Financial strategies play a decisive role in determining a company’s trajectory. Among these, the significance of business savings often escapes the limelight despite its pivotal role in bolstering resilience and facilitating expansion. Meanwhile, this essential financial tool can significantly contribute to maximizing growth and provides even more advantages — from ensuring liquidity during downturns to seizing unexpected opportunities.
Let’s learn how companies can leverage bank business savings accounts’ capabilities to manage finances more efficiently and thrive in a bumpy economic landscape.
What is the business savings account?
Let’s start with defining a business savings account. In essence, business savings accounts, are the tools banks and financial institutions offer to provide a secure avenue to park surplus funds. However, what sets them apart is their targeted features designed to address distinct financial goals and requirements of commercial entities.
Unlike checking accounts, primarily used for daily transactions, business savings accounts offer a space to store funds that a business doesn’t immediately need for operational purposes. Below, we’ll look at them in more detail.
The benefits behind business bank savings accounts
Embracing a bank business savings account represents more than just prudent financial management – it’s a strategic move that can significantly contribute to long-term business success. Here’s why business savings are a good idea:
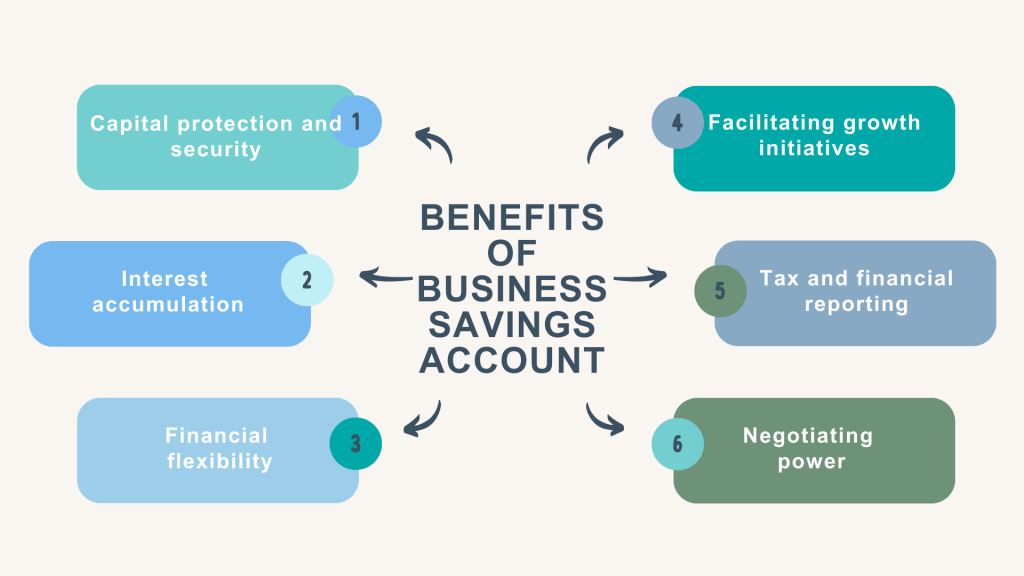
Benefits of business savings #1 – Capital protection and security
One of the primary advantages of a business savings account is the safety it provides for surplus capital. These accounts are insured by regulatory bodies up to a certain limit, shielding the business’s funds from unforeseen events such as bank insolvency or economic downturns.
Benefits of business savings #2 – Interest accumulation
Business savings accounts offer the opportunity for funds to earn interest. While interest rates might not be as high as riskier investment options, the advantage lies in the stability and predictability of returns. Over time, compounded interest can contribute substantially to the company’s finances.
Benefits of business savings #3 – Financial flexibility
Having a business savings account ensures liquidity for unforeseen expenses, such as equipment repairs, sudden inventory needs, or unexpected market shifts. This prevents the need to rely on credit lines or loans during emergencies, helping the business maintain its operational continuity.
Benefits of business savings #4 – Facilitating business growth initiatives
For companies eyeing expansion or planning to invest in new opportunities, a well-maintained savings account can become a good financial base. They can channel the funds accrued over time into strategic projects without disrupting day-to-day operations.
Benefits of business savings #5 -Tax and financial reporting
A dedicated business savings account streamlines financial management, aiding in accurate tax reporting and financial analysis. Clear separation between operational funds and saved capital simplifies the tracking of profits and expenses.
Benefits of business savings #6 -Negotiating better loan and credit lines terms
Accumulating a substantial balance in a business savings account can enhance a business’s relationship with its financial institution, potentially leading to better terms on loans, credit lines, or other banking services. At this points, you might end up with better conditions for your buisness’s credit cards, higher credit card limits, etc.
