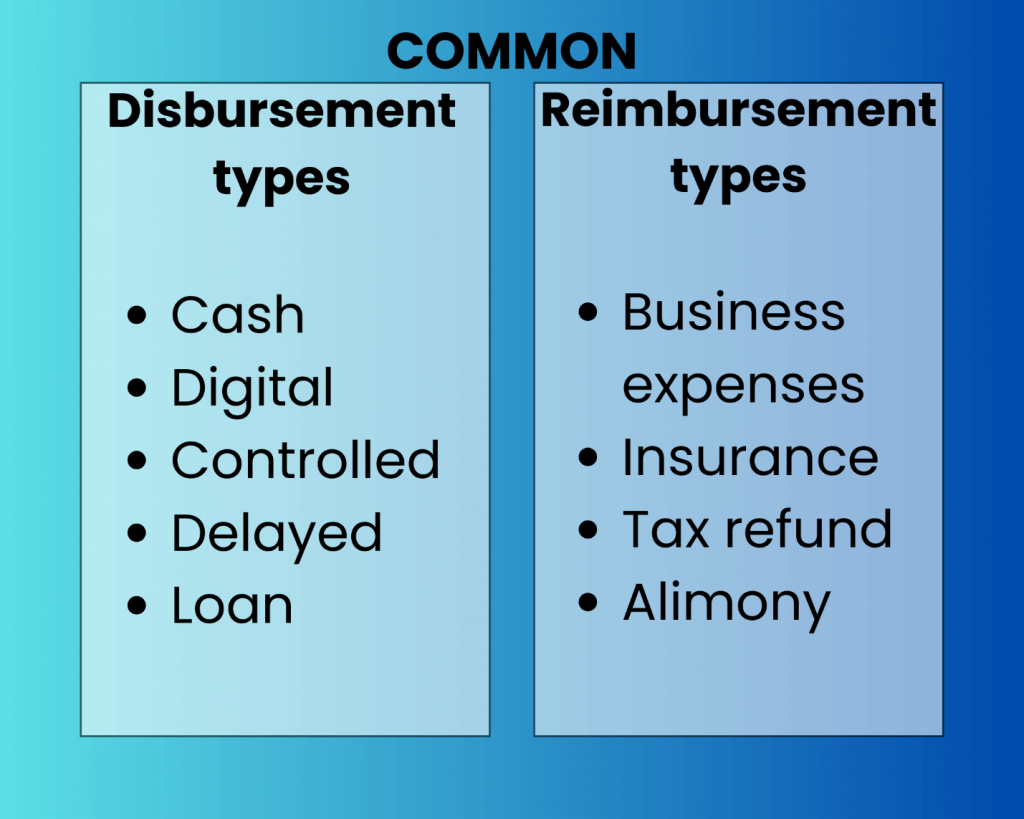
Types of disbursement
Let’s take a look at the most typical types of disbursements to get a better picture on how to distinguish it.
Cash disbursement and electronic or digital disbursements
Starting with the simple types, cash disbursements are those made in cash through a check or a cash register, while electronic or digital disbursements are made electronically, with the help of wire transfers or ACH payments.
Controlled disbursement
These are payments that are subject to approval before they are made. This type of disbursement is often used for large payments or payments to high-risk vendors. Controlled disbursements are provided by banks to their corporate clients, which allows the latter to reschedule and review their disbursements on a day-to-day basis with the benefit of earning on the cash by changing time when an amount of money is debited from their accounts.
Delayed disbursement
Also called remote disbursements, these payments aren’t made immediately. This type of disbursement is often used for payments that are subject to a hold or for payments that are made at a later date. Delayed disbursements were especially popular when banks used to process the payment only with the paper check, which made the process several business days long. With adoption of electronic transfers delayed disbursements became less wide-spread.
Loan disbursement (positive and negative loan disbursements)
A loan disbursement is the process of receiving the approved amount of money from the lender by the borrower. A positive disbursement results in a credit to an account, while a negative disbursement results in an account debit. A negative disbursement is the result of overpaying financial aid funds and later withdrawing them from an account.
In legal terms, a disbursement account is a deposit account in the name of the borrower maintained at a bank in the United States designated by the borrower to the lender or agent. Loans and funds are disbursed to the borrower by the lender through a disbursement account.
The typical examples here would be any financial aid like student loan disbursements or government grants and loans to businesses and individuals.
