Escheat is a legal concept that plays a vital role in the management of unclaimed property and assets. With its historical roots dating back centuries, escheat has evolved to serve various purposes in modern legal and financial systems.
This article aims to explore the definition, meaning, and purpose of escheat, shedding light on its significance and impact.
Escheatment explained
Owing property, people usually ensure it comes to their heirs or other beneficiaries after they are gone. Be it following the Will or rightful heirs claiming the property according to laws, assets usually get transferred from the former to new owners. However, when there are no heirs, or the property remains long unclaimed, which is not so rare, it becomes subject to escheat.
Escheat laws trace their origins to medieval England, where the concept emerged as a way to regulate property rights in the absence of a will or legitimate heirs. Over time, escheat laws spread to other jurisdictions and underwent refinements to address changing societal needs.
Dictionary definition
If you consult with a dictionary (Merriam-Webster, for instance), you might find that escheat means the reversion of property to the crown in England or the state in the U.S. when there are no legal heirs.
So basically, escheat stands for the state government’s right to take control of unclaimed property. The process of property revision under this right is, therefore, also called escheat or, sometimes, escheatment.
Key elements and principles of escheat
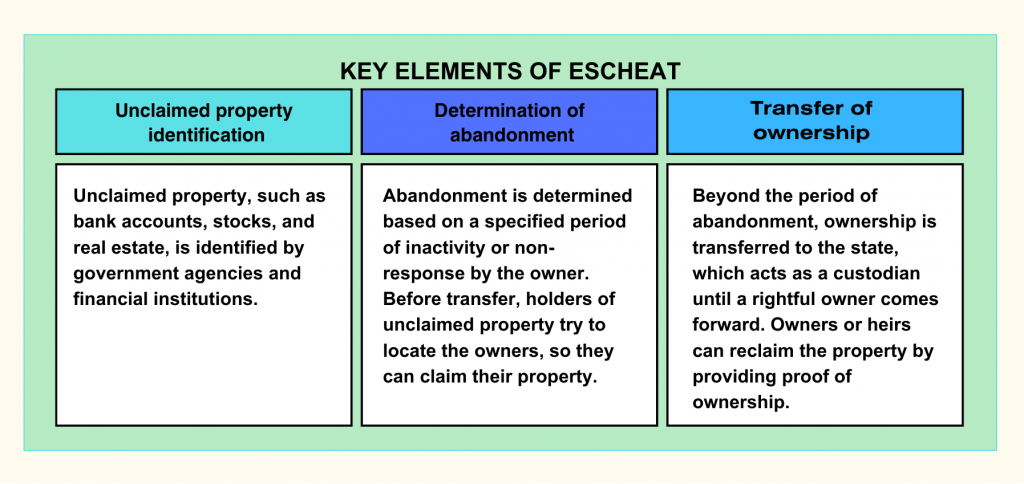
Escheat involves the transfer of unclaimed property and assets to the state when no rightful owner or heir can be identified. The process consists of key elements: identification of unclaimed property, determination of abandonment, and subsequent transfer of ownership to the state.
- Unclaimed property, such as bank accounts, stocks, and real estate, is identified by government agencies and financial institutions.
- Abandonment is determined based on a specified period of inactivity or non-response by the owner. Before transfer, holders of unclaimed property make efforts to locate and notify the owners, giving them an opportunity to claim their property.
- Once the period of abandonment has passed, ownership is transferred to the state, which acts as a custodian until a rightful owner comes forward. Provisions are in place for owners or heirs to reclaim escheated property by providing proof of ownership.
The purpose of escheat
Escheat aims to protect property rights, prevent asset abandonment, ensure equitable distribution, fund public programs, and promote economic stability within society.
Protecting property rights and preventing abandonment
One of the primary purposes of escheat is to safeguard property rights by preventing assets from becoming permanently abandoned. Escheat laws provide a mechanism to preserve and protect unclaimed property, ensuring that it does not go to waste or fall into wrongful hands. Just as businesses need to navigate legal and financial concepts like the Federal Employer Identification Number, understanding escheat helps maintain transparency and compliance.