The difference between a checking and savings account
It’s worth mentioning that business savings accounts and business checking accounts are two of the most common options for businesses. While both serve distinct purposes, understanding the differences between them is essential for effective financial management. Let’s break it down.
Savings accounts vs. checking accounts: purpose and usage
A business savings account is primarily designed for the purpose of accumulating funds over time. It functions as a secure place to store surplus cash that is not needed for immediate operational expenses. These accounts often come with higher interest rates compared to standard checking accounts, making them an attractive option for ventures looking to earn a bit of extra income on their idle funds.
Business savings accounts are suitable for setting aside money in a bank for future investments, emergency funds, or other long-term financial goals. Withdrawals from a savings account are typically limited, and you may be required to maintain a minimum balance to avoid fees.
A bank checking account, on the other hand, is specifically tailored for managing day-to-day financial transactions. It is the go-to account for receiving payments, making payments, issuing checks, and handling routine business expenses. These accounts offer the flexibility and accessibility required to keep your business operations running smoothly.
Business checking accounts usually come with features such as check-writing abilities, ATM access, and electronic payment options. They do not offer interest on the balance but are designed to accommodate frequent deposits and withdrawals without restrictions. Besides, you can link a checking bank account to a credit card for payments or transactions.
Savings accounts vs. a bank business checking account: transaction activity
Transaction activity in a business savings account is limited compared to a checking account. Typically, a savings account is subject to federal regulations, such as Regulation D, which restricts the number of withdrawals or transfers to six per month. Going beyond this limit may result in penalties or a requirement to convert the account to a checking account.
A bank checking account is built for high transaction volumes. It allows businesses to write checks, make electronic transfers, and withdraw cash regularly without limitations. This makes it suitable for covering daily operational expenses, such as paying suppliers, employees, and utility bills.
Savings accounts vs. a checking account: accessibility
Accessing funds from a business savings account can be a bit more cumbersome compared to a checking account. You may need to transfer funds to your checking account to cover immediate expenses. This extra step can help companies maintain discipline in saving for their financial goals.
Bank checking accounts provide quick and easy access to funds. They are the central hub for your business’s financial activities, allowing you to make payments and withdrawals effortlessly.
Bank business savings accounts vs. a business checking account: interest earnings
One of the key advantages of a business savings account is the potential to earn interest on your deposited funds. The interest rate may vary depending on the financial institution and the account type, but it offers a way to generate some passive income on your idle cash reserves.
Business checking accounts typically do not offer interest on the checking account balance. They are designed for the convenience of transactions rather than as an investment vehicle.
So, the choice between a business savings account and a bank checking account depends on your company’s financial goals and needs. Many businesses opt for a combination of both accounts to strike the right balance between accessibility and growth of their financial resources.
The difference between business savings accounts and a bank deposit
Often, people confuse a business savings account and a bank deposit, using these terms interchangeably. However, they are two different terms and denote different concepts.
When individuals or companies seek to park their money in a secure and liquid form, they often consider two primary options: a savings account and a bank deposit. While both options involve entrusting your funds to a financial institution, they have distinct characteristics and purposes. Let’s delve into the key differences between these two choices.
Bank account’s nature
A savings account, as mentioned above, is a specific type of a bank account offered by banks and credit unions. It is designed to help individuals and businesses save money over time while earning a modest amount of interest. Such accounts are accessible for making withdrawals, but they are not intended for frequent or daily transactions. They are an excellent choice for setting aside funds for future goals, emergencies, or planned expenses.
A bank deposit is a broader term that encompasses various types of accounts. When you deposit money into a bank, you are, in essence, creating a bank deposit. Bank deposits can be categorized into different types, and a savings account is just one specific type of a bank deposit.
Purpose and accessibility
The primary purpose of a savings account is to encourage saving and provide account holders with a safe place to keep their money while earning interest. While offering some level of liquidity, they may have limitations on the number of withdrawals or transfers you can make each month, typically due to federal regulations like Regulation D. This restriction aims to encourage account holders to maintain their business savings for longer periods.
A bank deposit is a broader term encompassing a range of accounts, each with its purpose and accessibility features. For instance, checking accounts are designed for everyday transactions, offering more flexibility in terms of withdrawals and payments. Certificates of deposit (CDs), another type of bank deposit, provide higher interest rates but require funds to be locked in for a predetermined period.