Other types of disbursements
Then there are some types of disbursements based on who the money is paid to:
- Dividend payments (made to shareholders of a company)
- Interest payments (made to creditors for the use of their money)
- Tax payments (made to the government to pay taxes)
- Vendor payments (made to vendors for goods or services that they’ve provided)
- Employee payments (made to employees for their wages and salaries)
There are disbursements that are common in our life but don’t belong to the sphere of business as such:
- Social security disbursements (made to retired and disabled people)
- Medicare disbursements (made to cover the cost of healthcare for seniors and people with disabilities)
- Medicaid disbursements (made to cover the cost of healthcare for low-income people)
What is reimbursement?
According to Investopedia, reimbursement is compensation paid by an organization for out-of-pocket expenses incurred or overpayment made by an employee, customer, or another party.
Most often reimbursements are associated with the expenses that employees had in the process of work or business trips. Reimbursements can cover air and taxi fares, accommodation and restaurant bills, training workshops, seminars tuition, utilities like phone bills, office supplies and others. Tax refunds are a form of reimbursements to taxpayers by the state. It has to be mentioned that self-employed individuals can reimburse themselves for business-related expenses, and such payments may be tax-deductible with the IRS.
Types of reimbursement
Though some types of reimbursements were mentioned above, let’s look at some details.
Business expenses
In the U.S., reimbursing business expenses is normally based on per diem rates set by the GSA (the General Services Administration). Per diem rates may differ for various locations and depend on some company-specific factors. A company may choose fixed per diem rates or change them according to the position and responsibilities of the employee.
Insurance reimbursement
Reimbursement is part of the insurance industry as well. When the policyholder has to cover their medical expenses out-of-pocket, the insurer reimburses it later. This happens when there’s no time to contact the insurer and figure out the extent to which the expenses are reimbursed or sometimes the insurance policy requires to pay some expenses out-of-pocket and then seek reimbursement.
Tax refund
Tax refund is the term that refers to a type of reimbursement made to a taxpayer for any excess amount paid in taxes to the federal or state government. Tax refund might look like a bonus, but essentially it’s the money returned for the previous overpayment. Careful calculation helps avoid overpaying taxes and leaves more money at hand.
Reimbursement alimony
This type of reimbursement belongs to a legal sector and is paid based on the judge’s order to an ex-spouse to reimburse their contribution to their spouse’s financial prospects. According to a divorce settlement, the spouse who provided financial support to the family, while the other studied might be entitled to compensation through reimbursement alimony from the spouse who graduated and works now.
Reimbursement vs disbursement
While a disbursement is a payment made from a fund (bank or business), or the one that has been debited from a payer’s account and credited to a payee’s account, reimbursement has a compensatory nature. Basically, it’s logical to look at reimbursements as payments covering original disbursements. A business can send a disbursement on behalf of a client, while the reimbursement is what the client pays to the company as a refund for the original payment.
One more trick to tell reimbursements and disbursements apart is to define whether the money was paid by an agent or a principle. A lawyer who sends a client an invoice with the legal fee and other expenses they incurred on the client’s behalf acts as an agent. We’re talking about a disbursement here.
On the other hand, a person who goes on a business trip and pays for accommodation, restaurant, and taxi from their pocket acts as a principal, as they needed and used the services themselves. The payment that covers their expenses is a reimbursement.
Synder and payment management
Automation of your operational procedures is one of the ways to effectively manage your payments with disbursements and reimbursements included. Synder can seamlessly sync transaction data from the sales channels and payment gateways you’re using into the books, making sure there are no duplicate entries or discrepancies. You can take advantage of either of the two sync modes Synder offers: Per Transaction sync, which gathers and records all related data about every single transaction your business has, or Daily Summary – a more general record of all transactions during a day.
If you want to learn more about Synder’s multiple features that can boost your business performance, sign up for a free trial with no commitment or credit card required or join our Weekly Public Demo.
Bottom line:
Disbursements and reimbursements are an essential part of cash flow analysis and financial management. Understanding the different types of disbursements and reimbursements, learning how they work, and telling them apart might help businesses and individuals better manage their cash flow and ensure that their payments are made on time and accurately. Various financial services today are able to provide the necessary tools to support both business and personal finance management.
Learn more reading our articles about the purpose of a cash flow statement and how to prepare a cash flow statement.






