The receivables turnover ratio is an important business metric, revealing how efficiently they collect customer payments. Monitoring this ratio helps businesses manage credit effectively, reduce the risk of bad debt, and make informed decisions to enhance financial health and operational efficiency.
Today, we’re looking at the receivables turnover ratio in more detail.
Level up your accounting with smart automation! Integrate financial data from all your sales channels in your accounting to have always accurate records ready for reporting, analysis, and taxation. See it in action with a 15-day free trial or spare a spot at our weekly public demo to have your questions answered.
Understanding accounts receivable
Before we get to the receivable turnover ratio, we need to take a quick look at accounts receivable.
Accounts receivable refer to the amounts customers owe a business for goods or services. When a sale is made on credit, meaning the customer can pay later, it gives rise to accounts receivable.
Accounts receivable play a critical role in a company’s financial health. They represent a claim to future cash inflows, and the efficient management of these receivables is essential for maintaining a steady cash flow. A well-managed accounts receivable process ensures the company can meet its short-term obligations, cover operating expenses, and invest in growth opportunities.
Related:
What Is Accounts Receivable: Understanding Your AR Accounts
What is receivable turnover ratio?
The receivables turnover ratio is a financial metric that helps assess how effectively a company manages its accounts receivable. It measures the number of times, on average, a company collects its accounts receivable during a specific period, such as a year. In other words, it indicates how quickly a business can convert its credit sales into cash.
A higher receivables turnover ratio is generally a good sign. It suggests that the company collects payments from customers more rapidly. This efficiency is crucial for maintaining liquidity and ensuring the company has the funds to cover its obligations and ongoing operations.
Conversely, a lower turnover ratio may indicate potential issues in collecting payments promptly, which could impact cash flow and overall financial stability.
How to calculate turnover ratio of receivables?
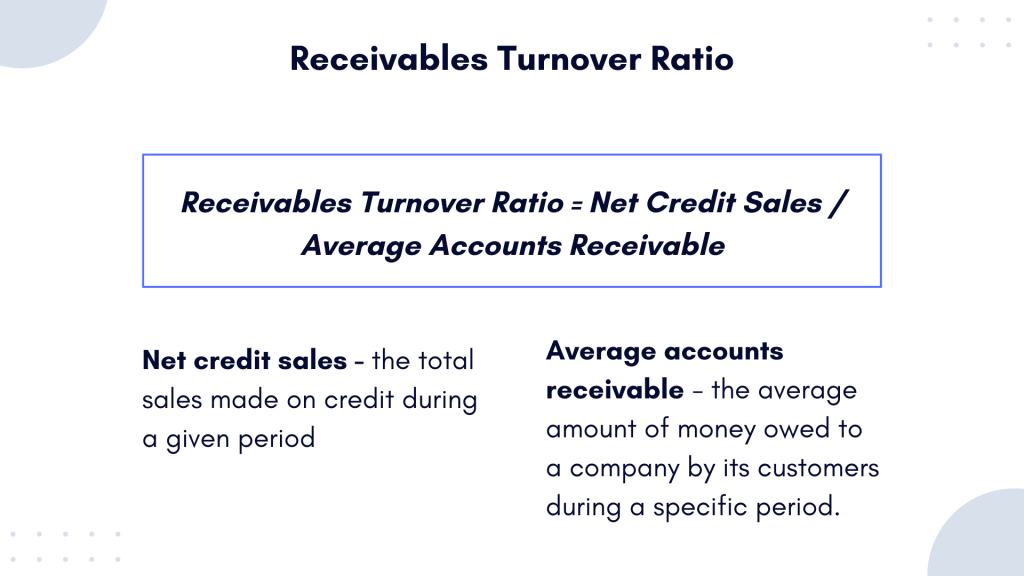
The receivables turnover ratio is calculated by dividing the net credit sales by the average accounts receivable for a specific period. Here’s the formula:
Receivables Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Sales / Average Accounts Receivable
Let’s break down the components of the formula
Net credit sales represents the total sales made on credit during a given period, excluding cash sales. It’s essentially the amount of sales for which customers have not made immediate payments.
Average accounts receivable represents the average amount of money owed to a company by its customers during a specific period. It is calculated by taking the sum of the beginning and ending accounts receivable for that period and then dividing that sum by 2.
Average Accounts Receivable = (Beginning Accounts Receivable + Ending Accounts Receivable) / 2
The beginning and ending accounts receivable are the amounts of money owed to the company at the start and end of the period, respectively.
Once you have these values, you can plug them into the formula to find the receivables turnover ratio.
This ratio provides insight into how many times, on average, a company collects its accounts receivable during the chosen time frame.
The meaning of a high or low turnover ratios in relation to financial health of a company
Now, let’s take a deeper look at what high and low receivables turnover ratios mean for a business. The receivables turnover ratio is a key indicator of how efficiently a company manages its accounts receivable, reflecting the speed at which it collects payments from customers.