Interest earnings
Savings accounts are known for providing interest on the deposited funds. The interest rate can vary depending on the financial institution, the type of savings account, and prevailing market conditions. While the interest earned may not be substantial, it allows account holders to grow their business savings over time.
The interest-earning aspect of a bank deposit can vary widely depending on the type of deposit account. Savings accounts and certain other deposit accounts, such as money market accounts, typically offer interest on the balance. However, checking accounts and some other forms of deposits may not provide interest earnings.
Liquidity and accessibility
Savings accounts strike a balance between accessibility and the growth of deposited funds. They provide a level of liquidity, allowing you to withdraw money when needed. However, they also encourage savers to limit frequent transactions to maintain their business savings goal.
The accessibility and liquidity of a bank deposit depend on the specific type of account. Checking accounts are highly liquid and designed for frequent transactions. In contrast, certain long-term bank deposits like CDs may have limited liquidity and require you to wait until the maturity date to access your funds without penalties.
As you can see, both savings accounts and bank deposits offer secure options for managing your money. The choice between the two depends on your financial goals, liquidity needs, and the level of interest you seek to earn on your deposited funds.
Business savings accounts available to business owners
When we take a closer look at the options available to business owners, we’ll see a plethora of them. It provides a certain level of flexibility in terms of how companies wan to accumulate their buisness money. Let’s look at these options in a bit more detail.
Basic business savings accounts
Basic business savings accounts serve as foundational financial tools for a business seeking to earn interest on their surplus cash while ensuring convenient access to their funds. These accounts are straightforward and accessible, making them a popular choice among small and medium-sized enterprises.
- Cost-effective and accessible
In most cases, basic business savings accounts come with low or even no monthly maintenance fees, making them cost-effective for enterprises of all sizes. To get started, you may need to meet a minimum opening deposit requirement, which can vary from one financial institution to another. - Emphasis on liquidity and ease of use
One of the primary advantages of basic business savings accounts is their focus on liquidity and ease of use. Funds can be easily deposited into these accounts and withdrawn as needed, providing the flexibility required to cover unexpected expenses or seize opportunities when they arise. - Consideration for interest rates
However, it’s essential to note that while these accounts offer accessibility and convenience, they often provide lower interest rates compared to other business savings options. For companies with significant cash reserves or long-term business savings goals, exploring alternatives like high-yield savings accounts or certificates of deposit (CDs) may be beneficial to maximize interest earnings over time.
High-yield savings account (something Prime Alliance or Live Oak Bank might offer you)
High-yield business savings accounts are a rewarding option for those wishing to balance liquidity with the potential for higher returns. They offer the opportunity to grow idle funds more efficiently than traditional savings accounts, but one should carefully consider the financial position and the associated requirements before selecting this option. For those with the financial capacity to meet the minimum balance and maintenance criteria, high-yield business savings accounts can be a valuable addition to their overall financial portfolio.
- Unlocking earnings potential
The primary allure of high-yield business savings accounts lies in their ability to generate more substantial earnings on idle funds. These elevated interest rates, often exceeding those of standard savings accounts, can provide a meaningful boost to a business’s overall financial strategy. For companies with substantial cash reserves, this means the potential for more substantial interest income, which can be a valuable source of revenue. - Considerations for higher returns
However, it’s important to note that higher interest rates typically come with certain prerequisites. To qualify for these attractive rates, financial institutions may impose higher minimum balance requirements compared to the basic option. In essence, they expect their clients to maintain a more substantial balance in the account to enjoy the enhanced interest rates. - Meeting account maintenance requirements
Some high-yield business savings accounts may come with additional account maintenance requirements. These requirements might include a commitment to maintain the account for a specific duration or limit the number of withdrawals or transfers allowed within a given period. These stipulations aim to incentivize clients to keep their funds within the account for longer periods, aligning with the bank’s goal of attracting stable deposits.
Money market account
Money market business accounts offer a balancing act between accessibility and interest earnings. They provide the flexibility to write checks and perform transactions while also allowingcompanies to grow their funds at a more competitive rate than a traditional savings account. However, they should be mindful of the minimum balance requirements and transaction limits associated with these accounts, ensuring that they align with their financial needs and goals.