Ensuring the equitable distribution of assets
Escheat serves as a mechanism for the equitable distribution of unclaimed property. By transferring ownership to the state, escheat laws help ensure that assets are not concentrated in the hands of a few individuals or entities, but rather used for the benefit of society as a whole.
Funding government programs and services
Another important purpose of escheat is to provide a source of funding for government programs and services. The assets and funds obtained through escheat can be used to support various public initiatives, such as education, infrastructure development, or social welfare programs. Escheat plays a role in funding government programs and services, just as businesses require effective payment solutions to manage their operations, where our article on Shopify Payment Gateways provides valuable insights regarding this topic.
Promoting economic stability
Escheat plays a role in maintaining economic stability by preventing the accumulation of dormant assets. By transferring unclaimed property to the state, escheat laws contribute to the efficient allocation of resources and promote active circulation of assets within the economy.
Escheat Laws and procedures
Escheat laws vary across jurisdictions, with each region having statutes and regulations governing the process.
These laws determine the criteria for identifying unclaimed property, the duration of abandonment, and the procedures for transferring ownership to the state. But basically, they include identifying and reporting unclaimed property and maintaining unclaimed assets databases so that people can search for and reclaim the property they have the right for.
Identification and classification of unclaimed property
Effective escheat systems involve the identification and classification of unclaimed property. This may include financial assets like dormant bank accounts, uncashed checks, and unclaimed insurance policies, as well as physical assets like abandoned real estate or forgotten safe deposit boxes.
Reporting and compliance requirements for property holders
Escheat laws typically place reporting and compliance obligations on holders of unclaimed property. Financial institutions, corporations, and other entities are required to report and remit unclaimed property to the appropriate state authorities, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Efforts to reunite owners with their assets
Many jurisdictions maintain centralized databases that provide public access to information on unclaimed property. These databases serve as valuable resources for individuals to search for and reclaim their lost assets, fostering efforts to reunite owners with their property.
Challenges and controversies surrounding escheat
Escheat laws are balancing on pretty controversial grounds, causing potential challenges. Let’s break them down.
Determining rightful ownership and establishing abandonment
One of the challenges in escheat procedures lies in determining rightful ownership and establishing abandonment. Differentiating between abandoned property and property with unresolved ownership disputes can be complex, requiring careful evaluation and legal considerations.
Balancing state interests with individual property rights
Escheat laws must strike a balance between the state’s interest in preserving unclaimed property and the rights of individuals to retain ownership of their assets. Striking this balance requires ensuring fairness, transparency, and providing opportunities for individuals to reclaim their property.
Ensuring fairness and transparency in escheat processes
Fairness and transparency are essential in escheat processes to prevent potential abuses and wrongful confiscations. Regular audits, clear guidelines, and robust legal safeguards are crucial to maintaining the integrity of escheat systems and protecting the rights of individuals and businesses.
What to anticipate in the future?
Escheat laws are continuously evolving to keep pace with technological advancements and changing societal needs. Jurisdictions are exploring ways to modernize escheat systems, such as leveraging automation and digital platforms to streamline processes and enhance efficiency.
Advancements in data analytics, artificial intelligence, and blockchain technology have the potential to revolutionize escheat procedures. These innovations can facilitate improved identification of unclaimed property, enhanced record-keeping, and more efficient efforts to reunite owners with their assets.
To address the challenges and controversies surrounding escheat, there is an ongoing need for reforms and improvements. Such efforts may include standardization of escheat laws, greater coordination among jurisdictions, and enhanced public awareness campaigns to promote property reclamation.
Conclusion
Escheat, with its rich historical background, serves a crucial role in modern legal and financial systems. By protecting property rights, ensuring equitable distribution, funding government programs, and promoting economic stability, escheat contributes to the overall welfare of society. However, challenges remain in striking the right balance between state interests and individual property rights. With ongoing advancements and reforms, escheat systems can continue to evolve and adapt to meet the needs of an ever-changing world, safeguarding unclaimed property and serving the best interests of all stakeholders.


%20(1).png)