What does a high receivables turnover speak of?
A high receivables turnover ratio suggests that a company is adept at converting its credit sales into cash quickly. For instance, if a business has a receivables turnover ratio of 8, it implies that, on average, it collects payments almost eight times within a given period. This efficiency is beneficial as it indicates a healthy cash flow, enabling the company to meet its financial obligations promptly and invest in growth opportunities.
Related:
Cash Flow Basics: Disbursement vs Reimbursement
What does a low receiveble turnover mean?
On the other hand, a low receivables turnover ratio may signal a slower collection of payments. For instance, if a company has a ratio of 3, it suggests that, on average, it takes more time to collect payments from customers. While this might not always be a cause for concern, an excessively low ratio could indicate issues with credit policies, potential liquidity problems, or difficulties in managing accounts receivable effectively. In such cases, the company may face challenges in meeting its short-term obligations and may need to reconsider its credit terms or collections strategies to enhance financial health.
How does industry type or business model influence the interpretation of receivables turnover ratios?
The interpretation of the receivables turnover ratio is significantly influenced by the industry type and the specific business model a company operates within. Different industries and business models inherently involve varying payment cycles and customer behaviors, which directly impact how one assesses the efficiency of receivables management.
For instance, in industries where credit terms are traditionally longer, such as manufacturing or capital-intensive sectors, a lower receivables turnover ratio may be considered normal. This is because customers in these industries typically require more time to pay for goods or services. On the other hand, in retail or service-oriented industries where transactions often involve quick payments, a higher turnover ratio is generally expected. Understanding these industry norms is crucial for a meaningful interpretation of the receivables turnover ratio.
Variations in business models can also shape the way we perceive this metric. Subscription-based businesses or those with recurring revenue streams might exhibit a more consistent and predictable receivables turnover ratio compared to businesses with one-time sales. In such cases, a stable, albeit lower, turnover ratio might indicate a reliable and steady flow of income.
Ultimately, recognizing the unique characteristics of an industry and business model is vital for a nuanced interpretation of the receivables turnover ratio, allowing for a more accurate assessment of a company’s financial health.
Strategies to enhance turnover ratio and boost financial performance
Companies implement a range of effective strategies to bolster their receivables turnover ratio. These strategies not only optimize cash flow but also contribute to overall financial resilience and growth. Here are key strategies to consider:
- Refining credit policies and terms
One can adjust credit policies to encourage prompt payments and tightening credit terms to minimize payment delays. For example, you can offer discounts for early payments or reduce the credit period from 30 days to 15 days. - Thorough credit checks
Conducting comprehensive credit assessments before extending credit can minimize the risk of delayed or defaulted payments. You can utilize credit scoring systems to evaluate the creditworthiness of customers before providing extended payment terms. - Proactive collections management
Implementing efficient collections practices can be a wise strategic move. Those include include timely follow-ups and transparent communication about payment expectations. For example, you can send automated payment reminders and promptly address any payment-related queries or issues. - Leveraging technology
Employing advanced technology, such as automated invoicing and payment systems, might help streamline and expedite the collections process. Implement a cloud-based invoicing platform that sends automated invoices and allows for seamless online payments. - Offering payment plans
A business can provide flexible payment plans to accommodate customers while ensuring a steady and predictable cash flow. Allowing customers to pay in installments over a specified period makes it more manageable for them to meet financial obligations.
The impact of these strategies on a company’s financial performance is significant. A strengthened receivables turnover ratio optimizes cash flow, ensuring funds are readily available for day-to-day operations, strategic investments, and expansion initiatives. Moreover, it reduces the reliance on external financing, enhancing financial autonomy and resilience in the face of economic uncertainties. The adoption of these strategies can help businesses build a robust financial foundation, empowering them to capitalize on growth opportunities and navigate challenges with greater confidence.
Bottom line
Long story short, the receivables turnover ratio is a crucial tool for businesses to gauge their efficiency in collecting customer payments. It provides insights into the speed at which credit sales are converted into cash, enabling companies to manage credit effectively, minimize the risk of bad debt, and make informed financial decisions.
A high receivables turnover ratio indicates swift payment collection, ensuring a healthy cash flow to meet short-term obligations and invest in growth. A low ratio may signal potential issues, prompting businesses to reassess credit policies and collections strategies. It’s essential to consider industry norms and business models when interpreting this ratio, recognizing that variations in payment cycles and customer behaviors influence its significance.
To enhance the ratio and overall financial performance, companies can implement strategies such as refining credit policies, conducting thorough credit checks, proactive collections management, leveraging technology, and offering flexible payment plans. These approaches not only optimize cash flow but also contribute to financial resilience and empower businesses to navigate challenges and seize growth opportunities with confidence.
Continue reading: Understand what purchase order is.
Share your thoughts
What accounting ratios you think are most critical to understand your business performance? Please share in the comments.. We’d love to hear from you!