- Check-writing privileges for convenient transactions
One of the distinguishing features of money market business accounts is their check-writing privileges. This capability empowers companies to make payments directly from the account, just as they would with a checking account. This feature is particularly useful for managing day-to-day expenses, paying suppliers, vendors, and contractors, and handling operational costs efficiently. - Enhanced liquidity with certain limitations
While money market business accounts provide enhanced liquidity and accessibility, they often come with specific limitations designed to maintain a balance between accessibility and interest-earning potential. These limitations can include higher minimum balance requirements compared to regular savings accounts. Financial institutions typically require to maintain a minimum balance to enjoy the benefits of a money market account, such as higher interest rates and check-writing privileges. - Transaction allowances
Money market accounts may also have limited transaction allowances when compared to regular checking accounts. This means that clients may encounter restrictions on the number of transactions they can perform within a specific period, such as a monthly cycle. Exceeding these transaction limits may result in fees or the need to convert the account to a different type. - Competitive interest rates
The primary advantage of money market business accounts is their ability to provide competitive interest rates while offering convenient transaction capabilities. Companies can earn interest on their balance, which can be especially attractive when compared to the lower interest rates typically associated with bank basic savings accounts.
Certificate of deposit (CD)
Business certificates of deposit offer a balance between growth potential through higher interest rates and the commitment of funds for a predetermined period. Companies should evaluate their financial goals, risk tolerance, and the timing of their capital needs when deciding on a CD term. This strategic approach can help them leverage the benefits of CDs to enhance their financial position and achieve long-term objectives.
- Higher returns through competitive interest rates
One of the primary attractions of business CDs is the prospect of higher returns compared to standard savings accounts. The interest rates associated with CDs tend to be more favorable, making them an attractive choice for those looking to maximize their interest income on surplus funds. - Term length and flexibility
The flexibility of business CDs lies in the variety of term lengths available, catering to different financial goals and risk tolerances. These terms can range from a few months to several years, allowing to choose a timeframe that aligns with a business’s specific objectives. Short-term CDs, such as those with terms of three to six months, are ideal forcompanies seeking quick access to their funds after a brief period, while longer-term CDs, with terms of one to five years or more, offer higher interest rates for those willing to commit their funds for an extended duration. - Locked funds until maturity
However, it’s important to understand that the key characteristic of a business CD is the locking of funds until the CD matures. During this period, clients typically cannot access the funds they’ve deposited without incurring penalties or forfeiting a portion of the interest earned. This lock-in feature is a trade-off for the higher interest rates offered by CDs. - Protection against interest rate fluctuations
A significant advantage of CDs is their insulation from fluctuations in interest rates. Once a business commits to a CD with a fixed interest rate, that rate remains consistent throughout the CD’s term. This can be particularly advantageous when interest rates in the broader market are expected to decline, as clients can secure a higher rate for the entire term. - Consideration for early withdrawals
While CDs are designed for term-based business savings, companies should carefully consider their liquidity needs before opting for a CD. Early withdrawals from a CD can result in penalties, which may negate the interest gains or even reduce the principal amount. Therefore, it’s essential to assess financial circumstances and objectives thoroughly proir to choosing a CD term.
As you can see, businesses have a choice of savings account options available. The list is not extensive, and there are more variants, catering to the needs of businesses of various types and sizes. The above are the most popular buisness savings options to consider.
Understanding APY, fees, and other key nuances for choosing the best savings account
Selecting the right savings account is a crucial financial decision, and it’s essential to consider various factors beyond just the interest rate. To make an informed choice, here are some critical nuances to understand when evaluating savings accounts:
Annual Percentage Yield (APY)
- The Annual Percentage Yield (APY) is a crucial factor in determining how much your money will grow in your savings account.
- APY represents the actual interest earned on your balance, factoring in compounding, and is usually expressed as a percentage.
- When comparing savings accounts, opt for the account with the highest APY, as it will offer the most significant potential for your business savings to grow over time.
Interest rate types
- Savings accounts can have variable or fixed interest rates. Variable rates can change over time, while fixed rates remain constant for a specified period.
- Consider your preference for rate stability. Fixed rates may provide predictability, while variable rates can potentially offer higher returns if market conditions are favorable.
Fees
- Pay close attention to account fees, as they can erode your business savings over time.
- Common fees associated with savings accounts include monthly maintenance fees, withdrawal fees (especially for excessive transactions), and minimum balance fees.
- Look for accounts with minimal or no fees, and be aware of the requirements to avoid fees, such as maintaining a minimum balance.
Minimum balance requirements
- Many savings accounts require a minimum balance to open the account and avoid fees.
- Consider your financial situation and ensure that the minimum balance requirement aligns with your ability to maintain that balance consistently.
Access and liquidity
- Assess the ease of accessing your funds. Some accounts may limit the number of withdrawals or transfers you can make each month due to federal regulations like Regulation D.
- If you anticipate needing frequent access to your funds, choose an account that offers the necessary liquidity without incurring penalties.
Online vs. brick-and-mortar banks
- Online banks often offer higher APYs and lower fees due to reduced overhead costs.
- Brick-and-mortar banks may provide in-person support and convenience, but their savings accounts might have lower interest rates and higher fees.
- Consider which factors are more important to you: a higher return on your business savings or physical access to a bank branch.
Account features
- Some savings accounts come with additional features, such as mobile banking apps, ATM access, and automatic transfers.
- Evaluate these features based on your convenience and preferences.
Federal deposit insurance
- Ensure that your chosen bank is FDIC-insured (or NCUA-insured for credit unions) to protect your deposits up to the maximum allowable limit (currently $250,000 per account holder).
Customer service and reputation
- Research the bank’s customer service reputation through reviews and ratings. Prompt and efficient customer support can be invaluable.
Long-term goals
- Consider your business goals and the role this account will play in your overall financial plan. If you’re saving for a short-term goal, liquidity and ease of access may be more critical. For long-term goals, focus on maximizing growth potential.
Compare multiple options
- Don’t settle for the first option you come across. Compare several options, paying attention to the nuances mentioned above, to ensure that your choice aligns with your financial objectives.
As you can see, choosing the best savings account requires a comprehensive assessment of your financial needs, goals, and preferences. Understanding the nuances of APY, fees, access, and other factors will help you make an informed decision that supports your financial well-being and growth.
How to get a business savings account?
Getting a business savings account is a crucial step in managing your company’s finances. To open one, follow these steps:
- Research your options
Start by researching banks, credit unions, and financial institutions that offer business savings accounts. Consider checking out options like Oak Bank, Alliance Bank, JPMorgan Chase, and local credit unions in your area. Look at their offerings, interest rates, and fees. - Check eligibility
Ensure that your business meets the eligibility criteria set by the bank or credit union. This may include providing your business’s EIN (Employer Identification Number) and meeting any minimum balance requirements. - Review your credit score
Your personal and business scores may be considered during the application process. A strong score can enhance your chances of approval, while a poor score may affect the terms offered. - Gather documentation
Be prepared to provide essential documentation, such as your business’s legal documents, tax ID, and financial statements. Some banks may require additional documentation like a business plan or proof of business insurance. - Visit the nearest branch
If you prefer a brick-and-mortar bank like Oak Bank, visit the nearest branch. You can inquire about their business savings account options, discuss terms, and start the application process in person. - Apply online
Alternatively, you can apply for a bank savings account online. Visit the bank’s website, fill out the application form, and upload any required documents. Make sure to provide accurate information, including your business’s zip code. - Consider service fees
Be aware of any potential bank service fees. Banks often charge a monthly service fee, but some accounts may waive this fee if you maintain a minimum balance or meet certain transaction criteria. - Review terms and conditions
Carefully read and understand the terms and conditions. Pay attention to interest rates, transaction limits, withdrawal penalties, and any other terms that may affect your account’s management. - Wait for approval
After submitting your application, the bank will review your information. Approval timelines can vary, but once accepted, you’ll receive instructions on the fundingprocess. - Link to other accounts
If you plan to link your bank savings account to a business credit card or other financial products, inquire with the bank about the process and any potential benefits. - Enjoy peace of mind
Once your bank business savings account is open, you can start saving and earning interest. Consider it an essential financial tool for your business’s future, much like life insurance is for personal financial security.
By following these steps and considering factors like your score and the monthly fee, you can successfully open a bank business savings account that aligns with your financial goals and helps you secure your business’s financial future.
Conclusion
As you can see, a well-managed business savings account isn’t just a financial tool; it’s a strategic asset that can fortify a small business against uncertainties and propel it toward growth. By comprehending the nuances of accounts like those offered by TD Bank and Chase Business, and aligning them with their financial objectives, entrepreneurs can harness the power of business savings accounts to navigate the ever-evolving business landscape with confidence. Whether it’s optimizing liquidity, generating passive income, or seizing opportunities as they arise, a well-managed business savings account, much like a reliable life insurance policy, remains a cornerstone of financial success for enterprises of all sizes. So, whether you’re safeguarding your business funds or considering a wire transfer to your checking account, your business savings account plays a pivotal role in your financial strategy.
Read about Pros and Cons of PayPal or Xero alternatives.





